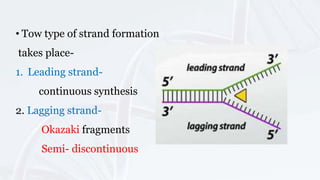
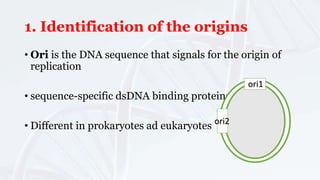
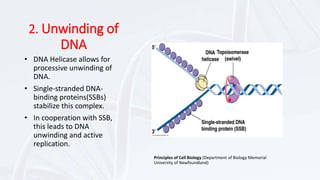
DNA replication involves the accurate duplication of DNA before cell division, producing two identical strands from one original molecule through a semi-conservative method. It is initiated at specific origins, with leading strands synthesized continuously and lagging strands forming in fragments, requiring RNA primers. Key components include helicase for unwinding, DNA polymerase for adding nucleotides, and ligase for sealing the gaps, while the structure of chromatin is reconstituted after replication.