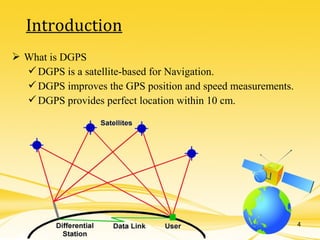
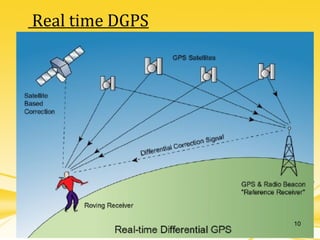
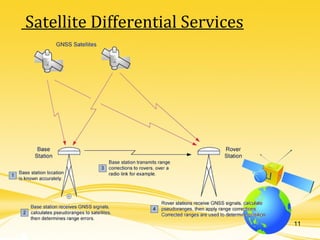
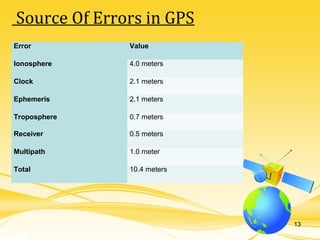
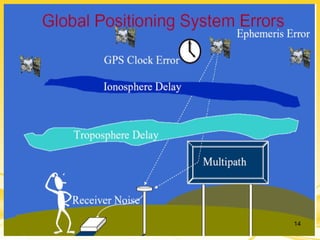
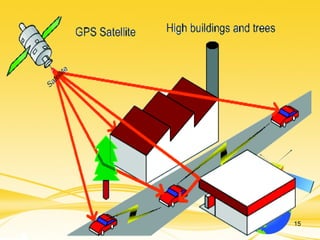
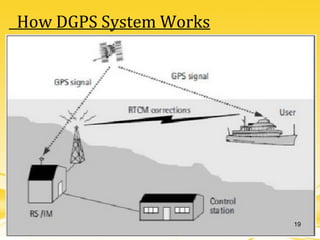
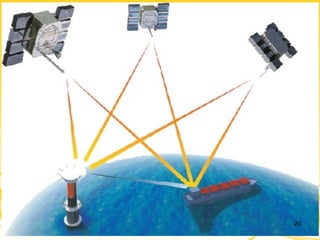
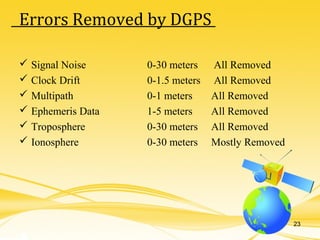
This document discusses differential GPS (DGPS), which improves the accuracy of GPS positioning. DGPS works by using a stationary base station with a known location to calculate errors in the GPS signal caused by things like ionospheric delay. This error data is transmitted to a mobile GPS receiver to correct its position. With DGPS, location can be measured to within 10 cm or less, providing a more precise position than standard GPS alone. The document outlines the history and development of DGPS, how the system works, sources of GPS errors, advantages and limitations of DGPS, and applications where DGPS is used.