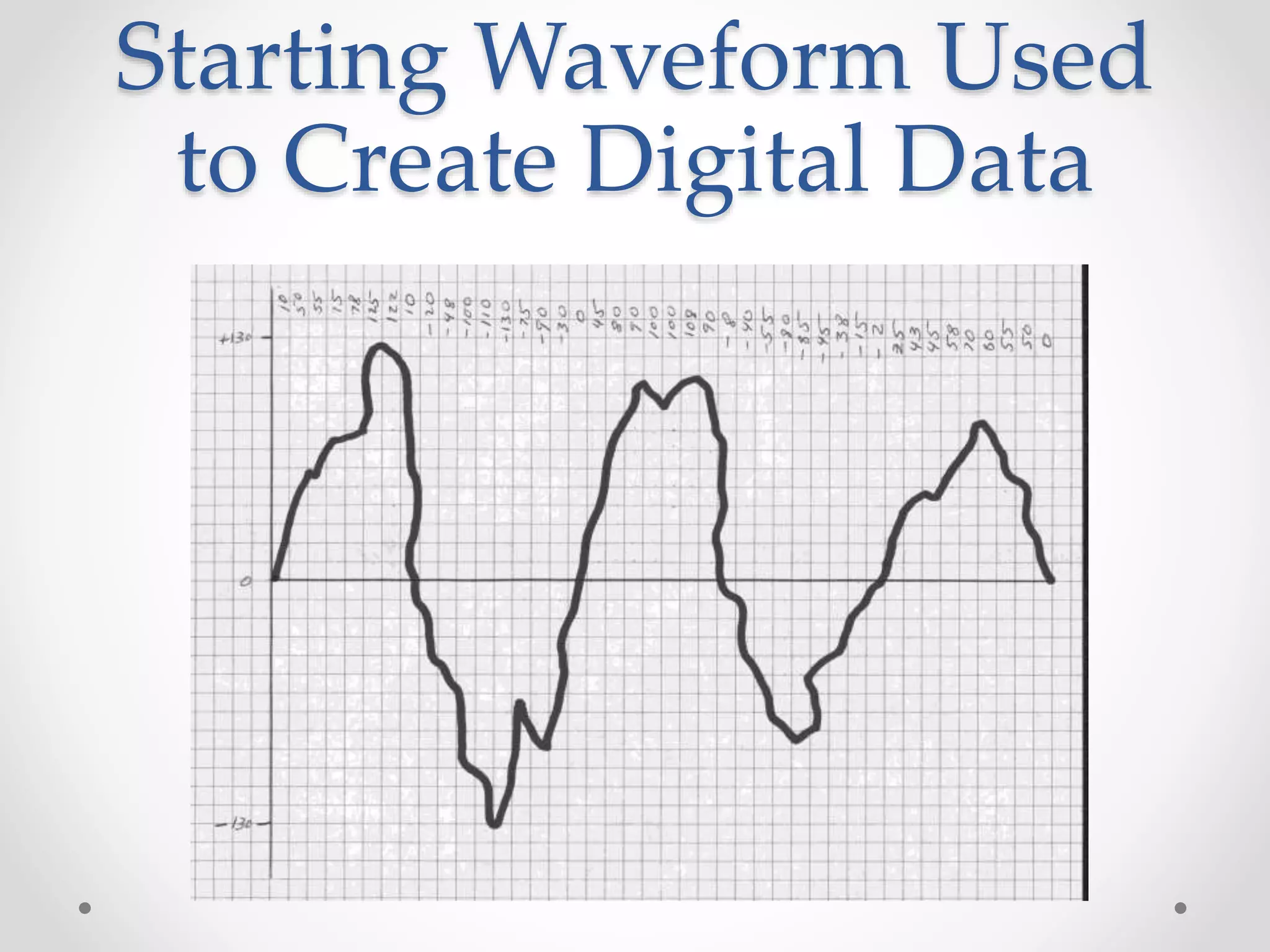
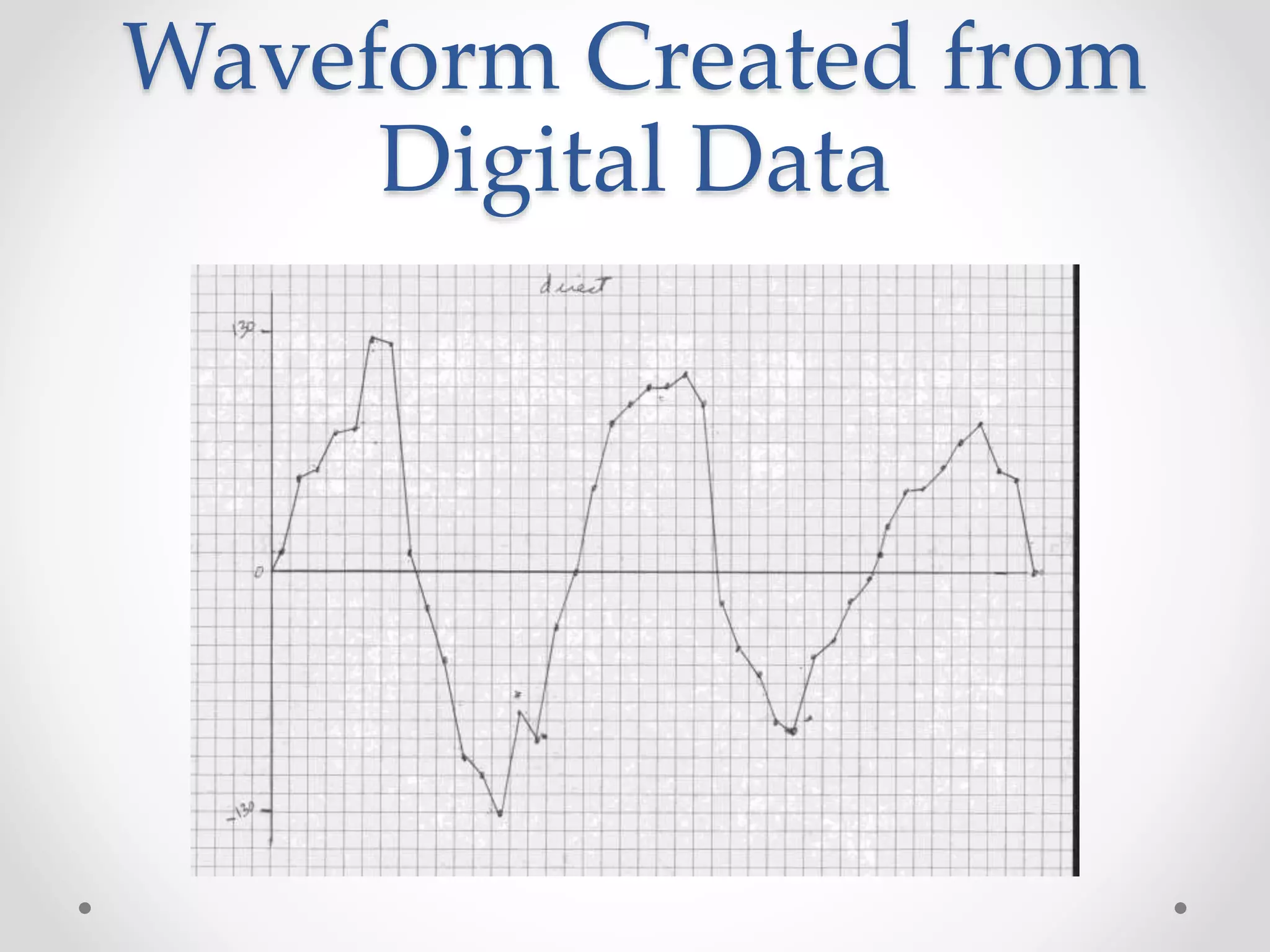
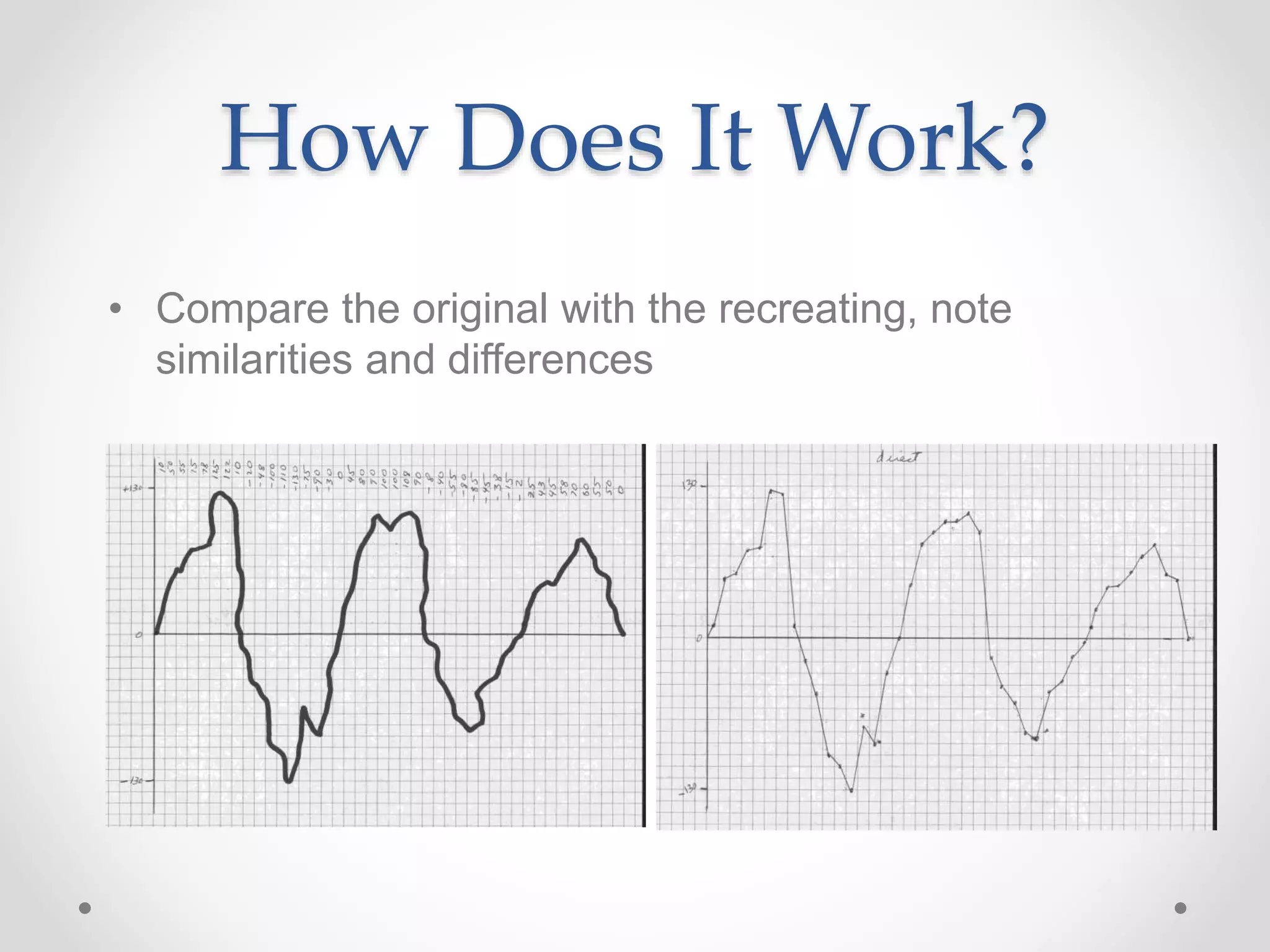
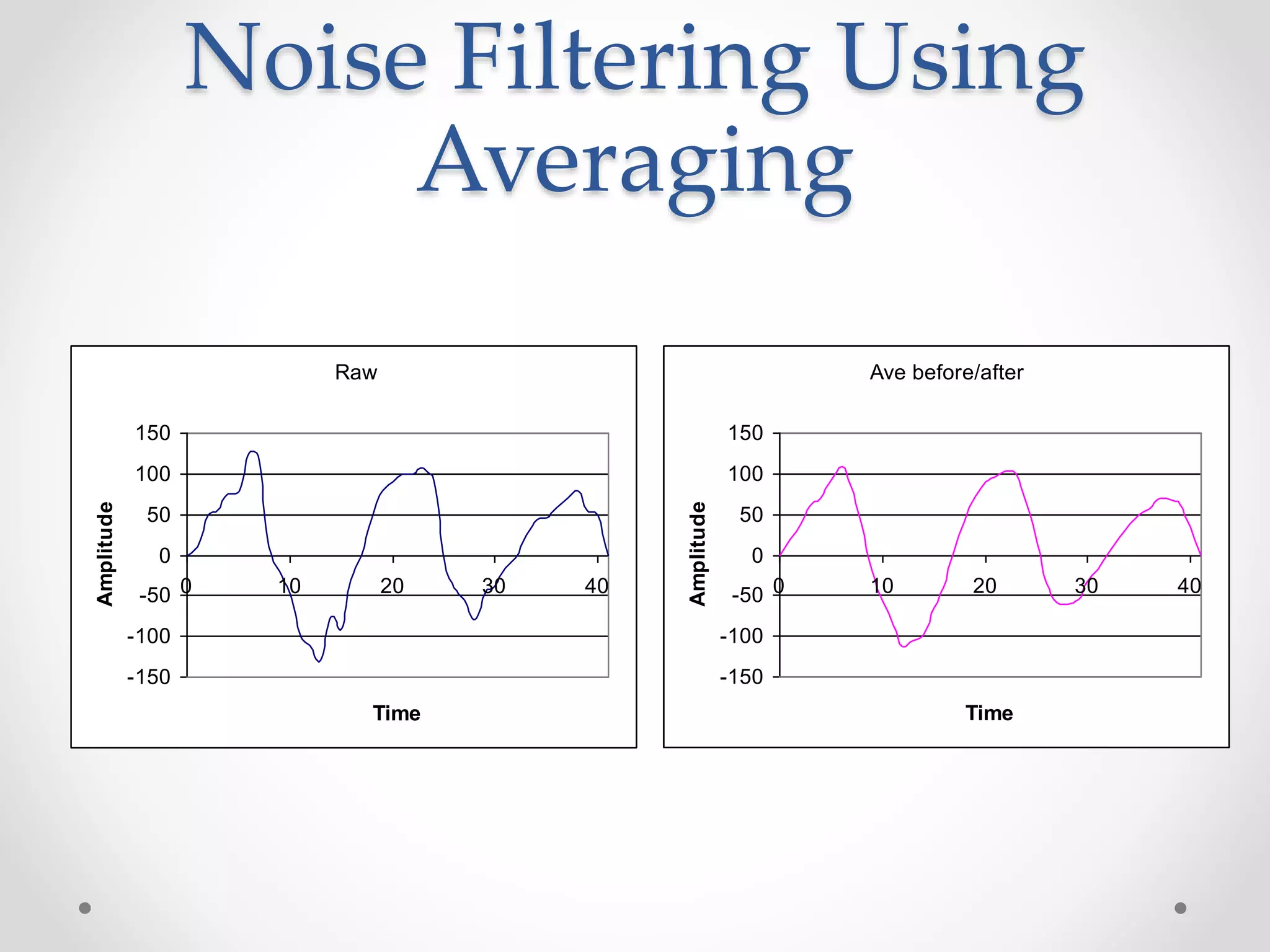
