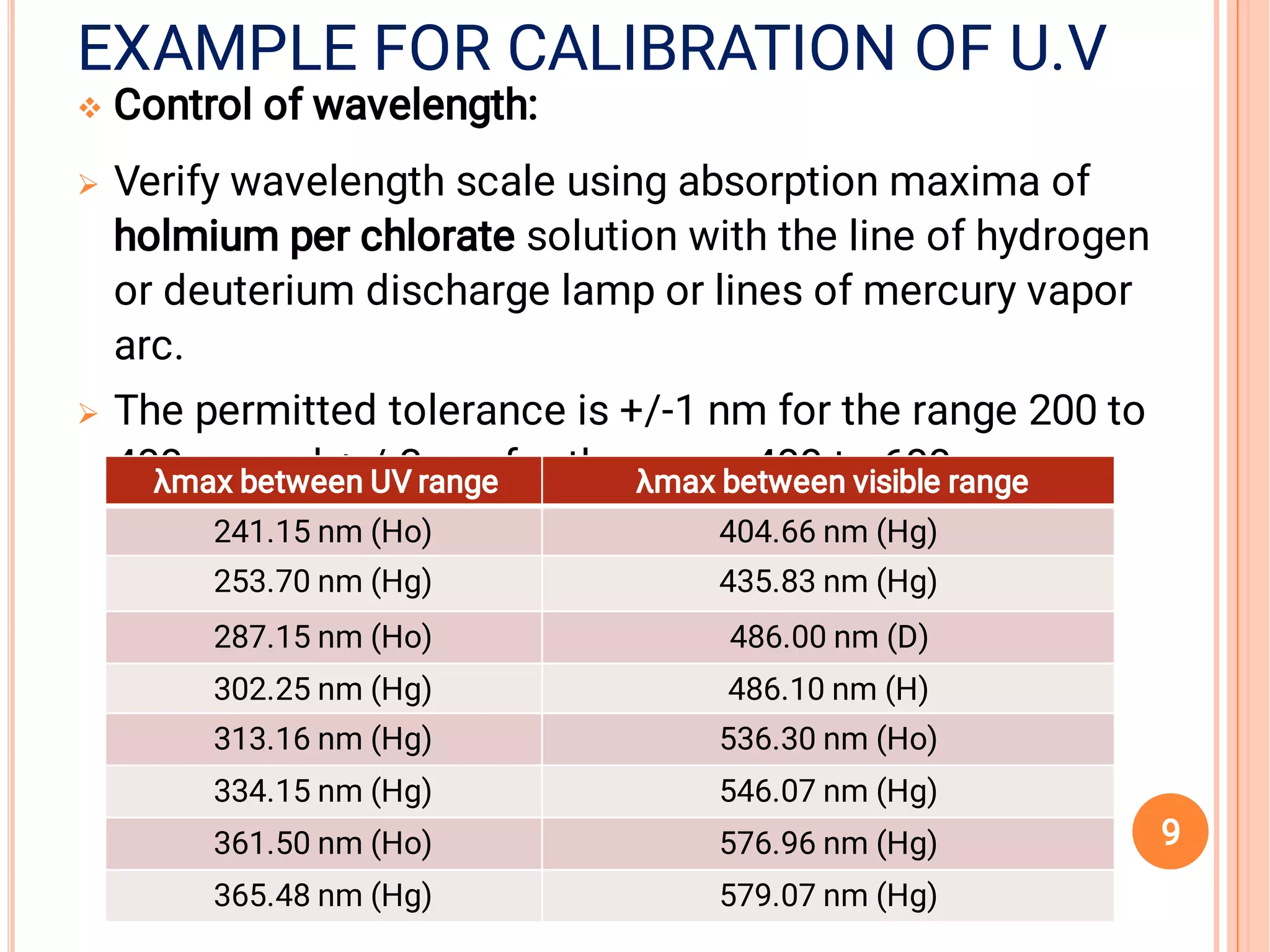
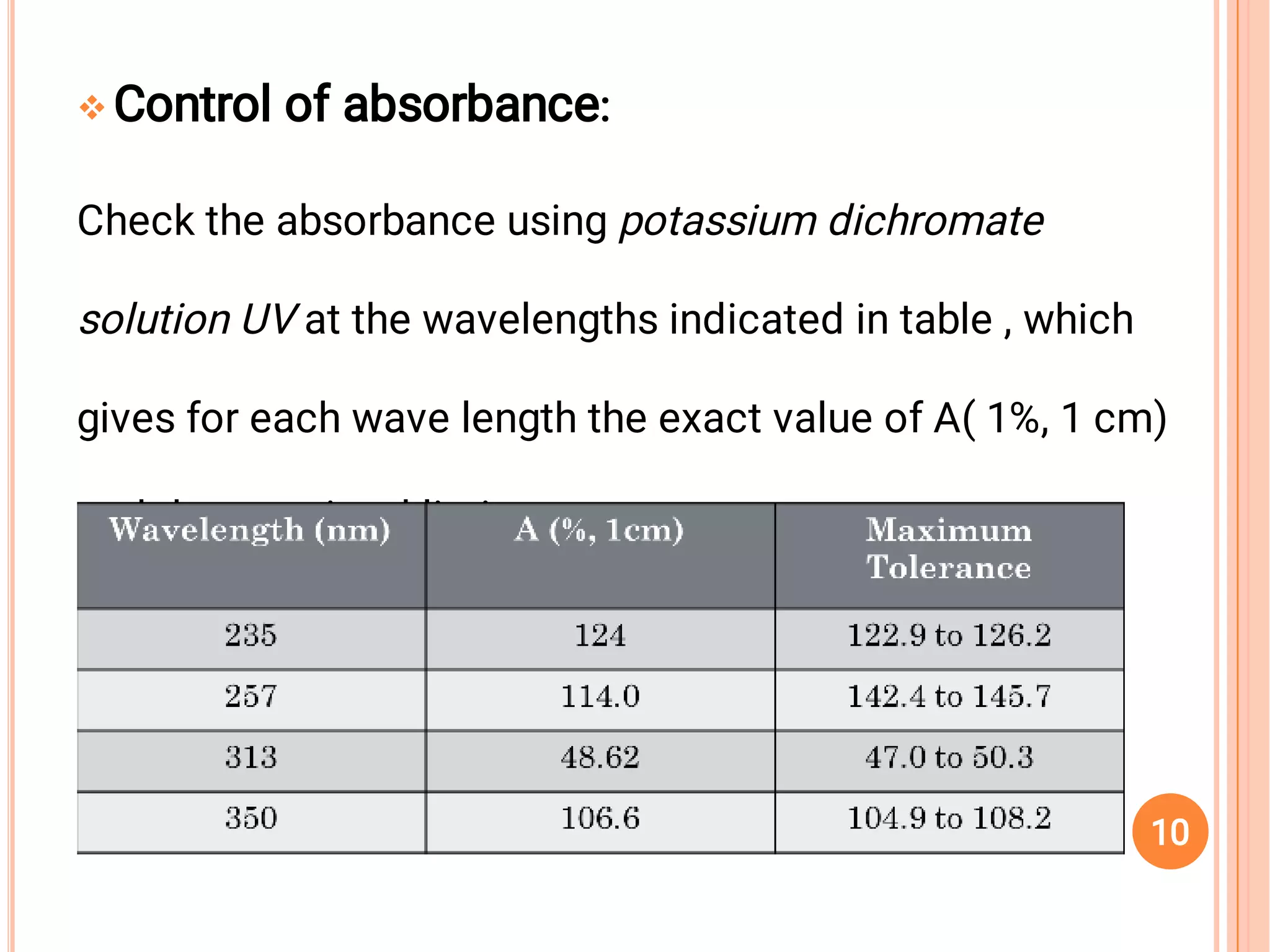
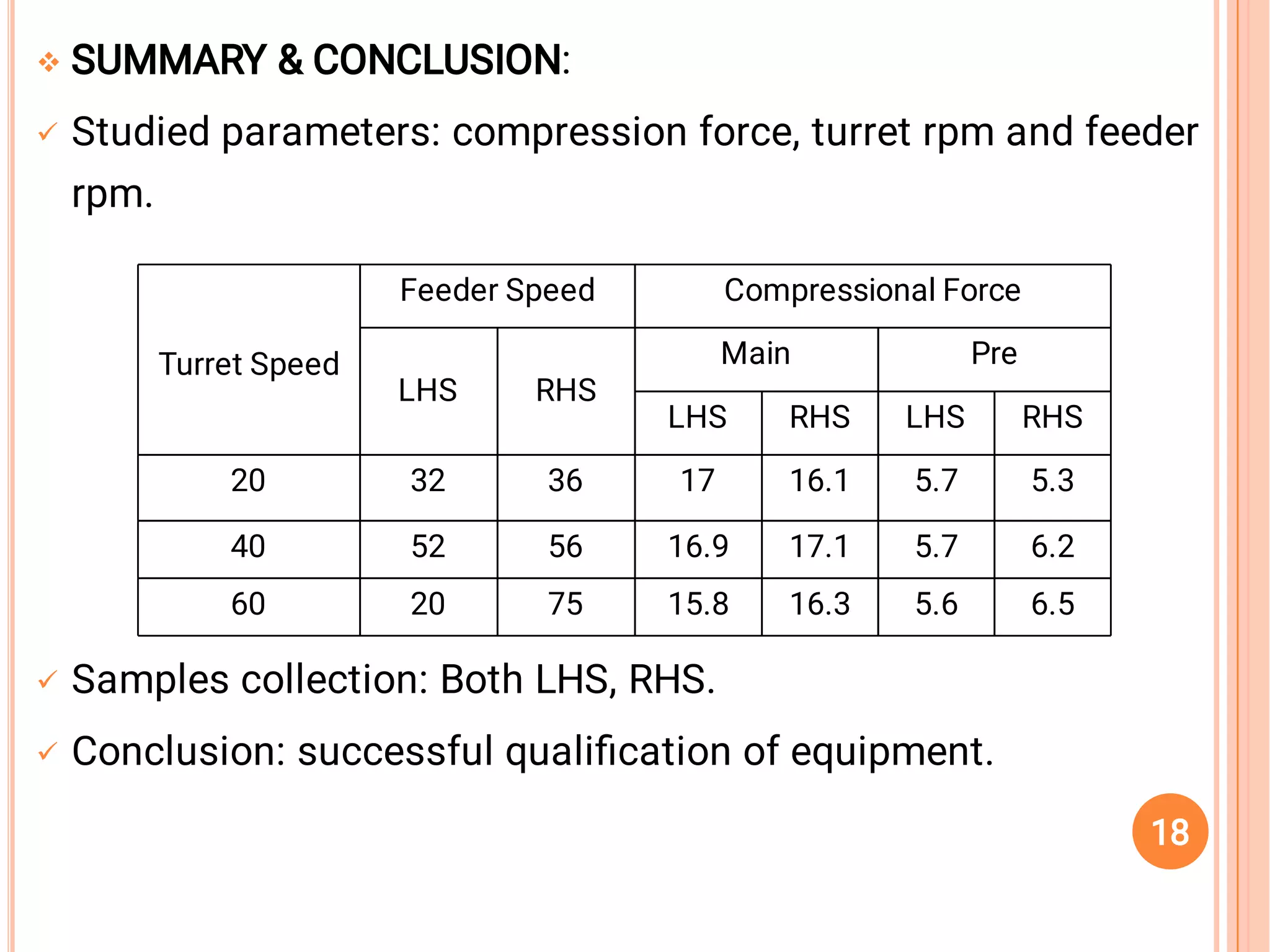
The document outlines the guidelines for the calibration and validation of equipment as per ICH and WHO standards in pharmaceutical settings. It emphasizes the importance of maintaining accuracy, traceability, and proper procedures for the operation and maintenance of various laboratory instruments and systems. Specific examples and procedures for calibration and validation, particularly for UV equipment and tablet compression machines, are also provided.