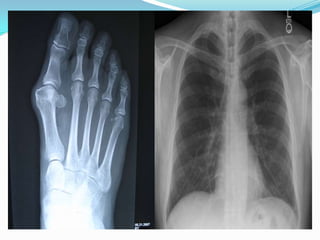
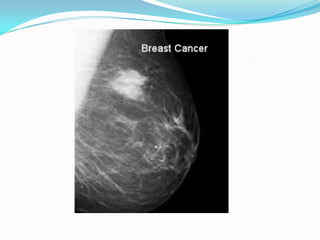
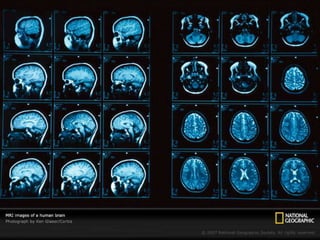
Radiography, a branch of radiology, utilizes imaging technologies like x-rays, MRI, and ultrasound for diagnosing and treating diseases. It encompasses two main fields: diagnostic radiology, which aids in disease diagnosis, and therapeutic radiology, or radiation oncology, focused on treating conditions like cancer. Common imaging techniques include CT scans, x-rays, MRIs, nuclear scans, and ultrasounds, each serving specific diagnostic purposes without necessarily exposing patients to radiation.