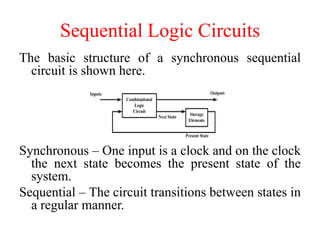
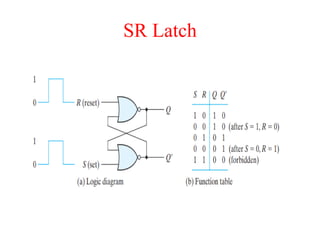
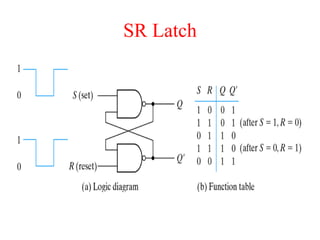
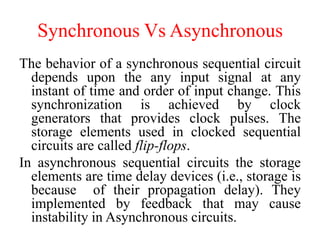
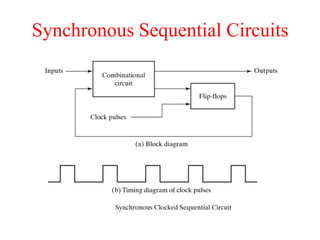
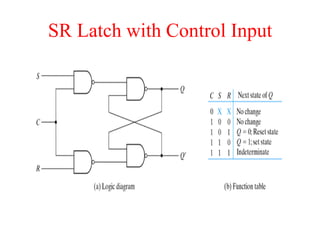
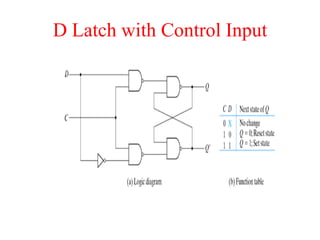
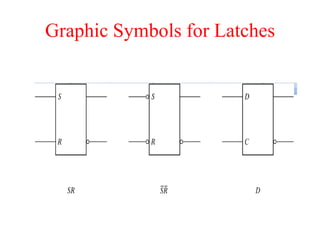
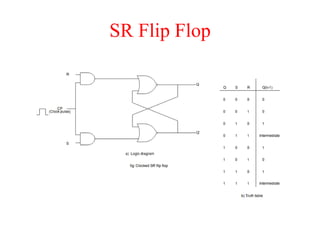
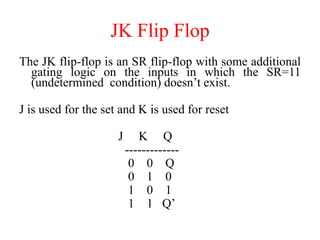
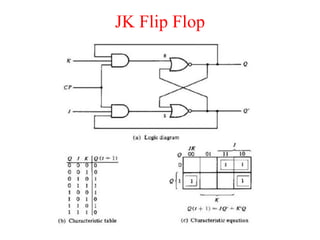
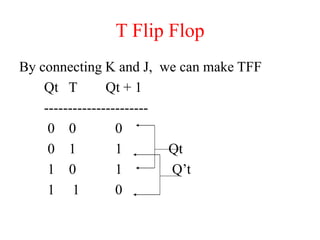
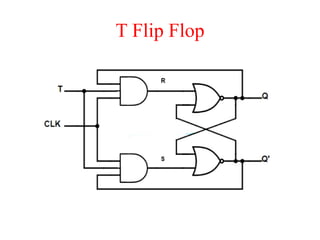
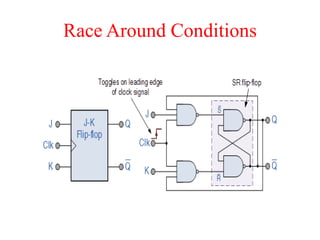
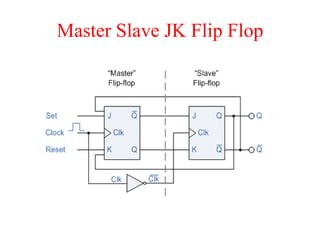
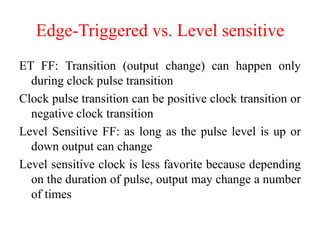
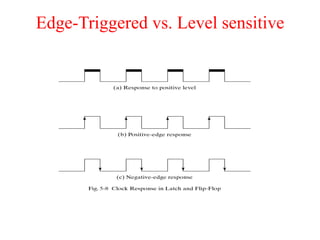
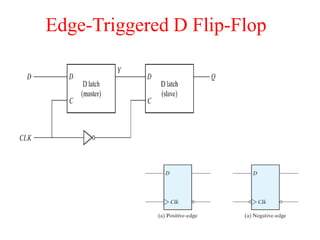
