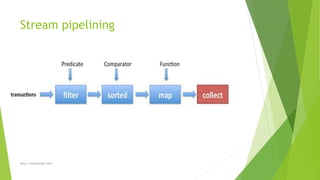
The document discusses Java 8 built-in functional interfaces including Predicate, Consumer, and Supplier, outlining their methods and functionalities. It highlights how Predicate is a functional interface despite having one abstract method, while Consumer and Supplier operate with different input-output mechanics. Additionally, it covers stream operations and pipelining, emphasizing the collect() method as a terminal operation.