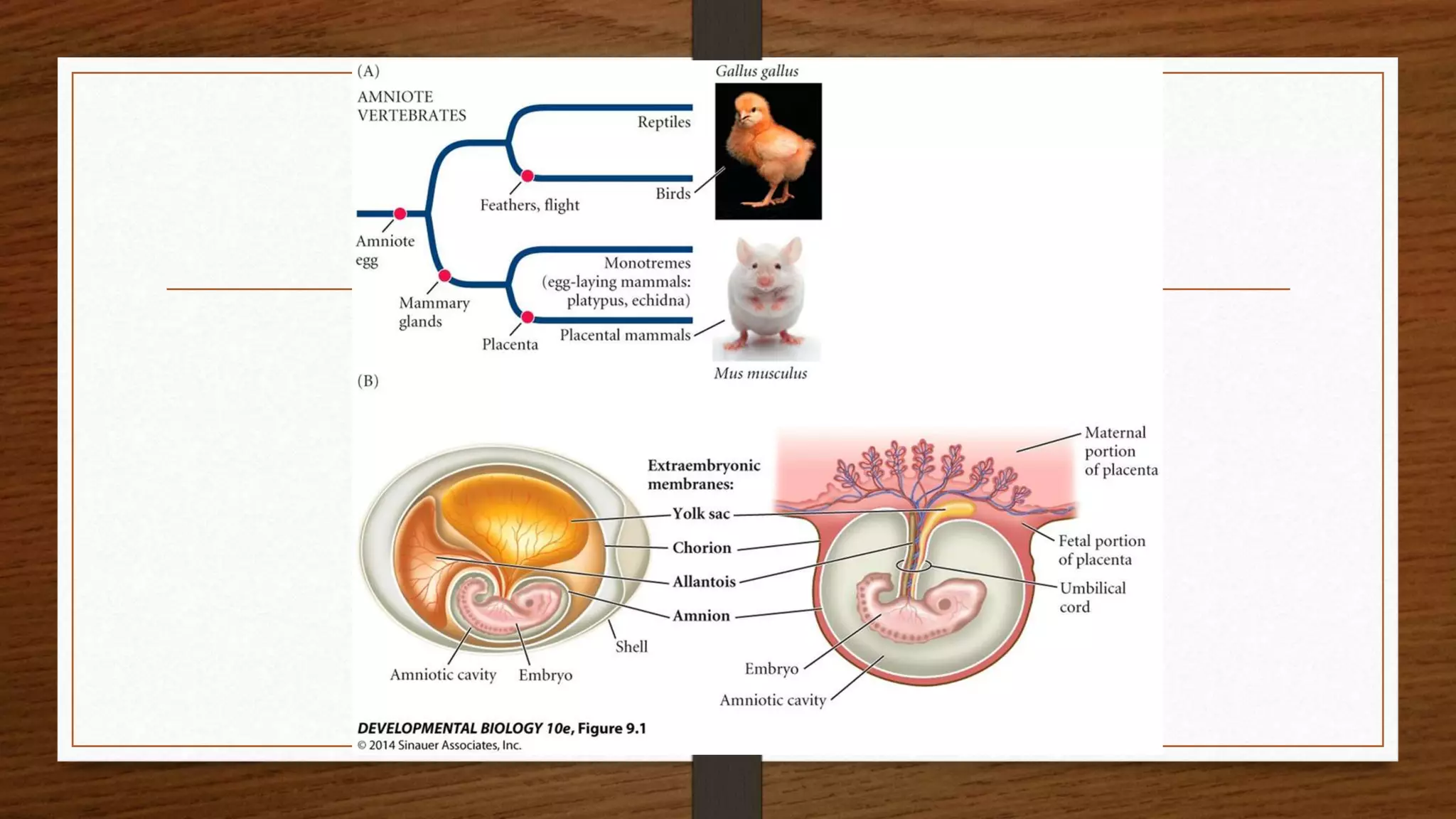
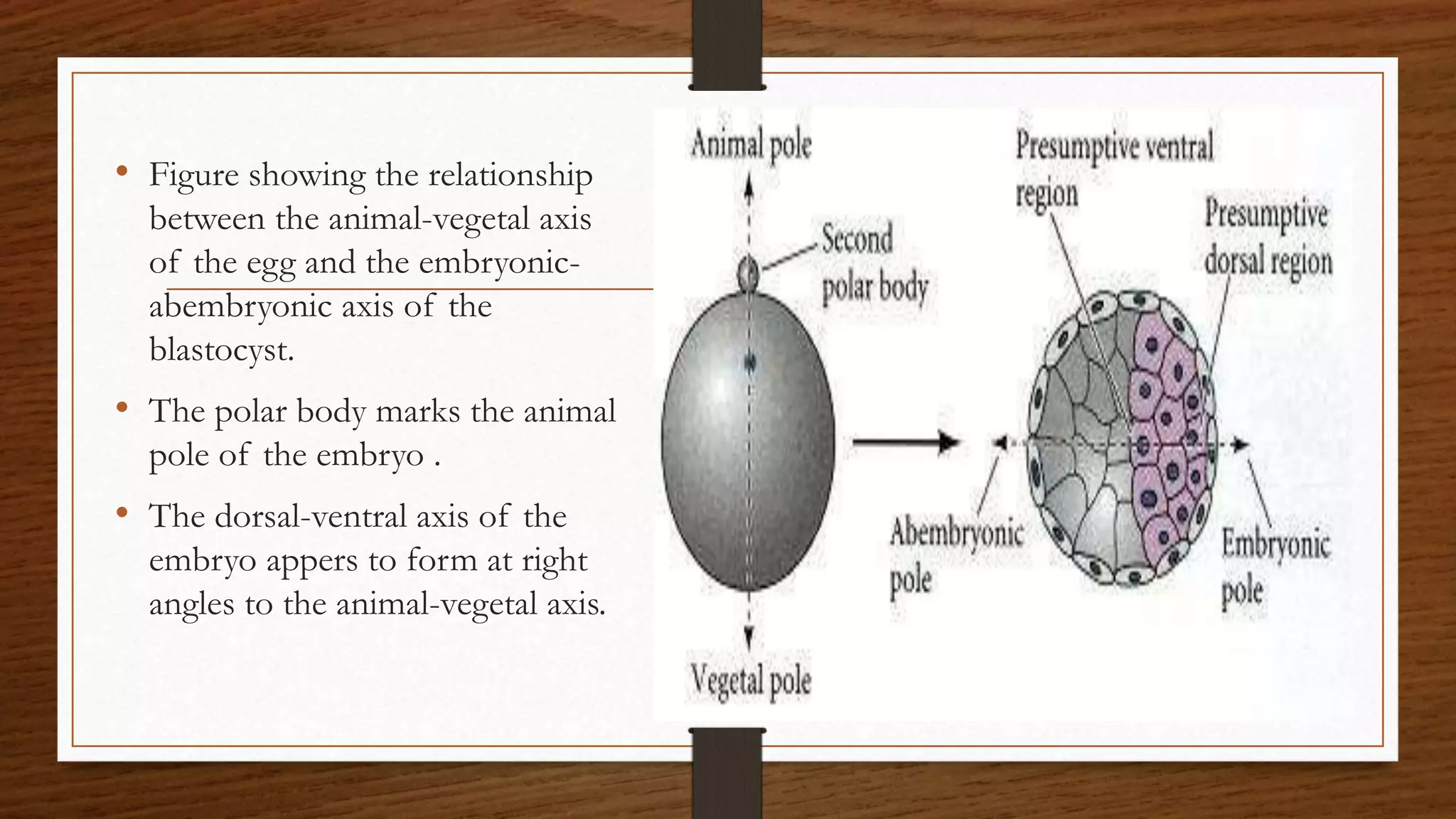
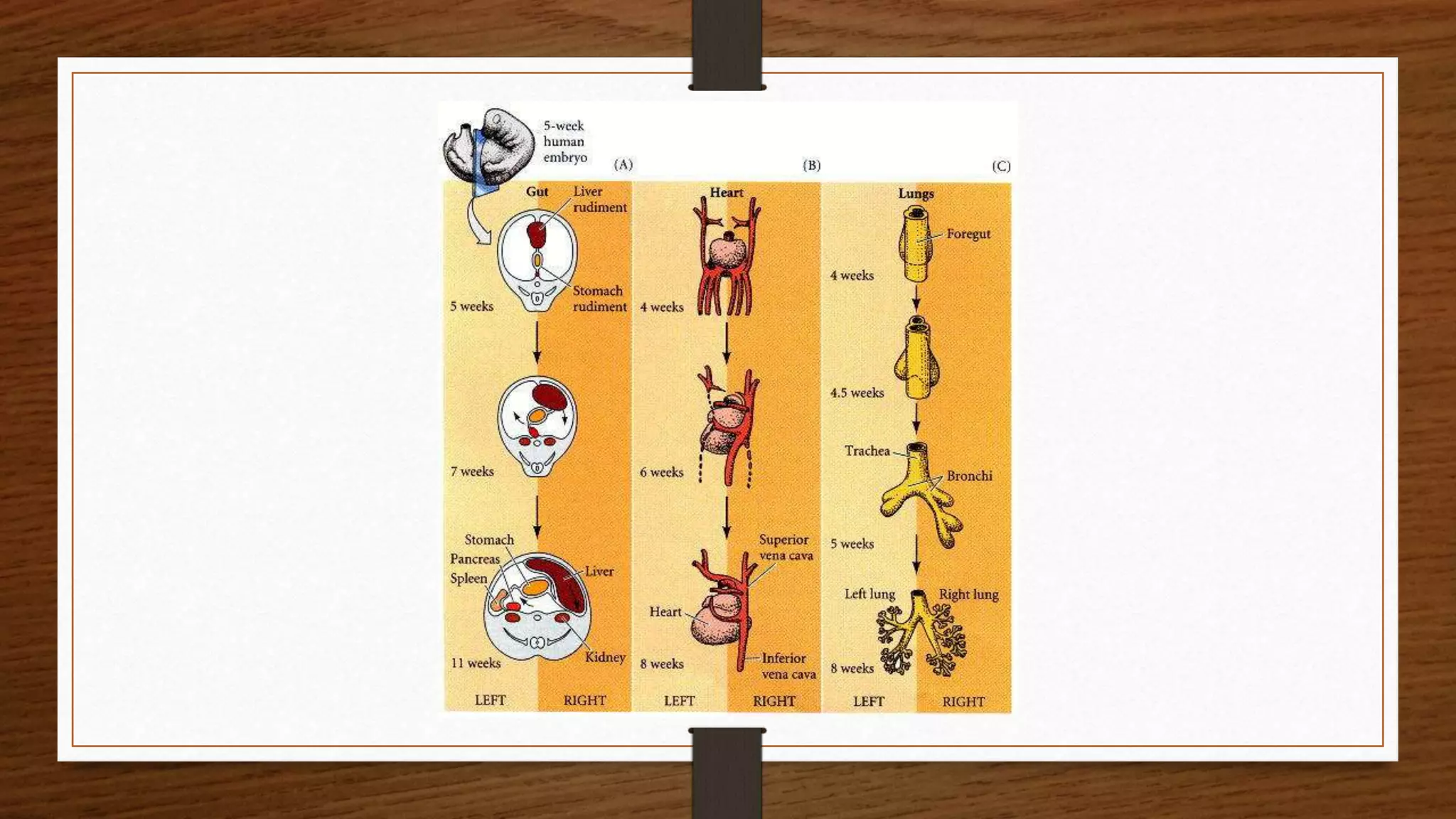
The document discusses the development and axis formation in birds and mammals, highlighting processes such as cleavage types, gastrulation, and embryonic development stages. It explains the mechanisms underlying the formation of the dorsal-ventral, anterior-posterior, and left-right axes during early development, emphasizing critical signaling centers and gene expressions involved. Additionally, it contrasts the specific developmental pathways in avian and mammalian species, including the role of the trophoblast and hox genes.