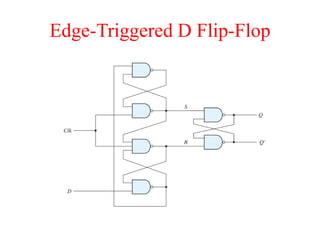
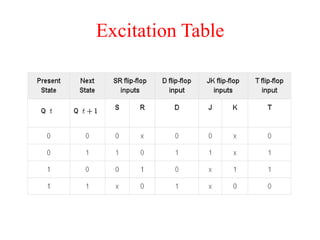
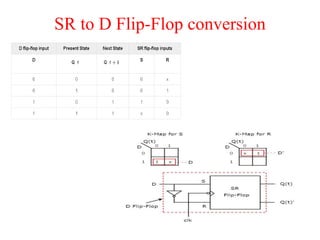
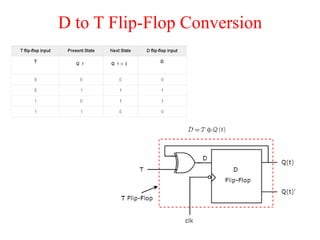
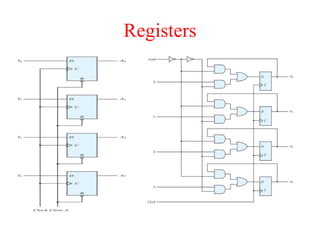
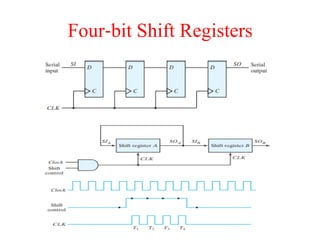
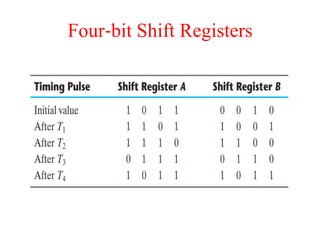
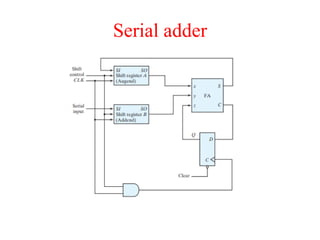
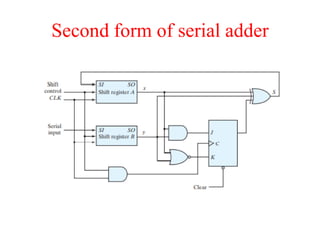
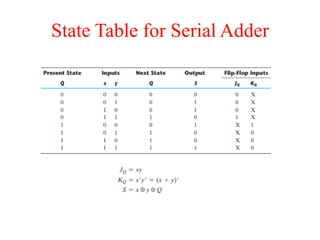
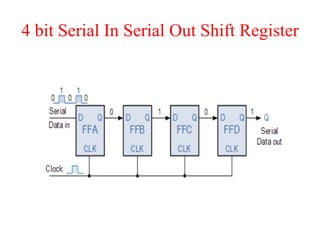
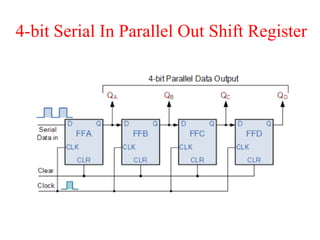
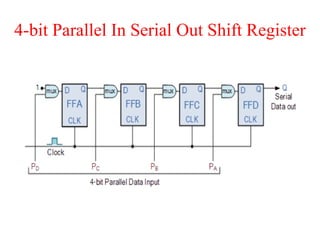
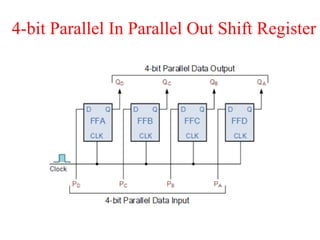
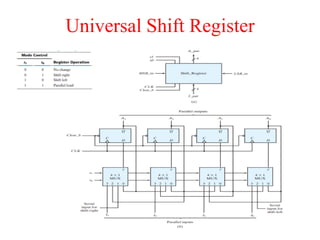
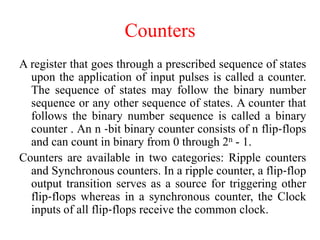
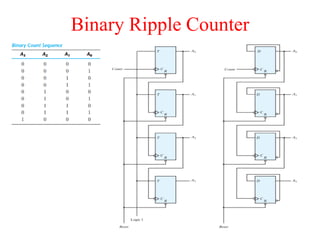
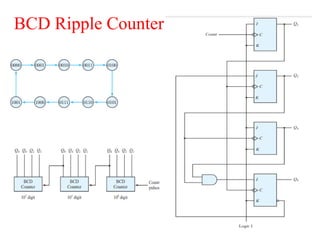
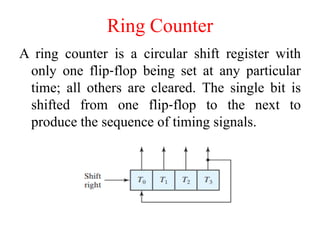
