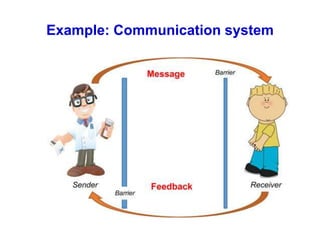
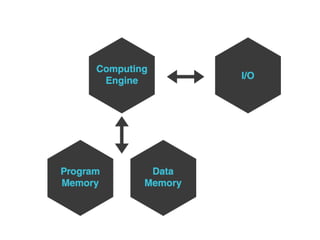
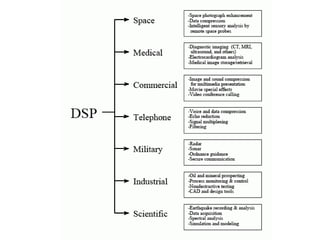
Digital Signal Processing (DSP) involves the manipulation of discrete signals using digital technology to perform various functions such as sound and image processing, and is key in telecommunications. DSP offers advantages over analog signal processing, including higher accuracy, flexibility, and ease of configuration, storage, and processing. Despite some disadvantages like additional complexity and frequency limitations, DSP is essential for modern applications, enhancing efficiency and adaptability in various fields.