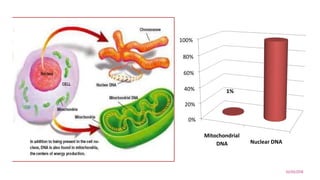
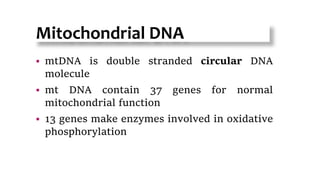
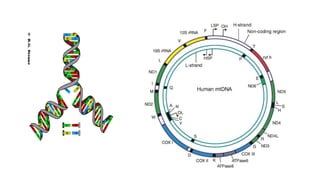
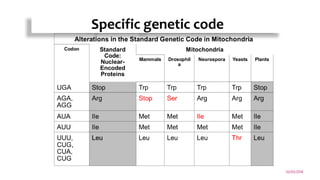
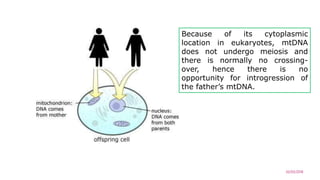
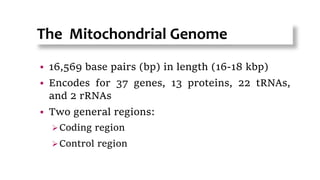
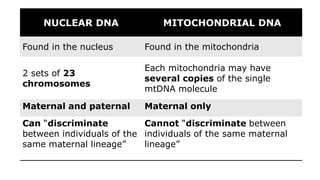
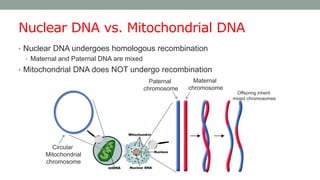
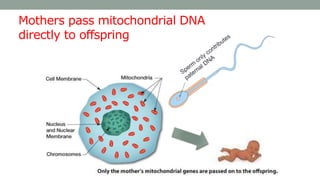
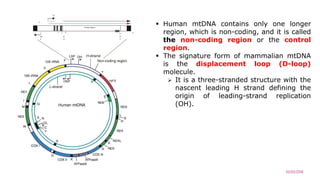
Mitochondrial DNA is typically less than 1% of an animal cell's DNA. Mitochondria contain their own genome in multiple copies that is distinct from nuclear DNA. Mitochondrial DNA is maternally inherited, circular, encodes 37 genes, and does not undergo recombination like nuclear DNA.