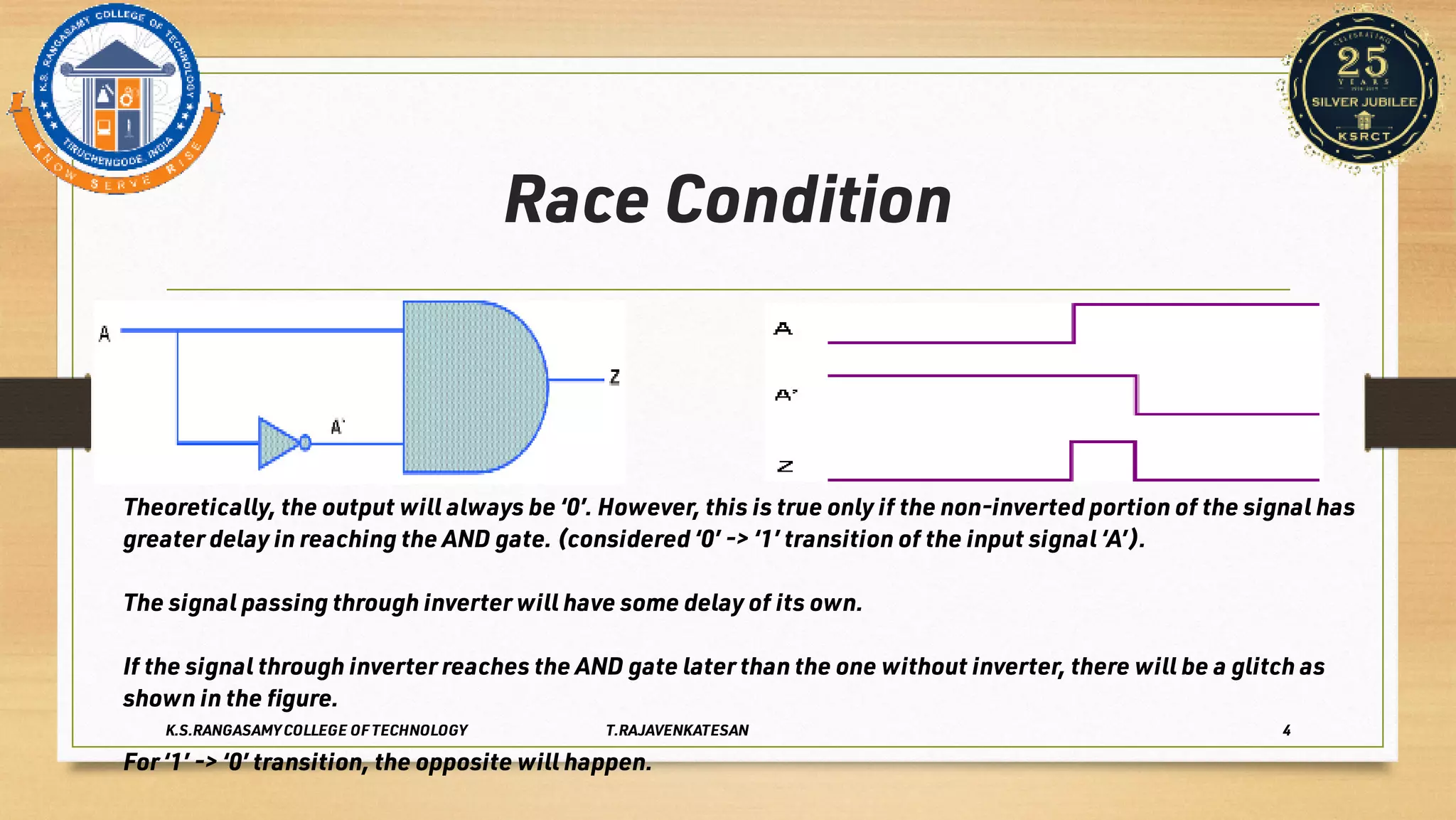
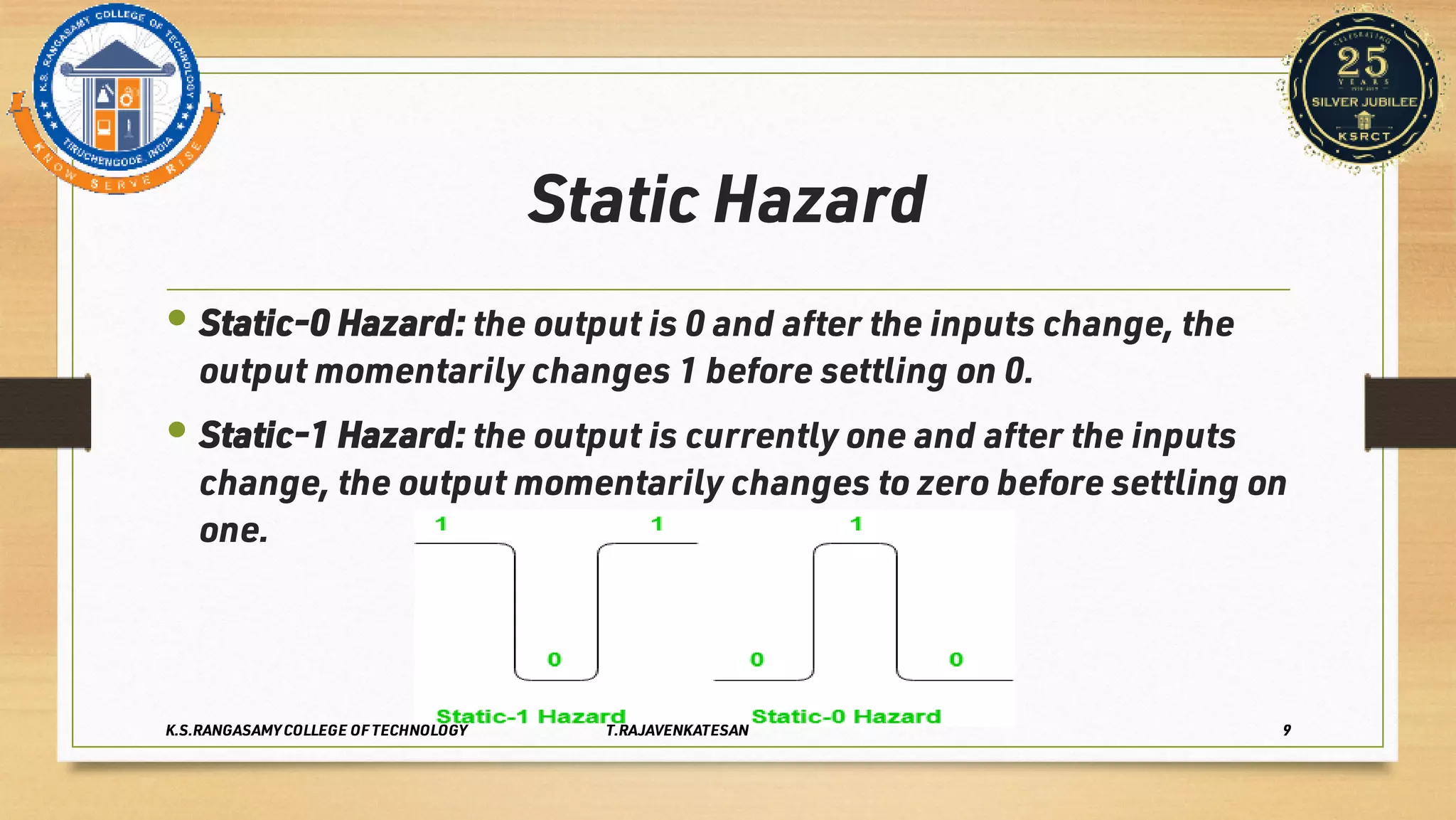
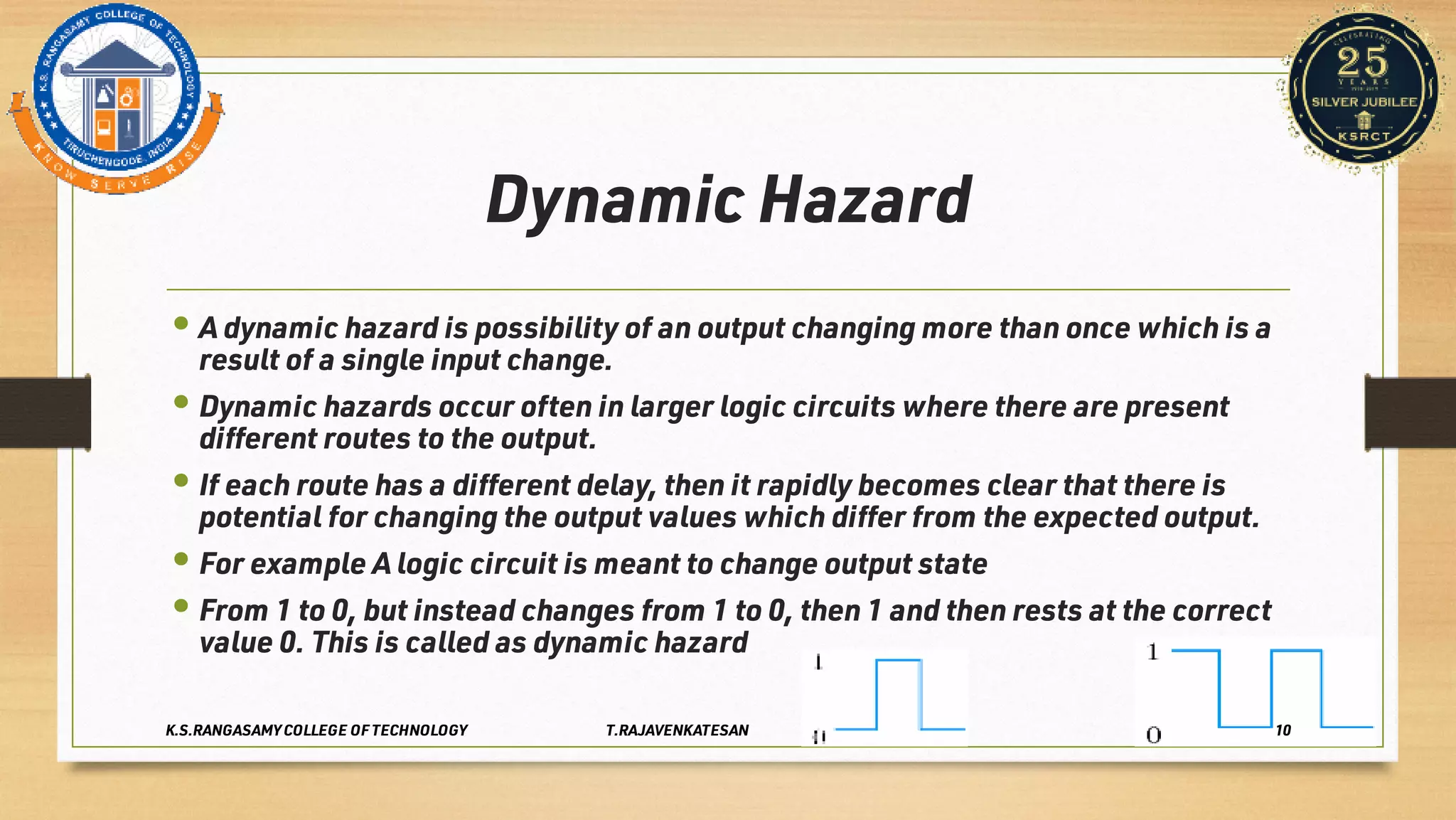
