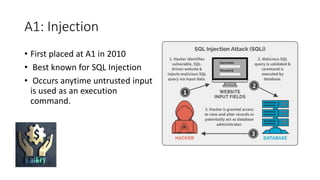
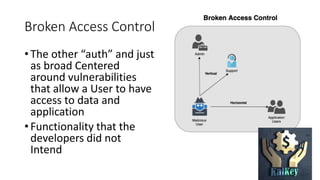
The OWASP Top 10 is a list of the most critical web application security vulnerabilities, released by OWASP and the broader security community, with the latest version in 2017. The vulnerabilities include injection, broken authentication, sensitive data exposure, and more, serving as a foundational guide for building application security. While comprehensive, the OWASP Top 10 does not encompass all potential vulnerabilities and emphasizes the importance of proper logging, monitoring, and tailored security measures.