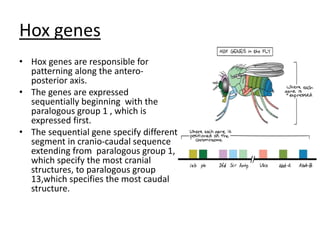
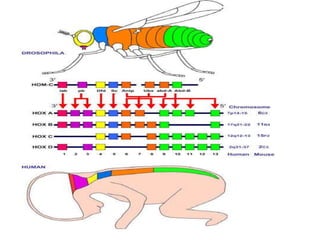
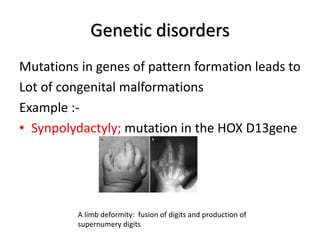
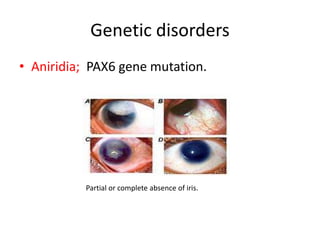
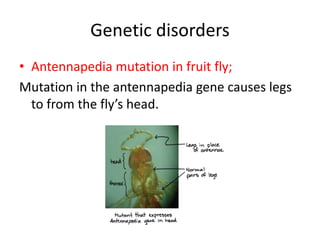
This document discusses pattern formation during embryogenesis. It begins by defining pattern formation as the development of spatial organization that establishes an organism's basic body plan and axes. Key genes that control pattern formation are homeotic genes, which regulate cell processes and contain a homeobox sequence. Hox genes pattern the anteroposterior axis by being expressed sequentially. In Drosophila melanogaster, cytoplasmic determinants, segmentation genes like gap and pair-rule genes, and homeotic genes work together to pattern each segment. Mutations in these pattern formation genes can lead to congenital malformations in humans and other organisms.