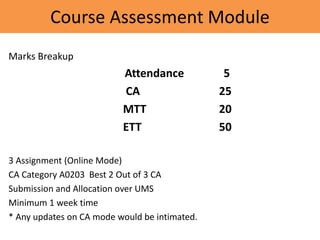
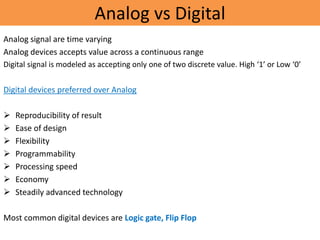
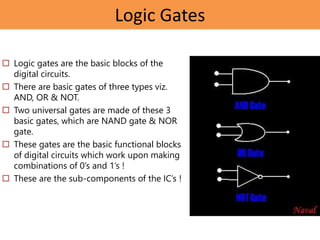
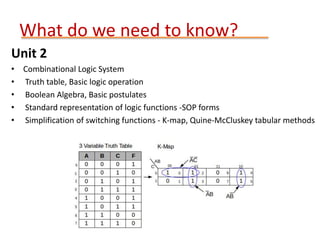
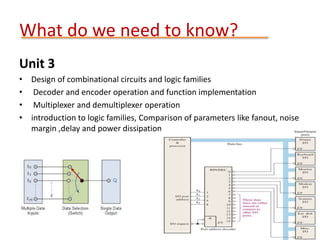
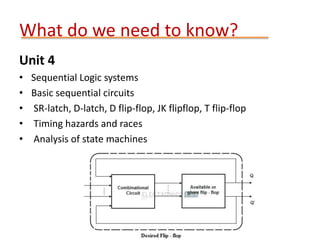
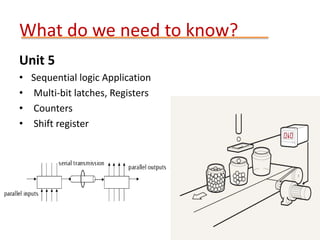
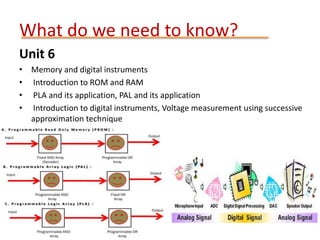
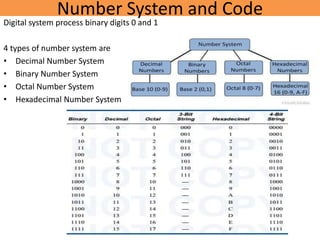
This document provides details about the ECE 213 Digital Electronics course. It includes information about the course instructor, textbook, assessment breakdown, topics to be covered in each unit including binary number systems, logic gates, combinational and sequential logic systems, memory and applications. The objectives are to understand digital concepts and apply them to analyze and design basic digital circuits and systems. The future scope of digital electronics is also highlighted due to advantages like reduced size, improved performance and secure data transmission using VLSI technology.

![Course details
[ LTP 3-0-0]
[ 3 lectures /week]
• Text Book
1. DIGITAL FUNDAMENTALS by THOMAS L. FLOYD , R. P JAIN, PEARSON
• Reference Book
1. DIGITAL LOGIC DESIGN by MORRIS MANO, PRENTICE HALL OF INDIA,
5th Edition, (2001)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductiontodigitalelectronicswhatwewillstudy-230226101603-8736bf17/85/Introduction-to-Digital-Electronics-What-we-will-study-ppt-2-320.jpg)