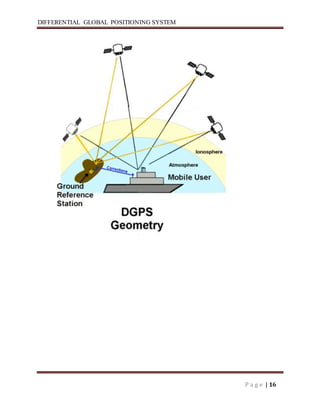
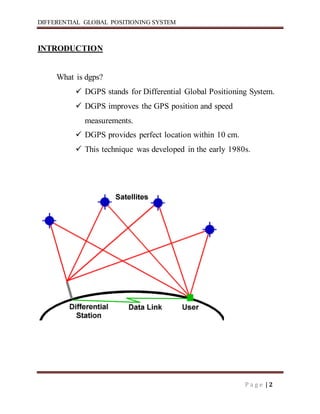
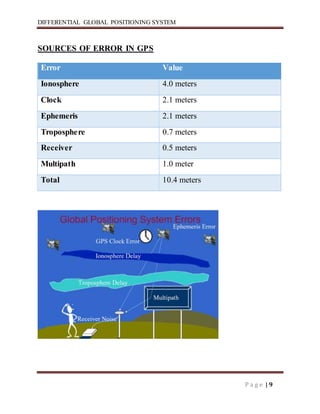
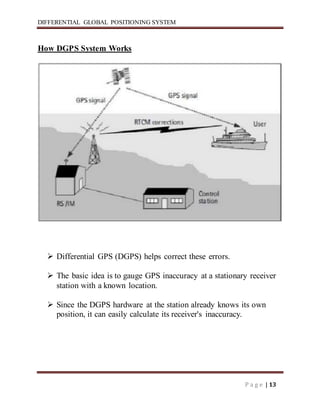
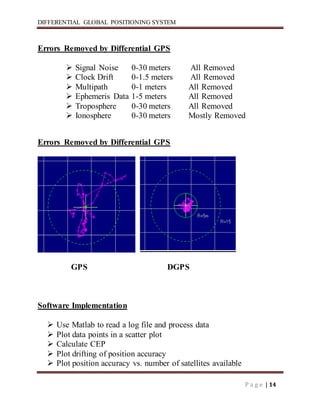
Differential GPS (DGPS) improves the accuracy of standard GPS by using a stationary reference unit to calculate errors in the GPS signal caused by things like atmospheric conditions. This error data is transmitted to a mobile GPS unit in real-time to correct its position reading. DGPS can achieve sub-meter level accuracy compared to the 15 meter accuracy of standard GPS. It works by having a base station calculate positioning errors compared to its known location and sending corrections to a roving unit. This allows the roving unit to correct its reported position and improve accuracy.










![DIFFERENTIAL GLOBAL POSITIONING SYSTEM
P a g e | 15
Opening and reading log file
R = input('What type of log file is it? 1=POSA 2=P20A 3=P20A
and DOPA ')
file = INPUTDLG('Enter the File name','Enter GPS log file to
open')
[time lat long height] = textread(file, ' %*s %f %*[^n]',
'delimiter',',')
Coordinate conversion
Local (North, East, Down)
Uses a reference point to find the change in direction
Converts to meters
Calculating a Position
Measure distance to satellites.
Obtain satellite positions.
Perform triangulation calculations. (Trilateration)
Adjust local clock bias.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dgpsseminar-150510084358-lva1-app6892/85/Dgps-seminar-15-320.jpg)