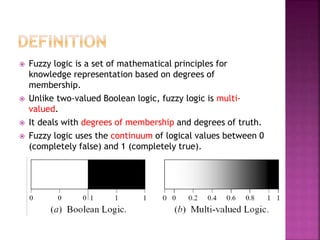
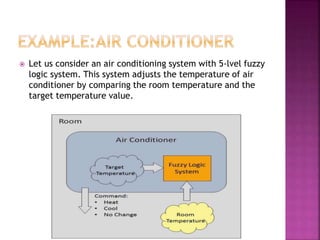
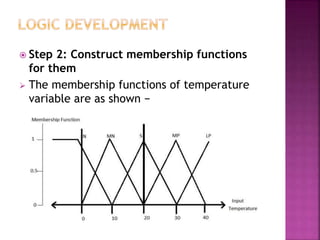
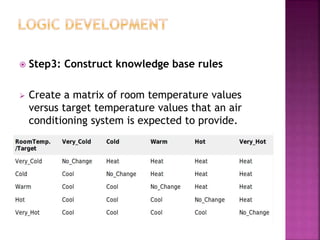
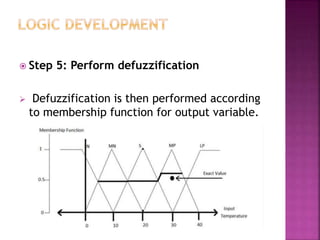
This document discusses fuzzy logic, a theory that describes degrees of truth and membership, differing from traditional Boolean logic by addressing vagueness and uncertainty. It outlines the development process of fuzzy systems, including specifying problems, defining linguistic variables, constructing rules, and applying these concepts in practical applications such as air conditioning systems. The pros and cons of fuzzy logic are also reviewed, highlighting its flexibility and human-like reasoning capabilities, while noting issues with systematic design and accuracy.