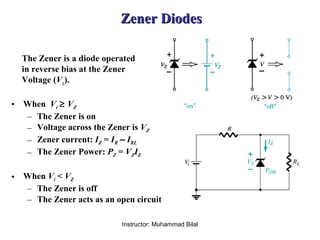
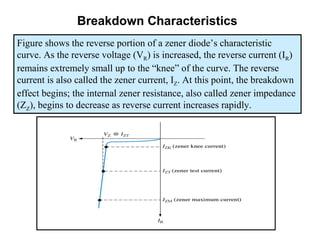
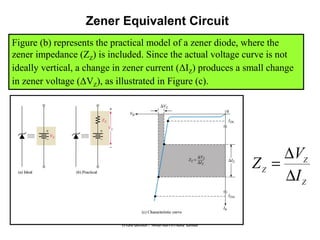
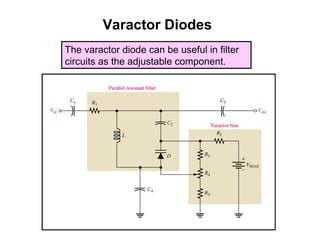
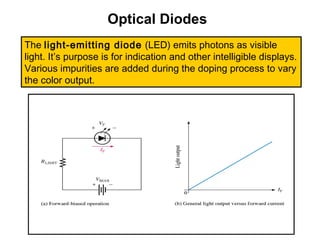
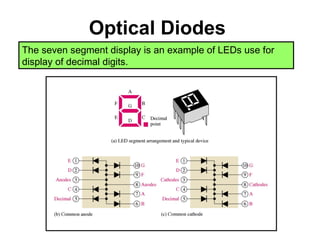
Zener diodes operate in reverse bias at the Zener voltage. When the reverse voltage is greater than or equal to the Zener voltage, the Zener diode is on and conducts a Zener current. When the reverse voltage is less than the Zener voltage, the diode is off. The breakdown characteristics of a Zener diode show that the reverse current remains small until the "knee" where breakdown begins and the internal Zener resistance decreases rapidly. The Zener equivalent circuit models the Zener impedance, so a change in Zener current produces a small change in Zener voltage.