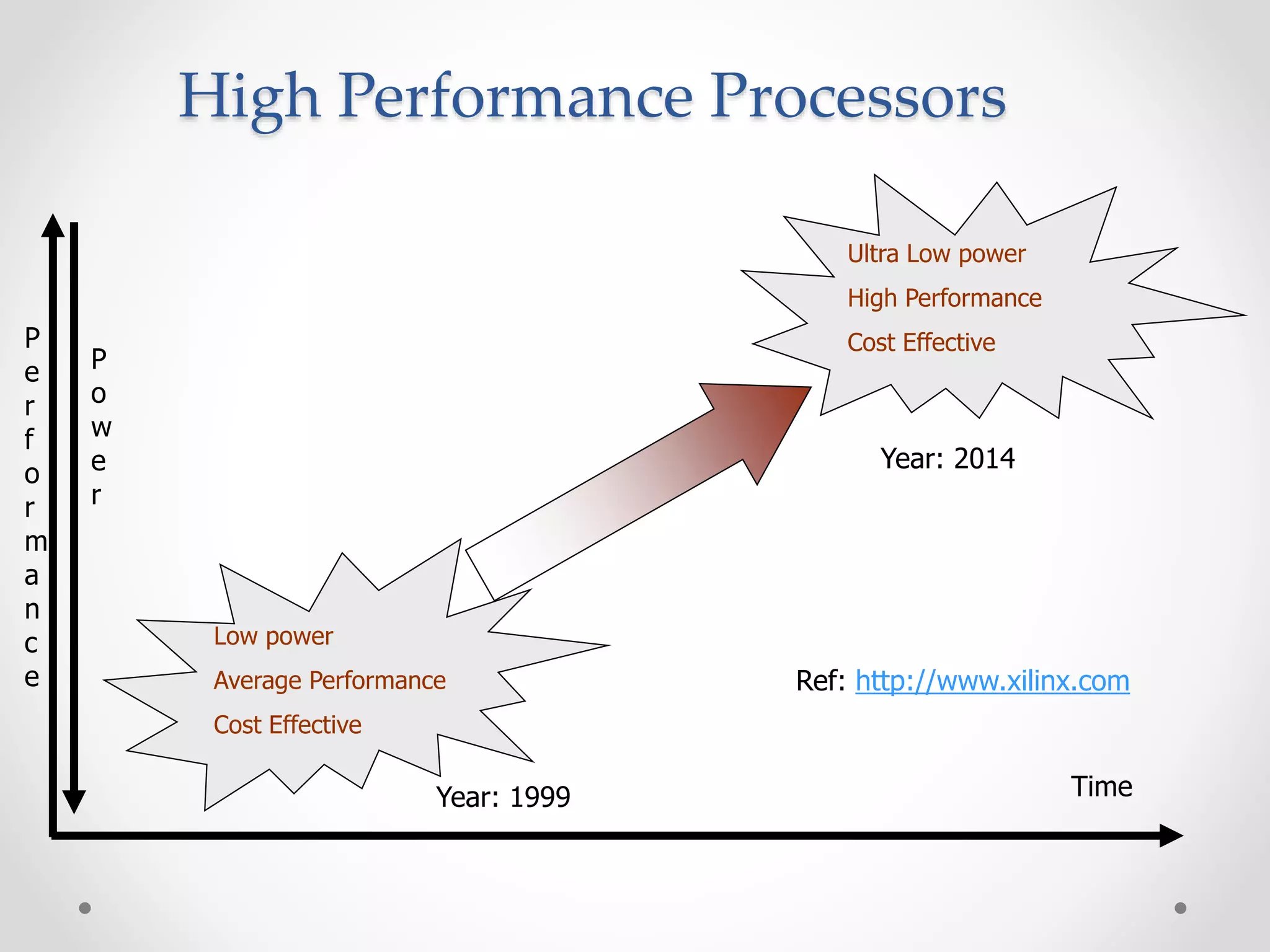
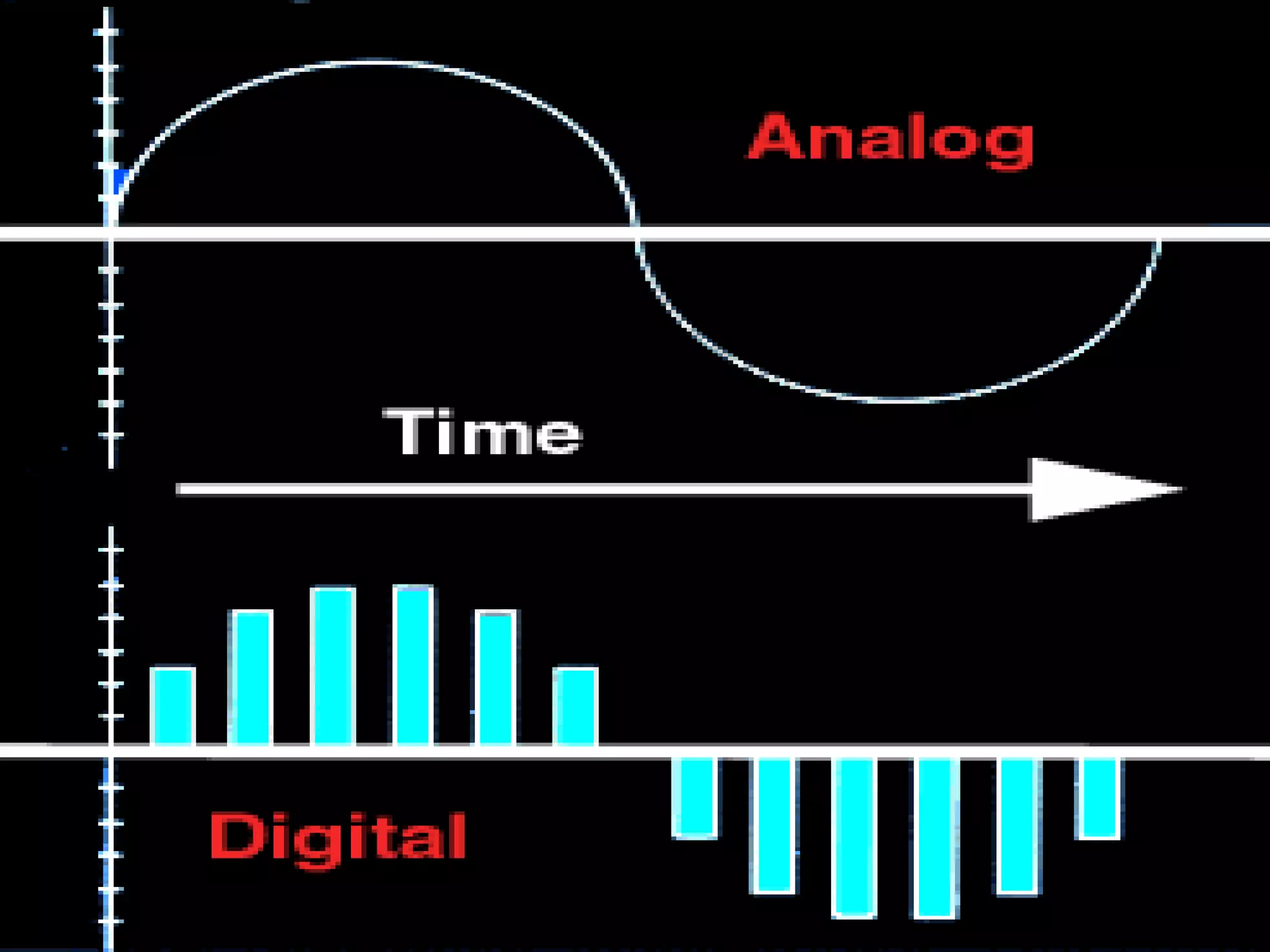
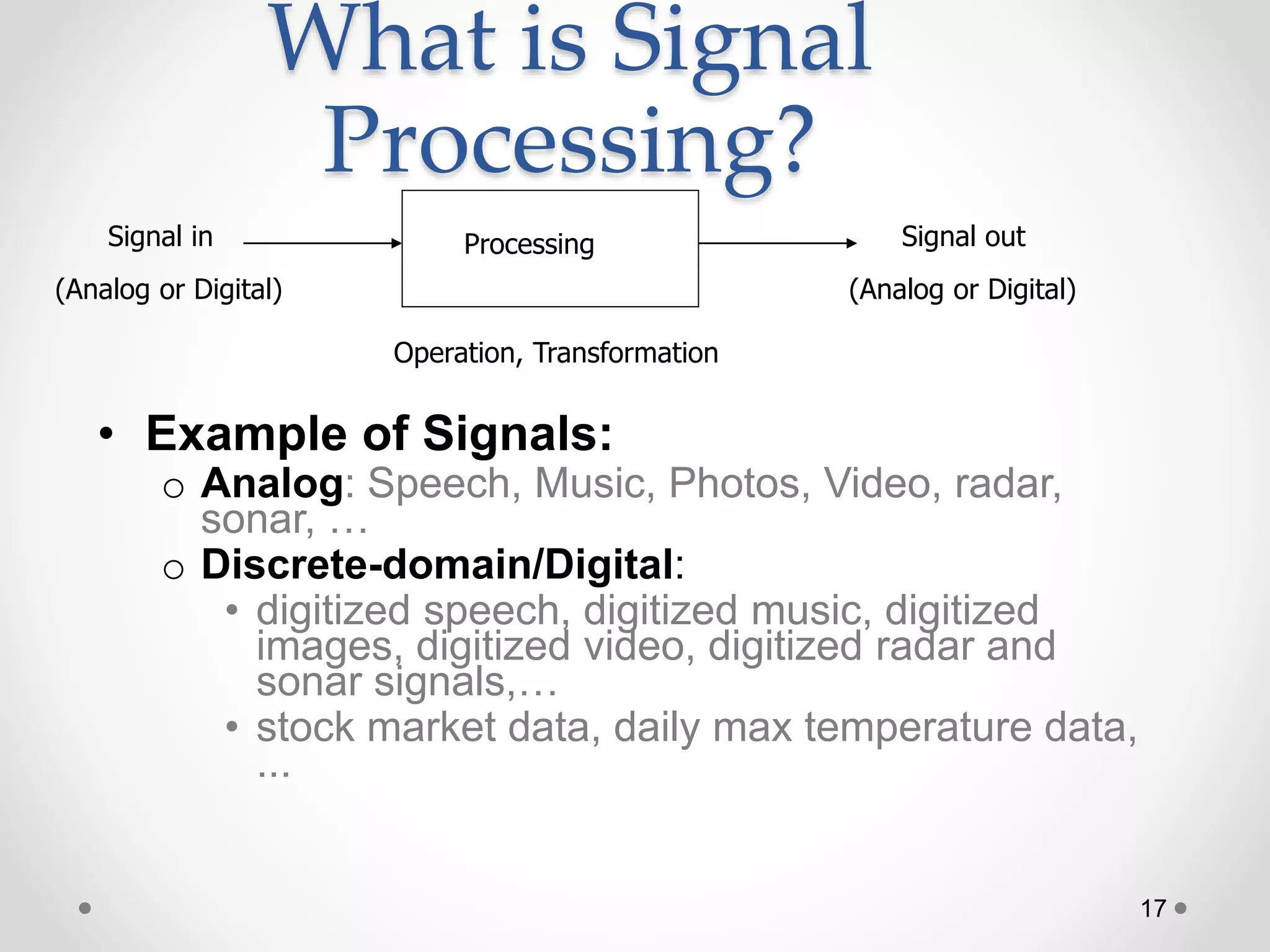
