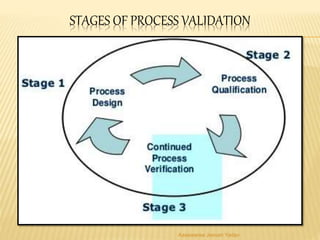
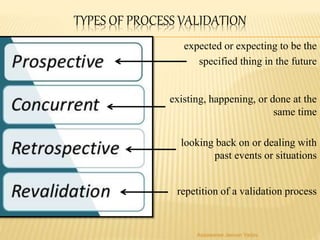
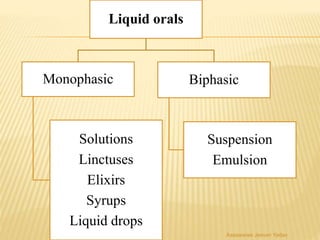
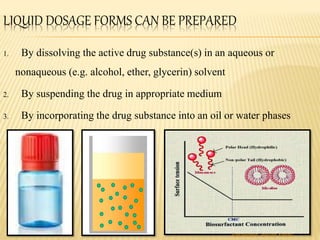
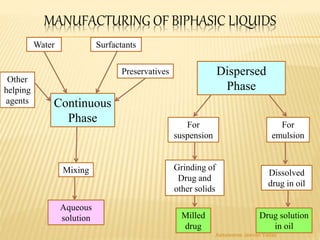
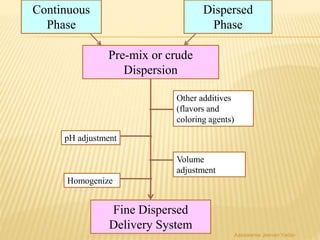
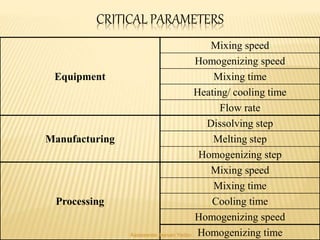
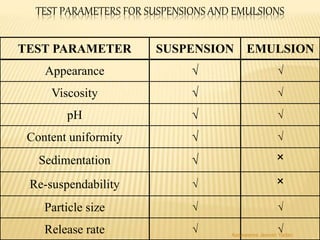
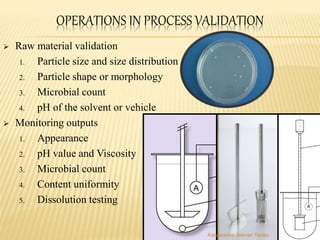
The document discusses the validation of liquid oral dosage forms. It defines validation and its objectives, which include ensuring consistency and reproducibility of the manufacturing process. The key stages of validation are described - pre-validation qualification, process validation, and validation maintenance. For liquid orals, the validation would include equipment, raw materials, the manufacturing process, microbiological quality, product specifications, stability, and packaging. Critical process parameters are identified and acceptance criteria defined. The validation report and requirements for revalidation with changes are also summarized.