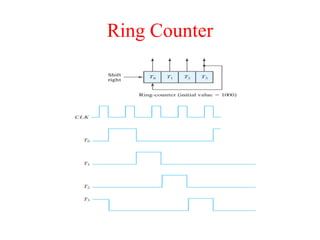
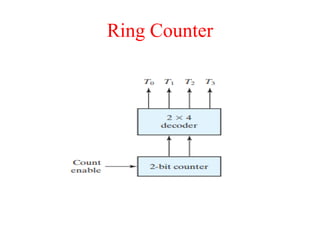
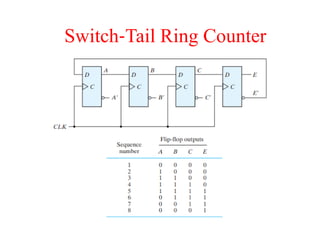
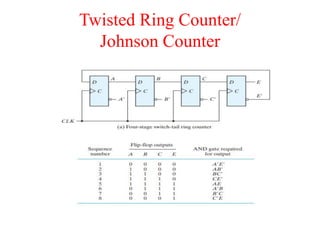
The document outlines a digital electronics course taught by Dr. K. Kannan, covering topics such as fundamental digital concepts, Boolean algebra, and the design of various combinational and sequential digital circuits. It emphasizes the analysis and design of memory elements and sequential circuits like flip-flops, counters, and shift registers, along with their applications in digital systems. The material discusses both synchronous and asynchronous logic designs, illustrating how different types of flip-flops and counters function within digital electronics.