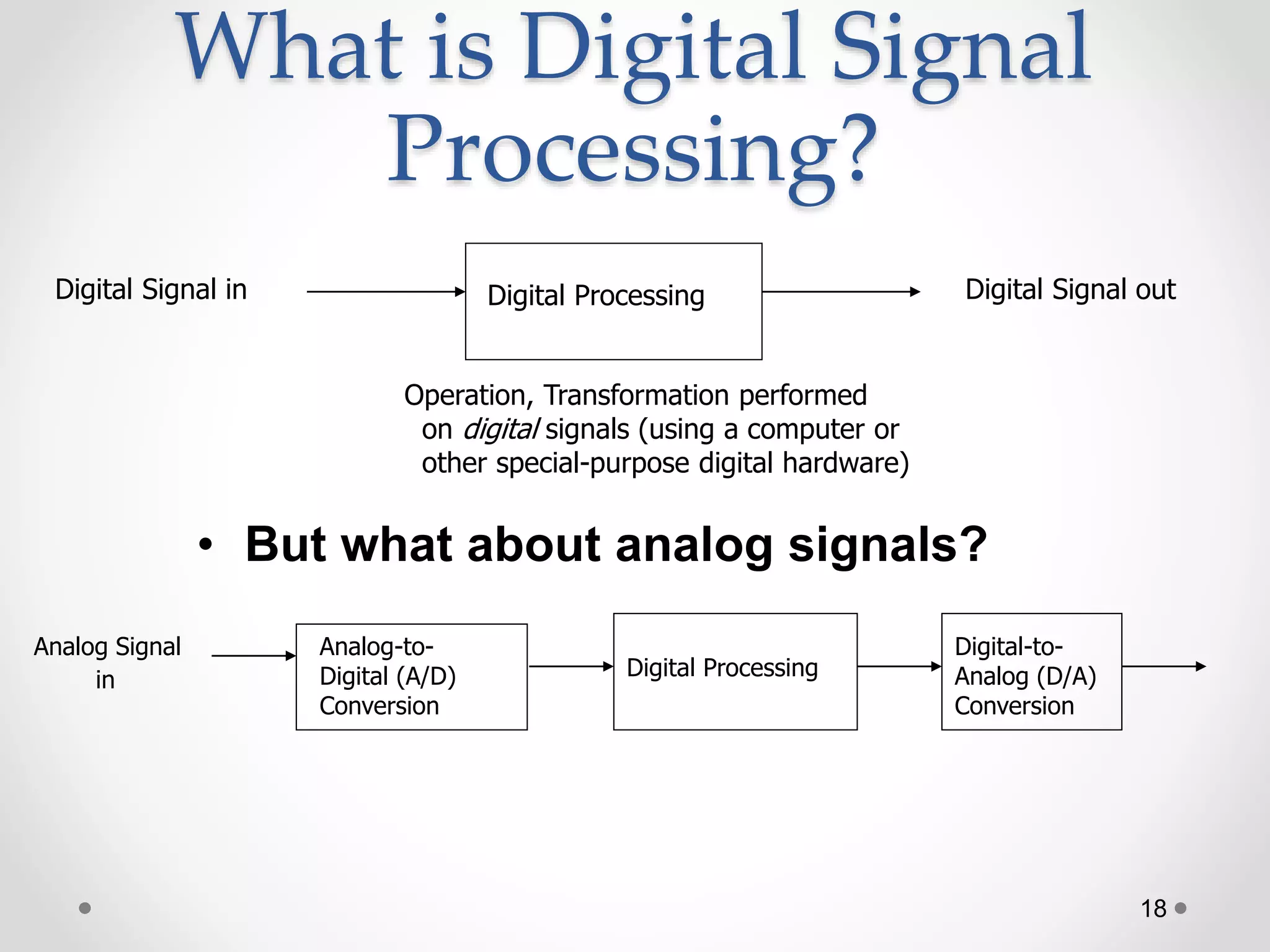
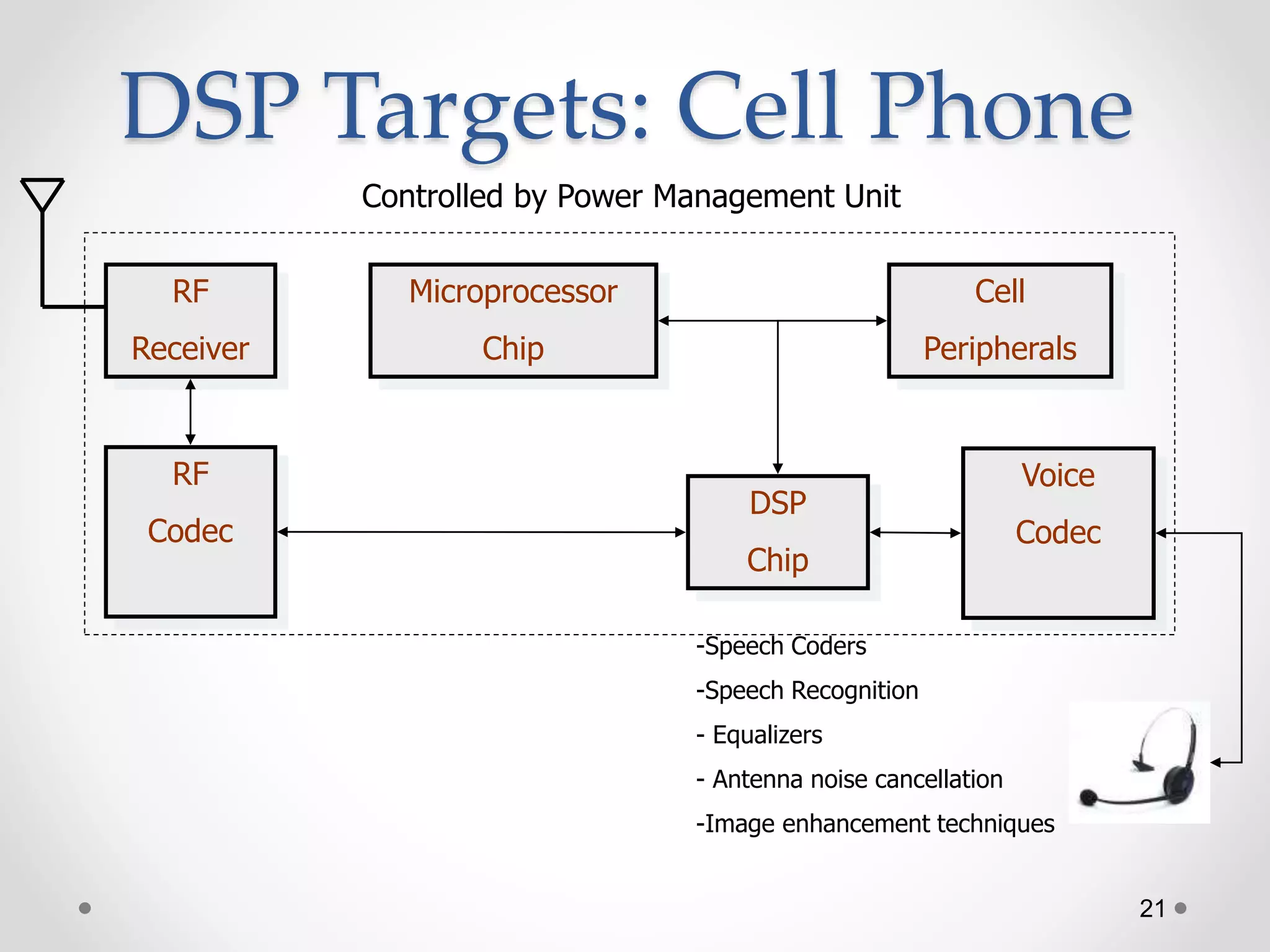
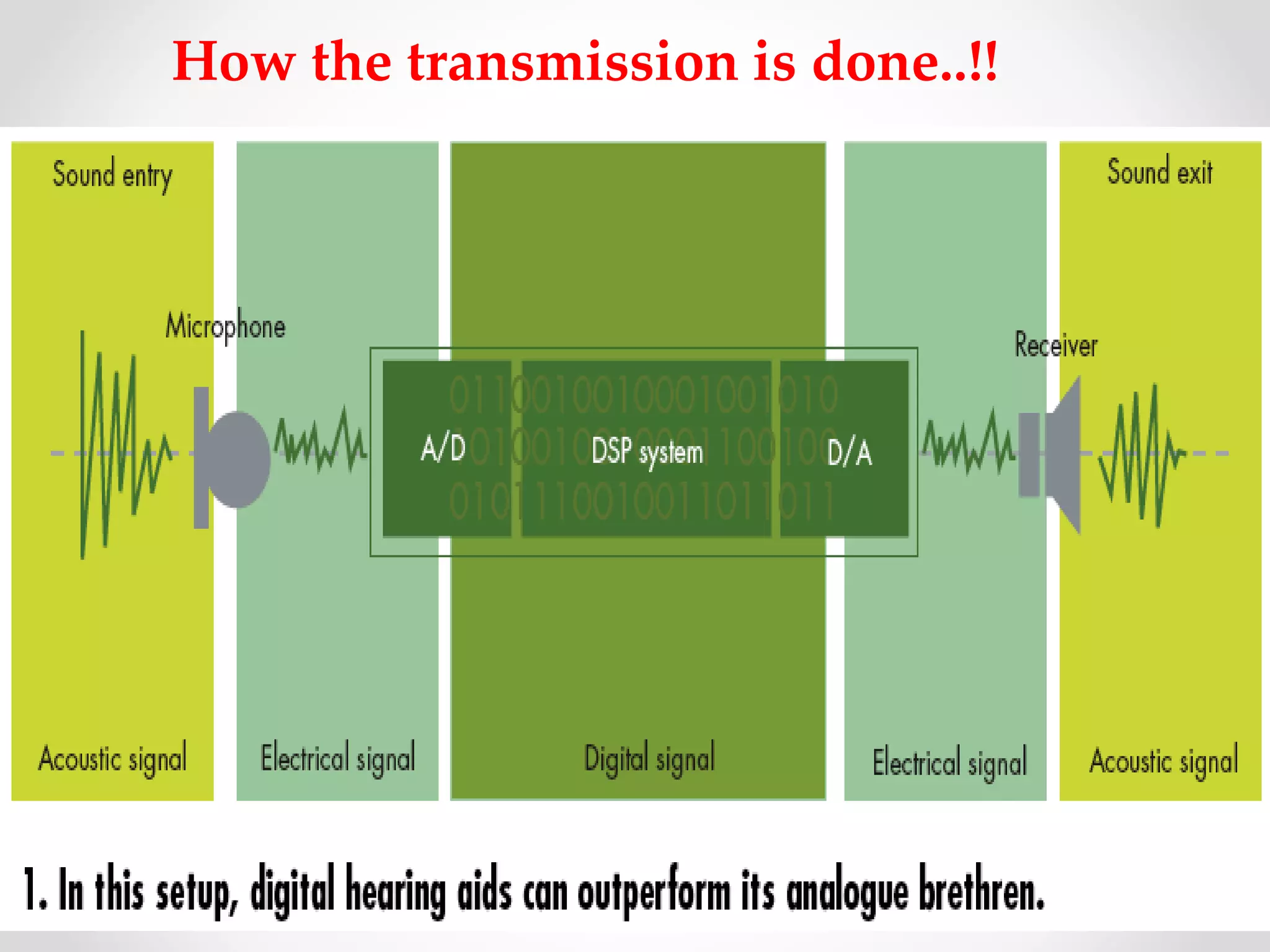
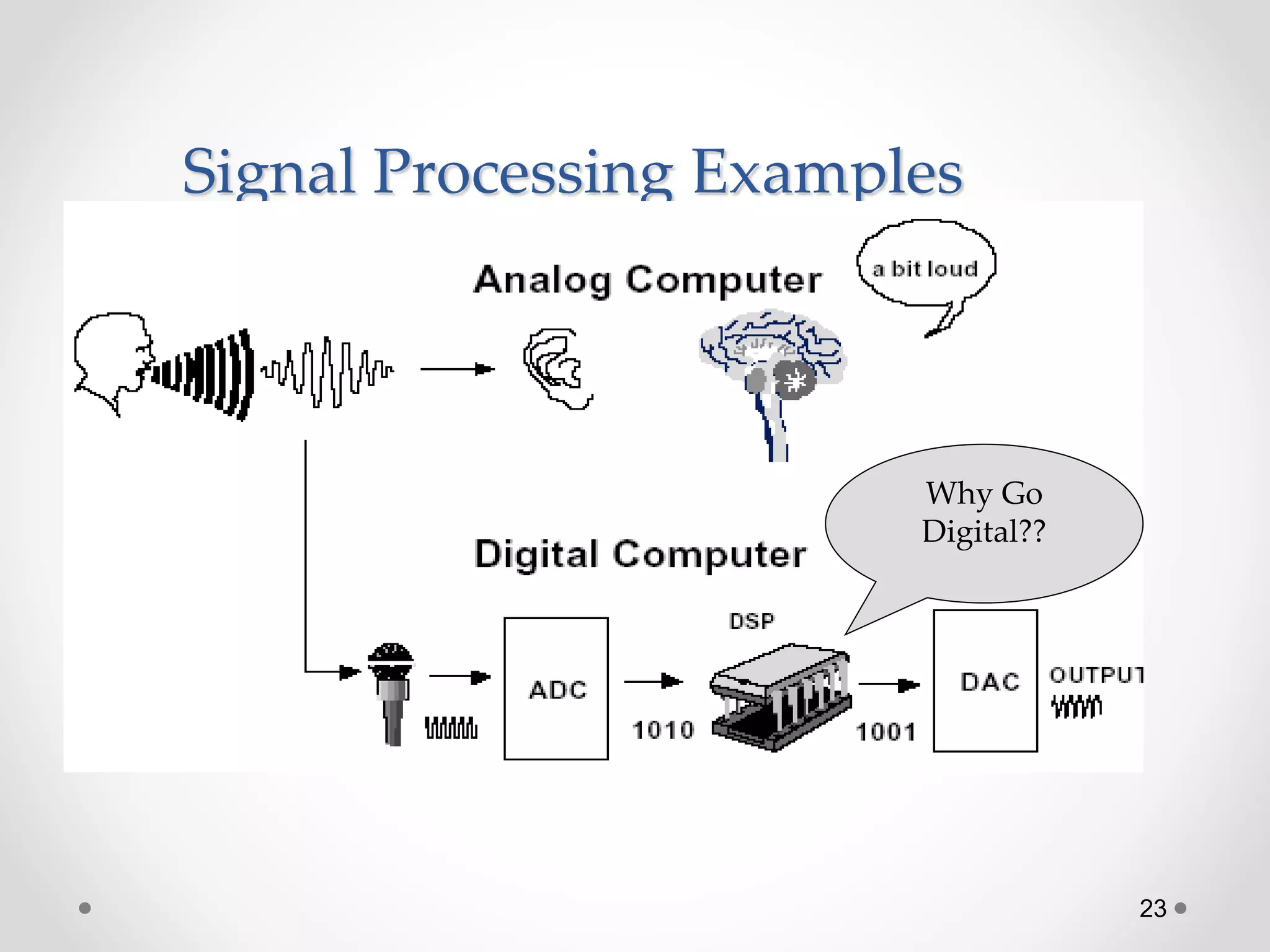