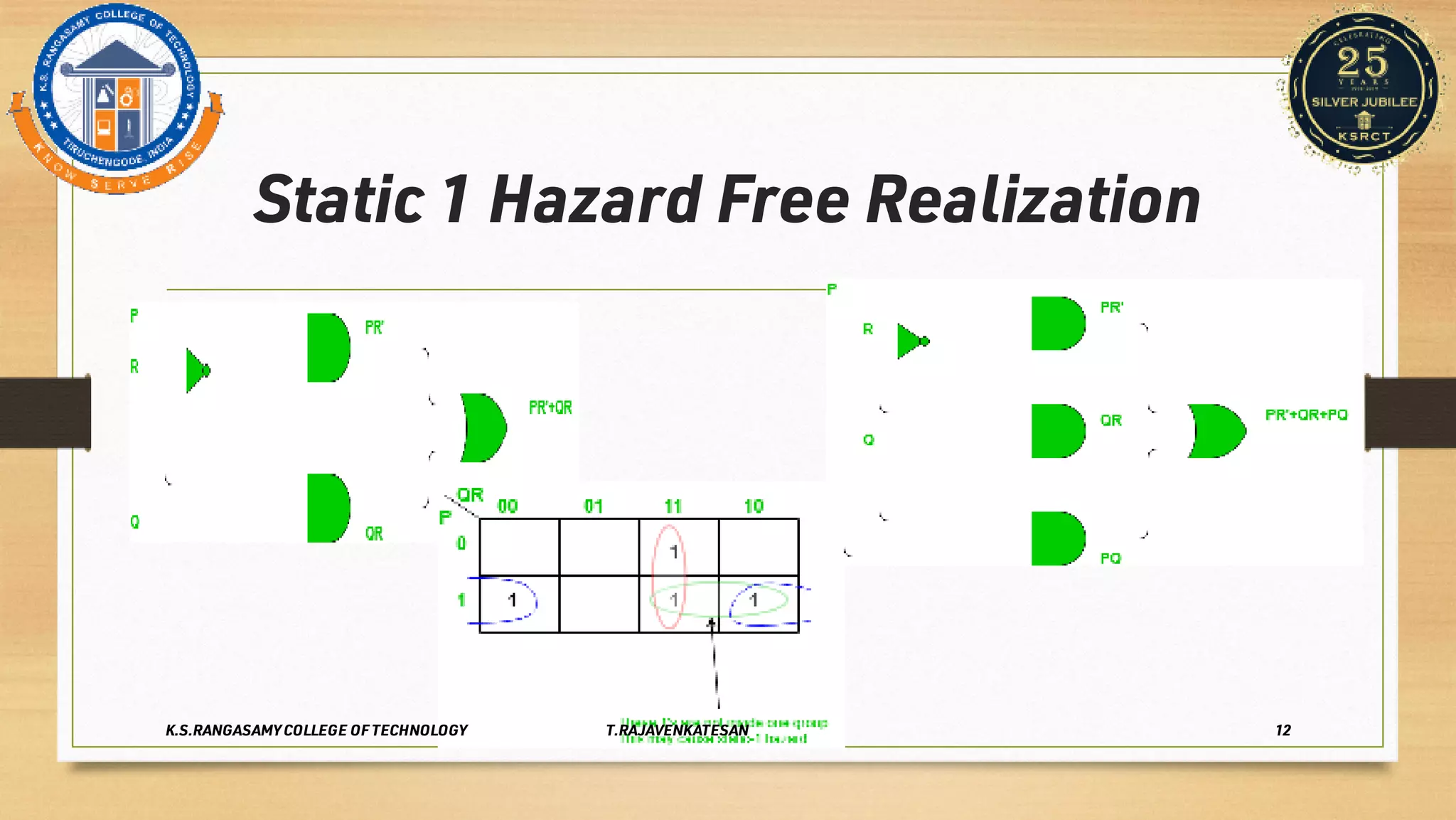
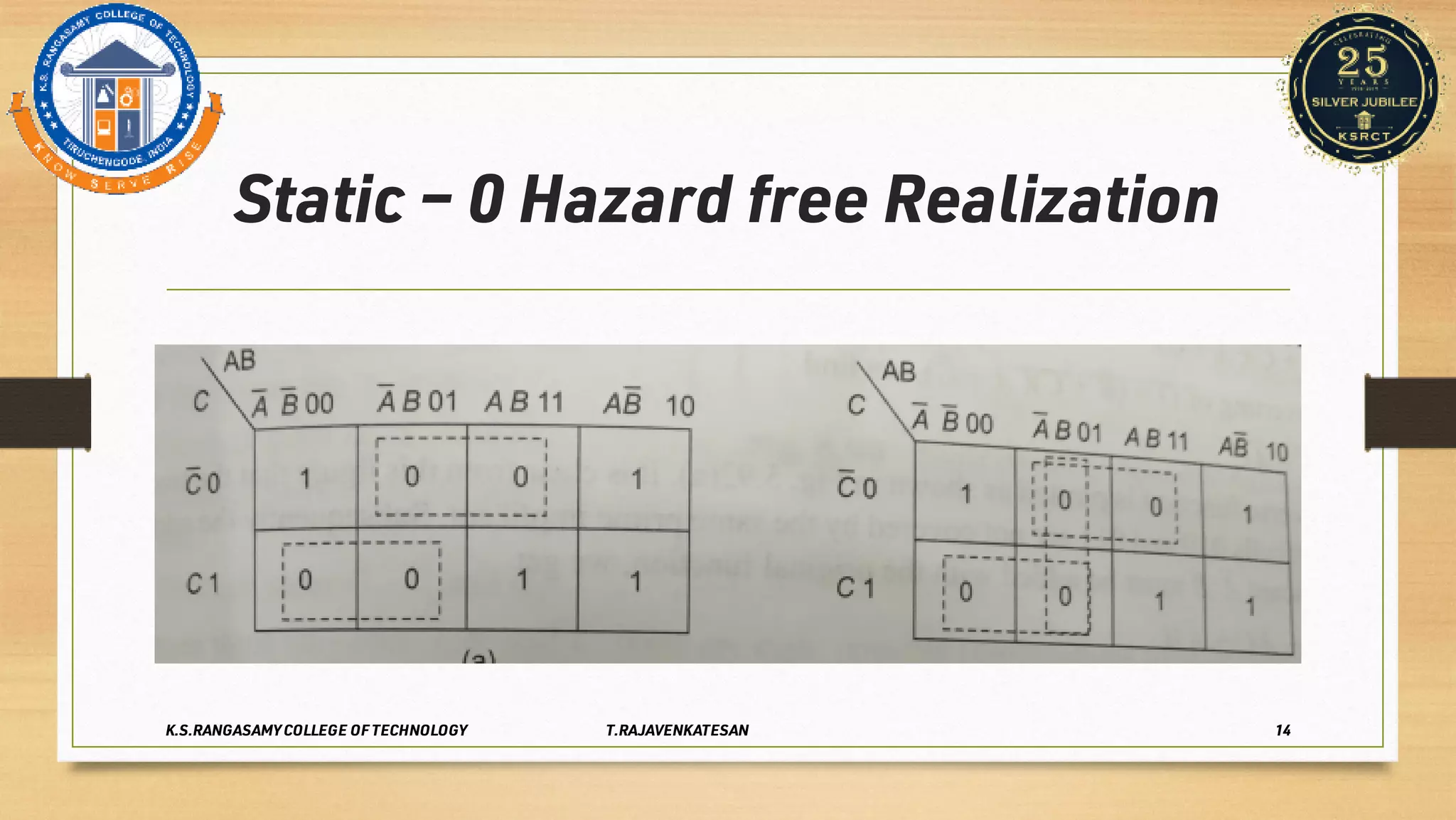
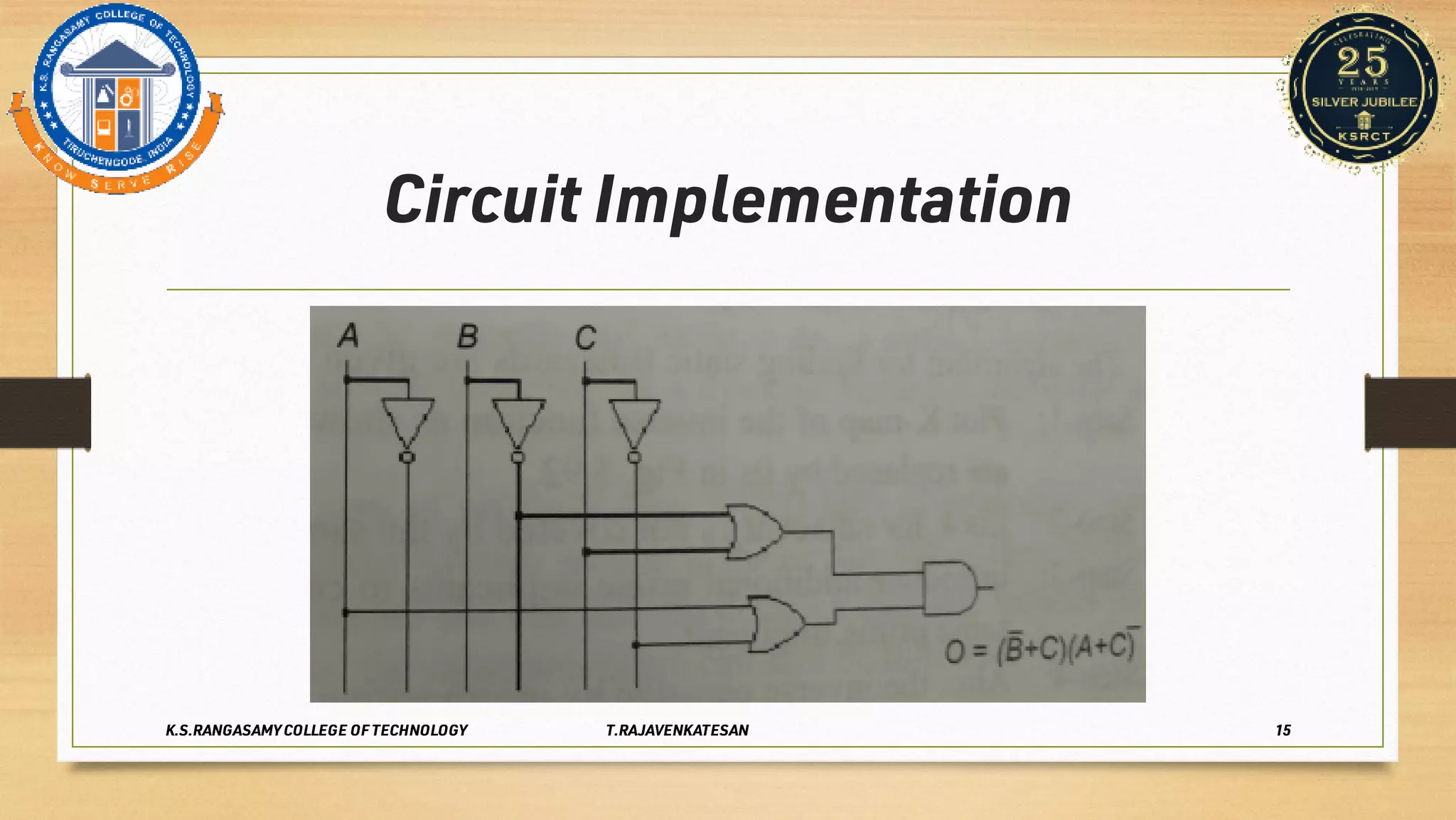
