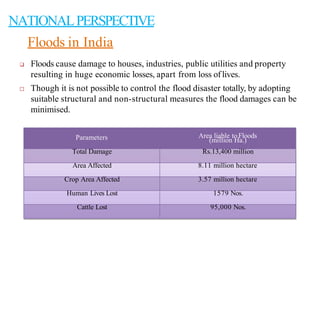
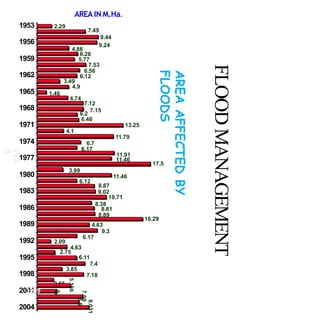
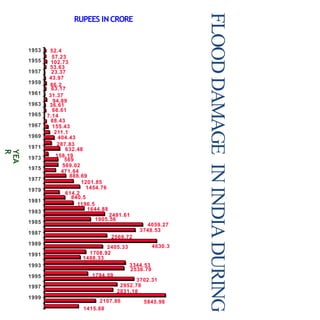
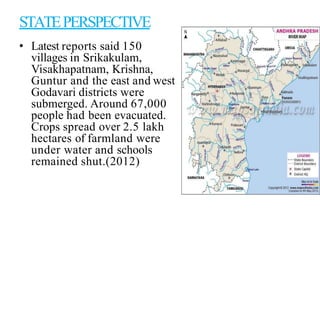
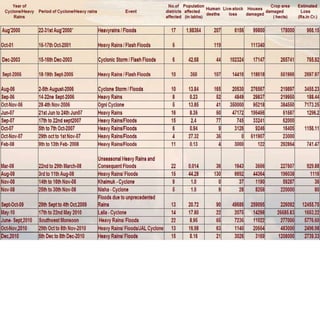
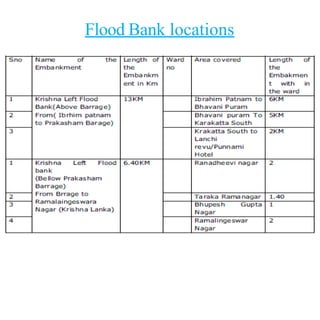
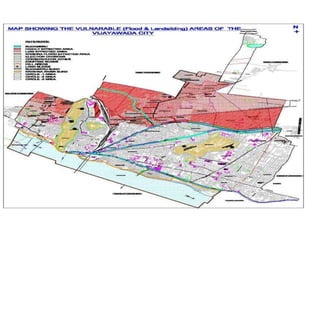
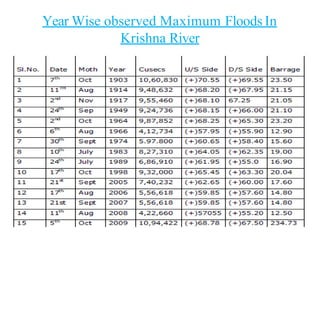
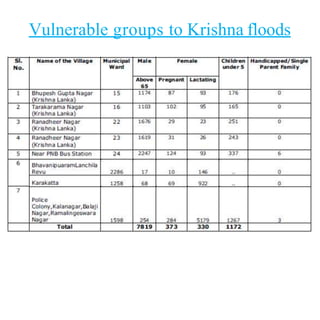
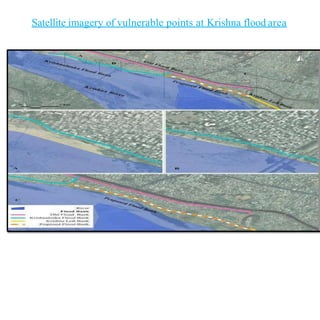
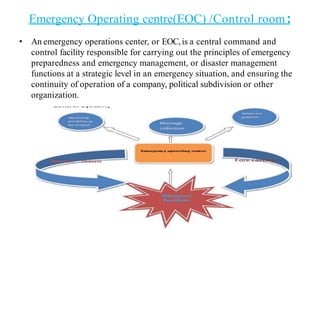
Floods are a common natural disaster in India that occur annually, causing widespread damage to lives and property. Some key points about floods and their management in India include:
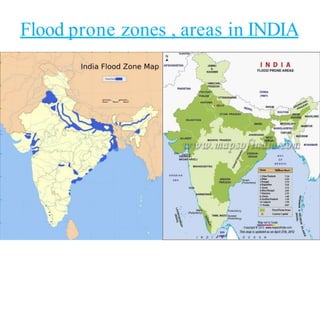
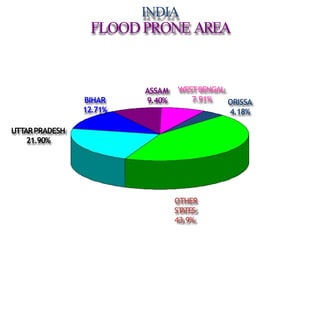
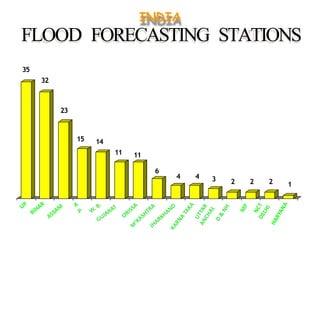
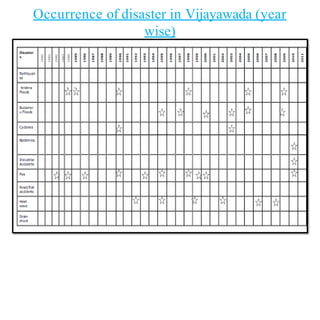
- The major flood-prone states are Uttar Pradesh, Bihar, Assam, and West Bengal.