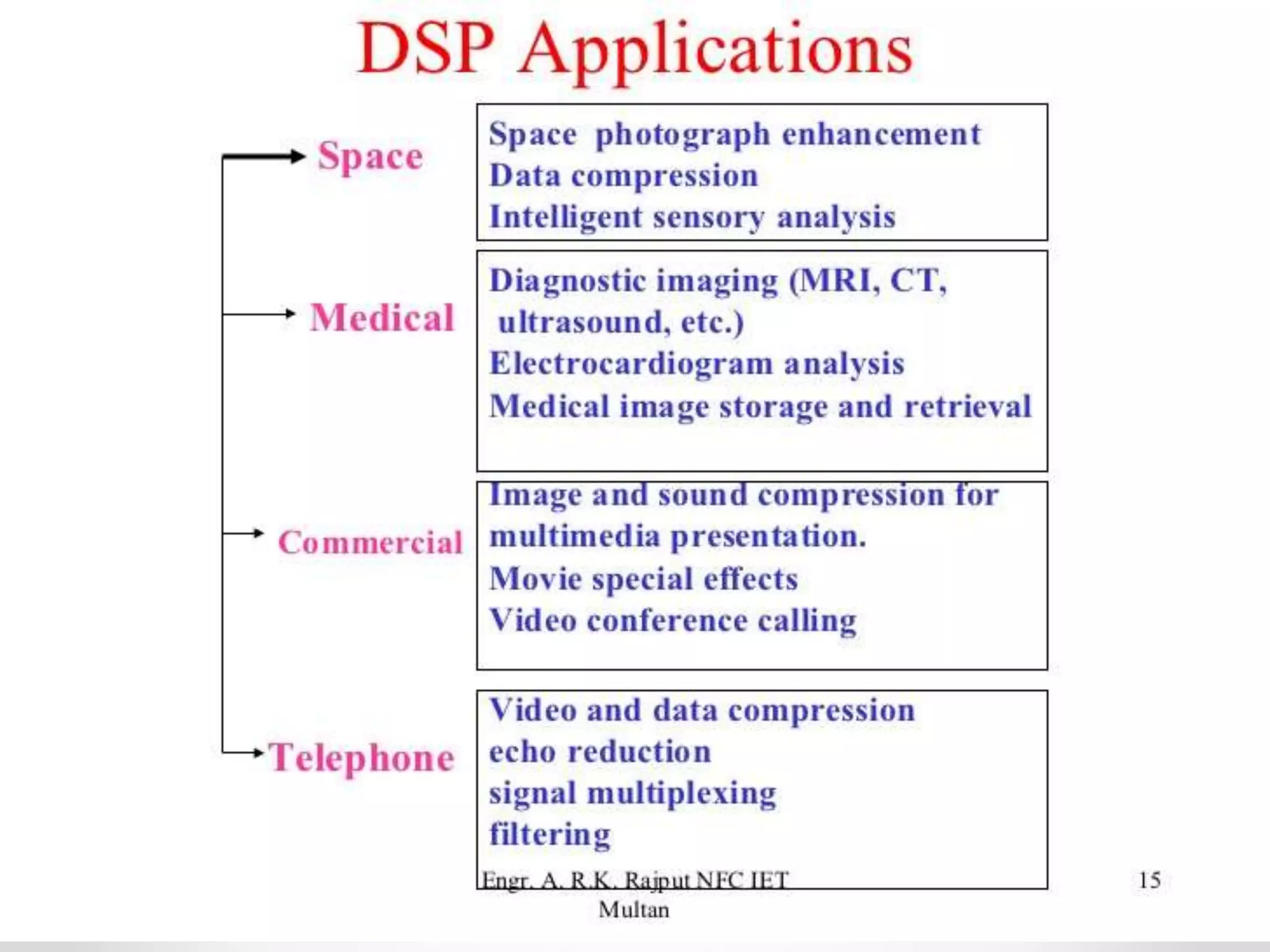
This document provides an introduction to digital signal processing (DSP). It explains that DSP involves converting analog signals to discrete digital values and then manipulating the digital data using mathematical operations. Common DSP operations include filtering, convolution, correlation and discrete transformations. DSP has advantages over analog processing like programmability, repeatability, and noise immunity. DSP is used in applications like audio processing, communications, and imaging. The document discusses how DSP works and provides examples of noise filtering on a sample waveform. It also outlines the types of DSP processors and lists some key advantages and disadvantages of digital signal processing.