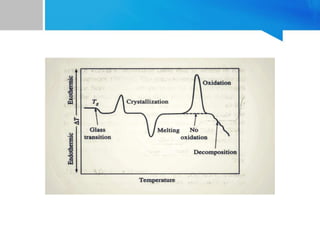
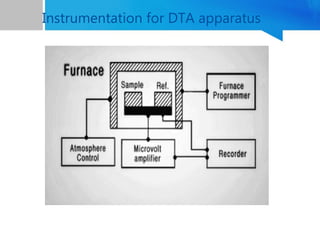
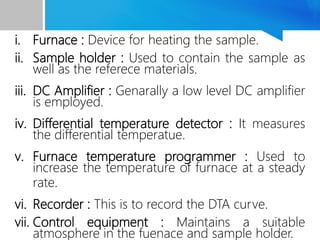
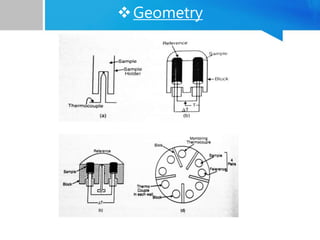
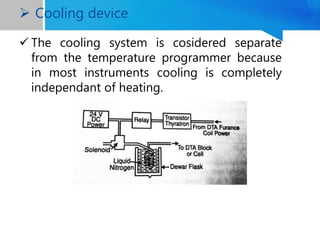
Differential thermal analysis (DTA) is a thermal analysis technique that measures the temperature difference between a sample and an inert reference material as they are heated or cooled under a controlled temperature program. During physical and chemical changes in the sample, it may absorb or release more or less heat than the reference. The temperature difference is recorded as a function of time or temperature to produce a DTA curve. Key components of a DTA instrument include a furnace, sample and reference holders, temperature sensors and programmer, recorder, and cooling system. DTA is used for applications such as determining heats of reaction, thermal properties, and identifying materials and their phase changes.