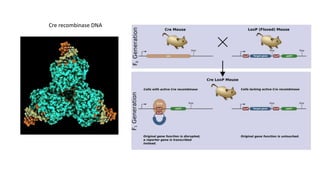
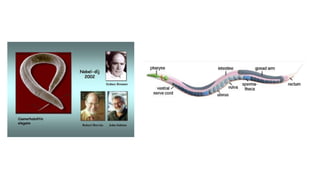
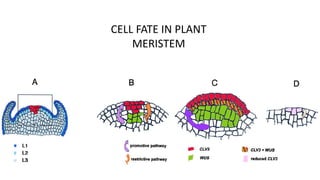
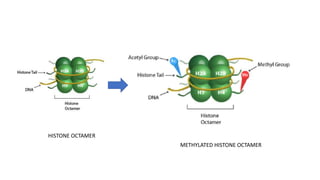
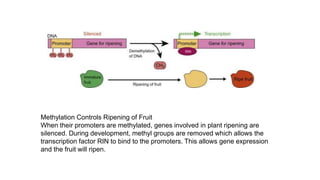
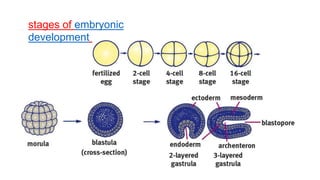
The document discusses cell lineage studies, tracing the developmental history of cells from precursors to differentiated states, with significant contributions from researchers like Dr. Sydney Brenner, who mapped cell lineage in C. elegans. It highlights the role of genetic and epigenetic factors in determining cell fate, including specific signaling pathways and environmental influences, particularly in plant and mammalian development. Furthermore, it addresses how alterations, such as those caused by prenatal ethanol exposure, can impact cell fate and development across generations.