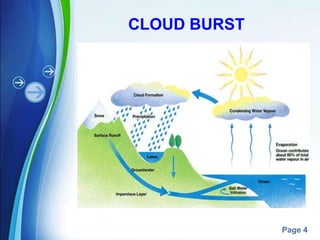
This document discusses cloud bursting, which is an extreme amount of precipitation over a short period of time capable of causing flash flooding. It defines cloud bursting as rainfall of over 100 mm per hour and explains that the rapid growth of large raindrops falling from convective clouds up to 15 km high can cause these events. The document also notes that hilly areas are more prone to cloud bursting when water flows down steep slopes quickly. While cloud bursts are difficult to predict precisely, areas likely to experience heavy rain can be identified. The impacts of cloud bursting include floods, damage, deforestation, and loss of life. An example of a devastating cloud burst is described from Leh, Ladakh in 2010 that killed 300 people.