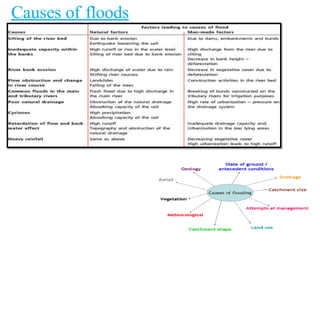
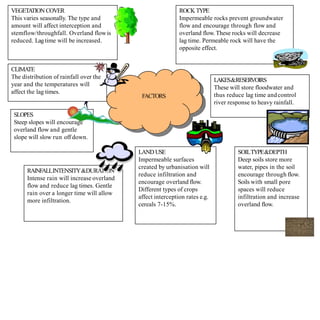
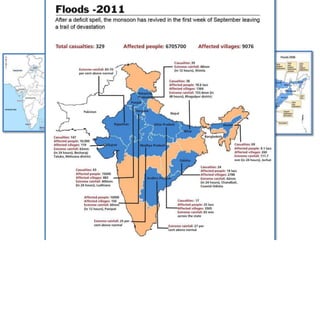
- Floods are caused by heavy rainfall, river overflow, coastal flooding, and sometimes dam/reservoir failures. They impact lives, infrastructure, agriculture, and the economy.
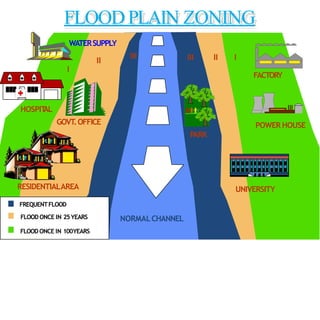
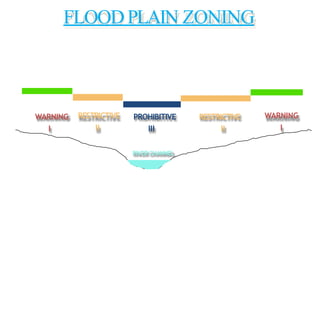
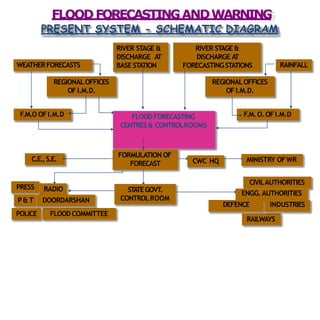
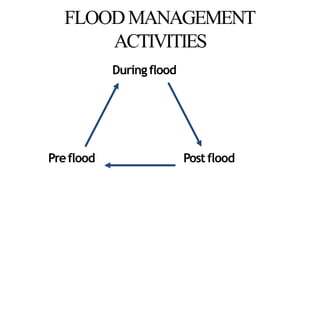
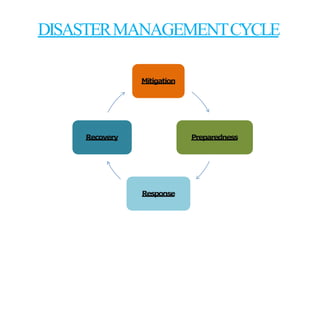
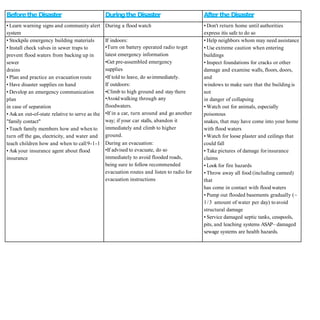
- Flood management involves forecasting, structural measures like dams and levees, and non-structural plans to minimize damage and warn communities. Zoning also directs development away from high risk flood areas.