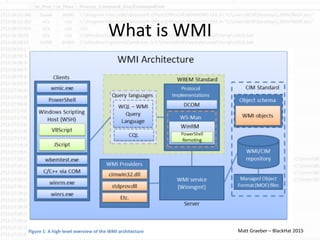
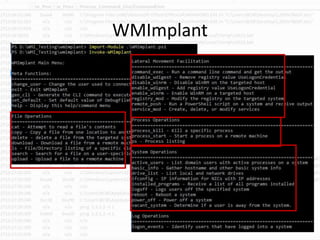
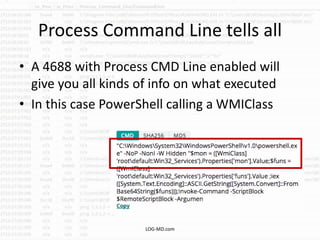
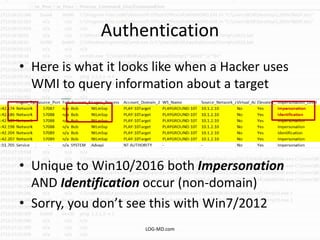
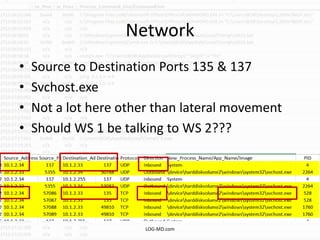
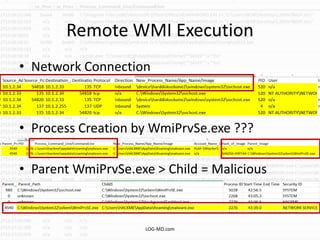
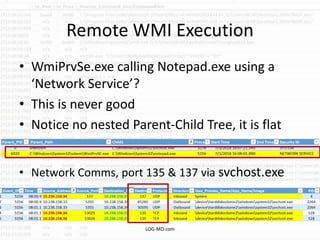
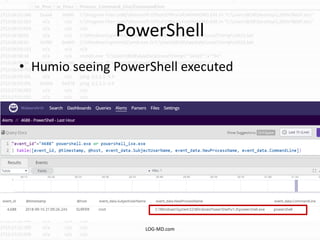
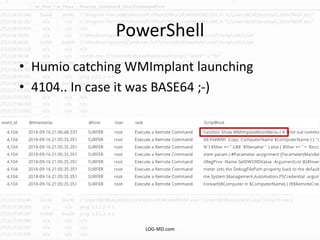
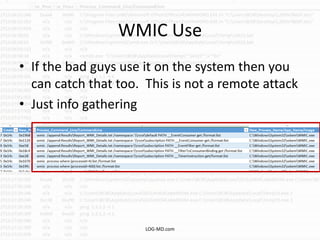
This document provides information on detecting WMI exploitation. It discusses how WMI can be used by adversaries to remotely execute payloads, persist, query systems, and more. It outlines various ways WMI is exploited, including installing malicious MOF files and DLLs. The document recommends enabling specific Windows event logs and logging options to detect WMI activity, such as Process Creation, Authentication, and PowerShell logs. It also discusses tools that can help hunt for WMI exploitation like LOG-MD, Sysinternals AutoRuns, and WMI Explorer.