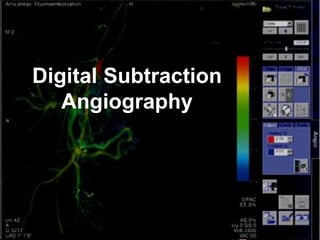
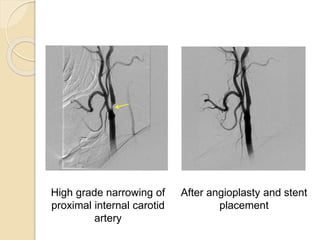
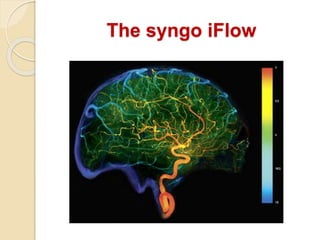
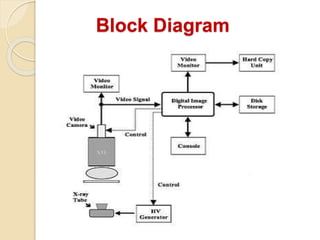
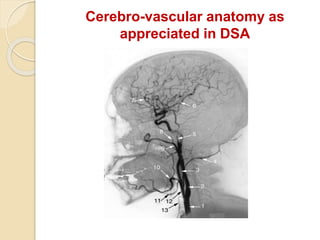
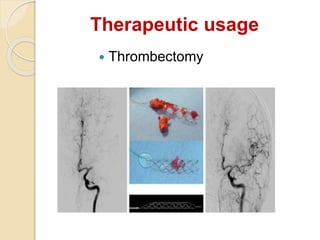
Digital subtraction angiography (DSA) is a fluoroscopy technique that uses iodinated contrast media and subtraction of bone structures to clearly visualize blood vessels. During a DSA procedure, a catheter is inserted into an artery and guided to the vessel of interest before injecting contrast dye and acquiring images. Multiple frames are taken in rapid succession and a mask image is subtracted from subsequent images, leaving an unobscured view of the opacified vessels. DSA allows for both diagnostic evaluation of vessels and interventional procedures such as angioplasty and stent placement.