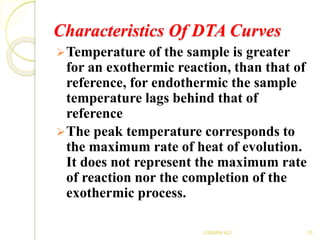
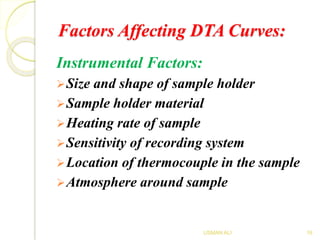
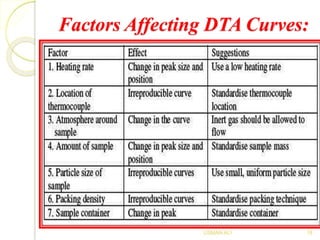
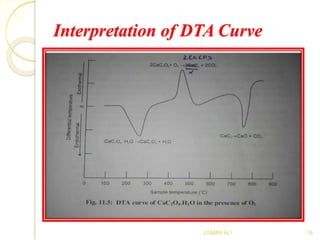
The document discusses Differential Thermal Analysis (DTA), covering its principles, characteristics of DTA curves, instrumentation, factors affecting DTA curves, and applications. DTA compares the temperature of a sample with a reference material to analyze physical and chemical changes during heating. The technique has significant applications in identifying compositions, studying thermal stabilities, and examining reactions in materials.