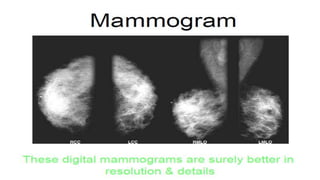
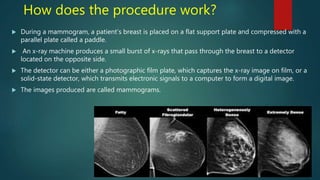
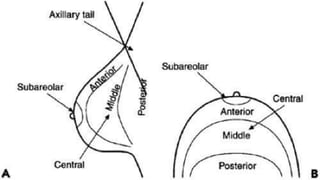
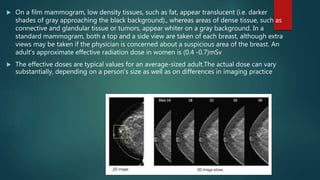
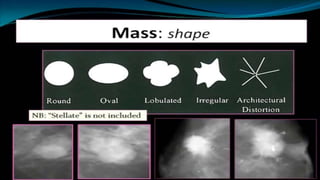
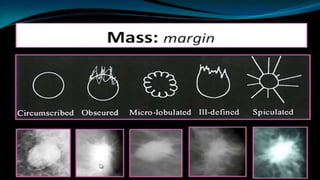
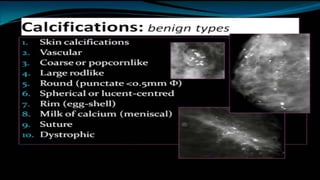
Mammography uses low-dose x-rays to examine the breast for early cancer detection. It has advanced from film to digital mammography and tomosynthesis, which creates 3D breast images. Computer-aided detection highlights abnormal areas. Screening mammograms aim to detect cancer in asymptomatic women, while diagnostic mammograms investigate symptoms. Benefits include early detection, but limitations include false positives and negatives due to breast density. Yearly mammograms after age 40 are recommended for breast cancer screening. Ultrasound provides localized breast images without radiation but cannot screen whole breasts. MRI is superior for dense breasts but has no radiation risk.