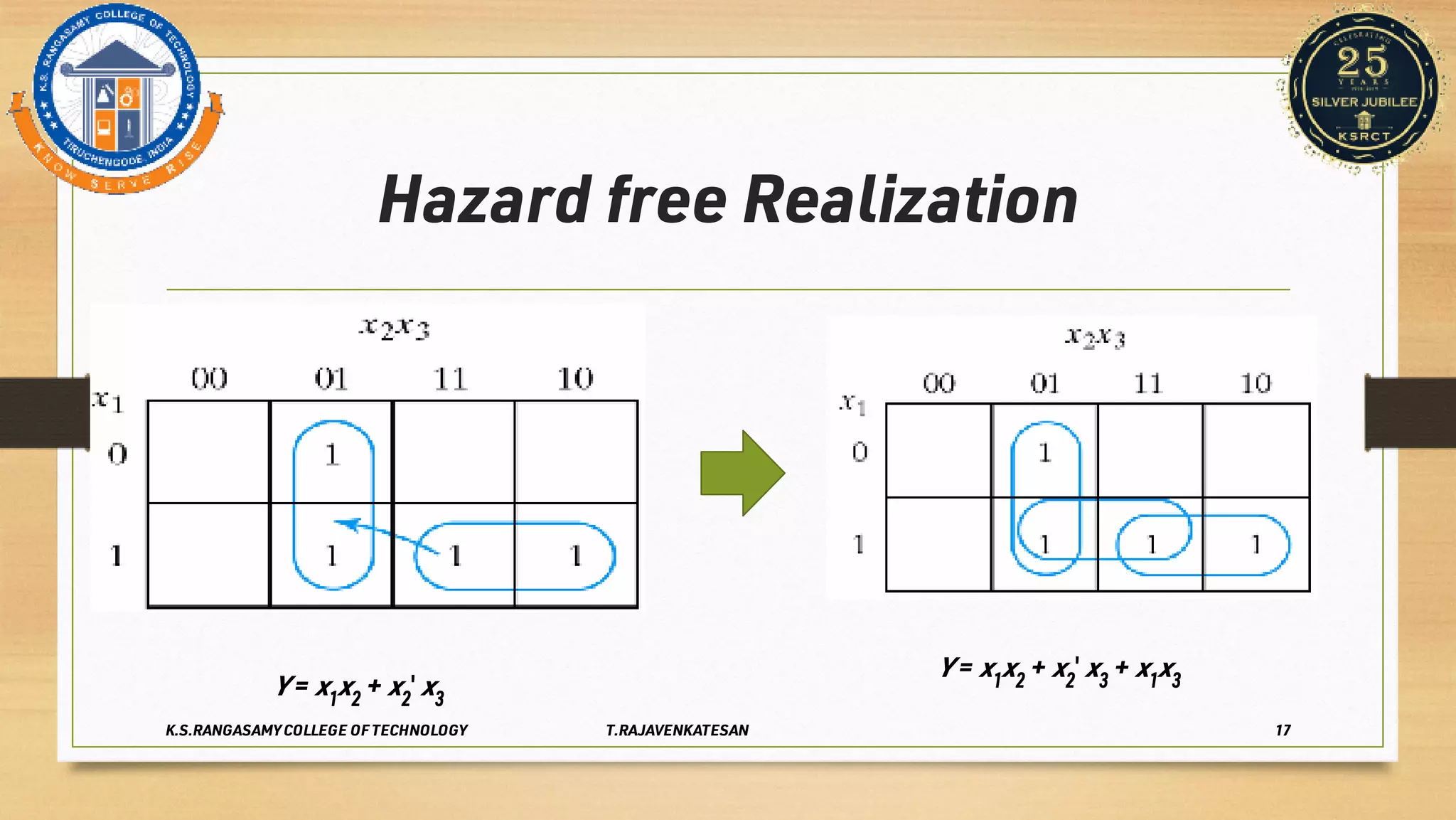
Race conditions and hazards can occur in digital logic circuits when the inputs arrive at gates in an unexpected sequence or order. This can lead to anomalous or undefined behavior of the logic gates. There are several types of hazards, including static hazards where the output temporarily changes before settling, dynamic hazards where the output changes multiple times in response to a single input change, and essential hazards specific to asynchronous sequential circuits. Hazards can be detected using K-maps and eliminated through proper circuit design and implementation techniques to ensure correct and reliable circuit function.