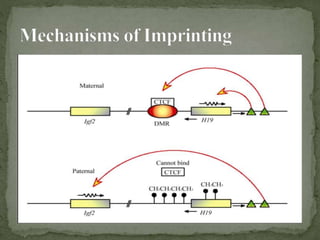
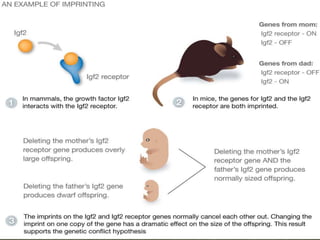
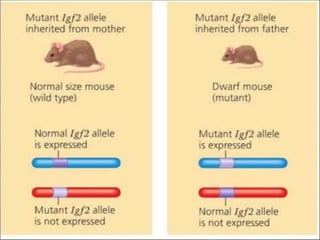
DNA imprinting is an epigenetic mechanism where the paternal and maternal genomes have functional differences due to heritable changes in gene expression and activity without altering the DNA sequence. Imprinting requires DNA methylation and histone modifications that silence genes during egg and sperm formation. Disturbances in imprinting can result in abnormal embryonic development and syndromes like Prader-Willi and Angelman, which occur when an imprinted gene's mutated allele is inherited from only one parent.