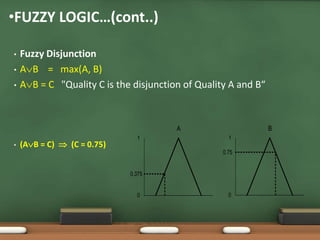
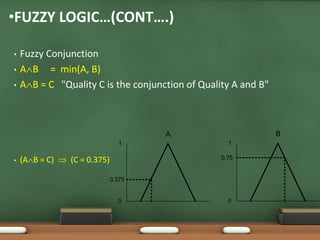
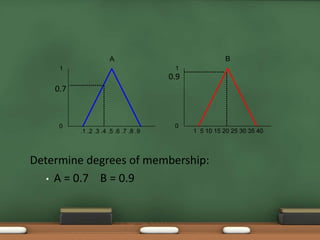
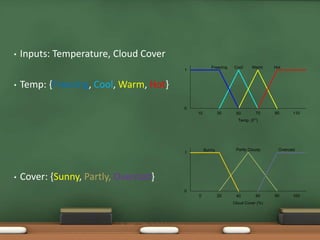
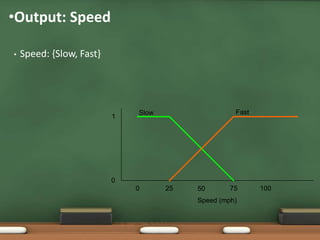
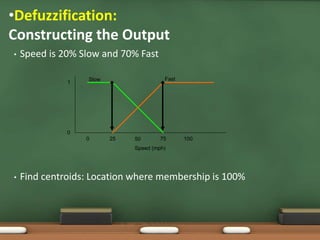
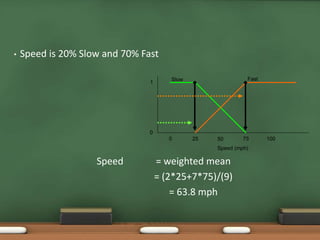
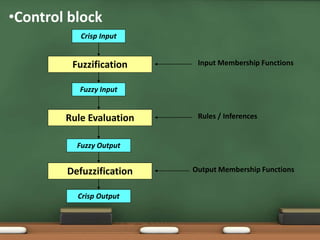
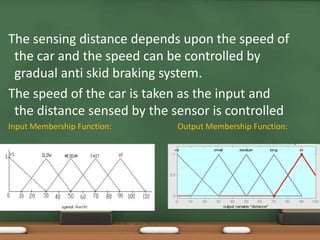
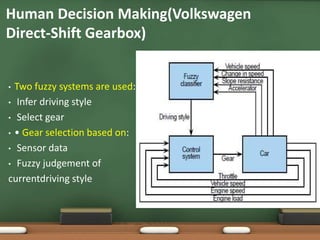
Fuzzy logic, introduced by Lotfi Zadeh in 1965, allows for partial set membership rather than strict true/false definitions, facilitating data processing akin to human reasoning. Applications of fuzzy logic range from controlling subway systems to automating vehicles and various household technologies, enhancing system performance and decision-making. The methodology involves fuzzification, rule evaluation, and defuzzification to translate human-like reasoning into machine actions.










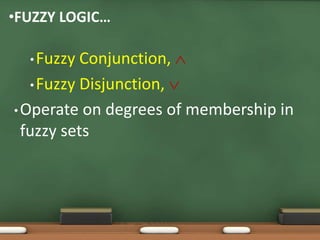










![REFERENCES
[1] Daniel Mcneil and Paul
Freiberger " Fuzzy Logic"
[2]http://www.quadralay.com/
www/Fuzzy/FAQ/FAQ00.html
[3]http://www.fll.uni.linz.ac.af/
pdhome.html
[4] http://soft.amcac.ac.jp/index-e.
html](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fuzzylogic2014-141203225358-conversion-gate02/85/Fuzzy-logic-2014-36-320.jpg)
