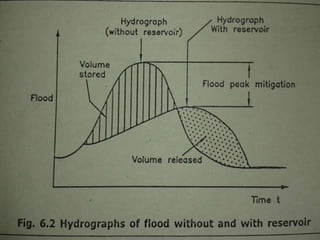
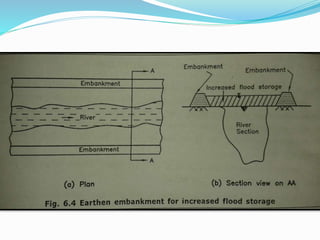
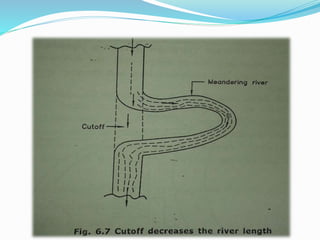
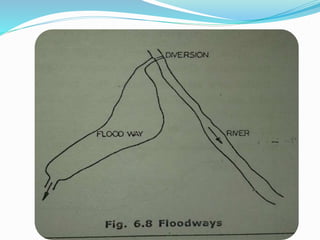
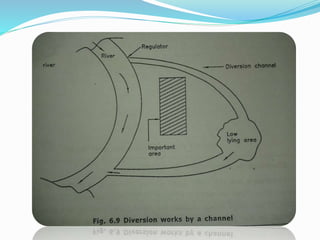
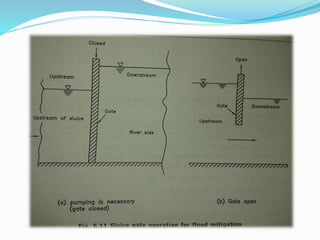
Flooding is caused by high rainfall that overwhelms the land's ability to drain water effectively, especially when the ground is saturated. Flooding often leads to water pollution and health issues. Flood control aims to prevent or reduce flood damage through various structural measures like dams, embankments, channel improvements and river diversions, as well as non-structural measures like forecasting, zoning, fighting, proofing and insurance. Recent major floods in India have displaced over 2 million people in Bihar in 2008 and affected 28 million across India, Bangladesh and Nepal in 2007.