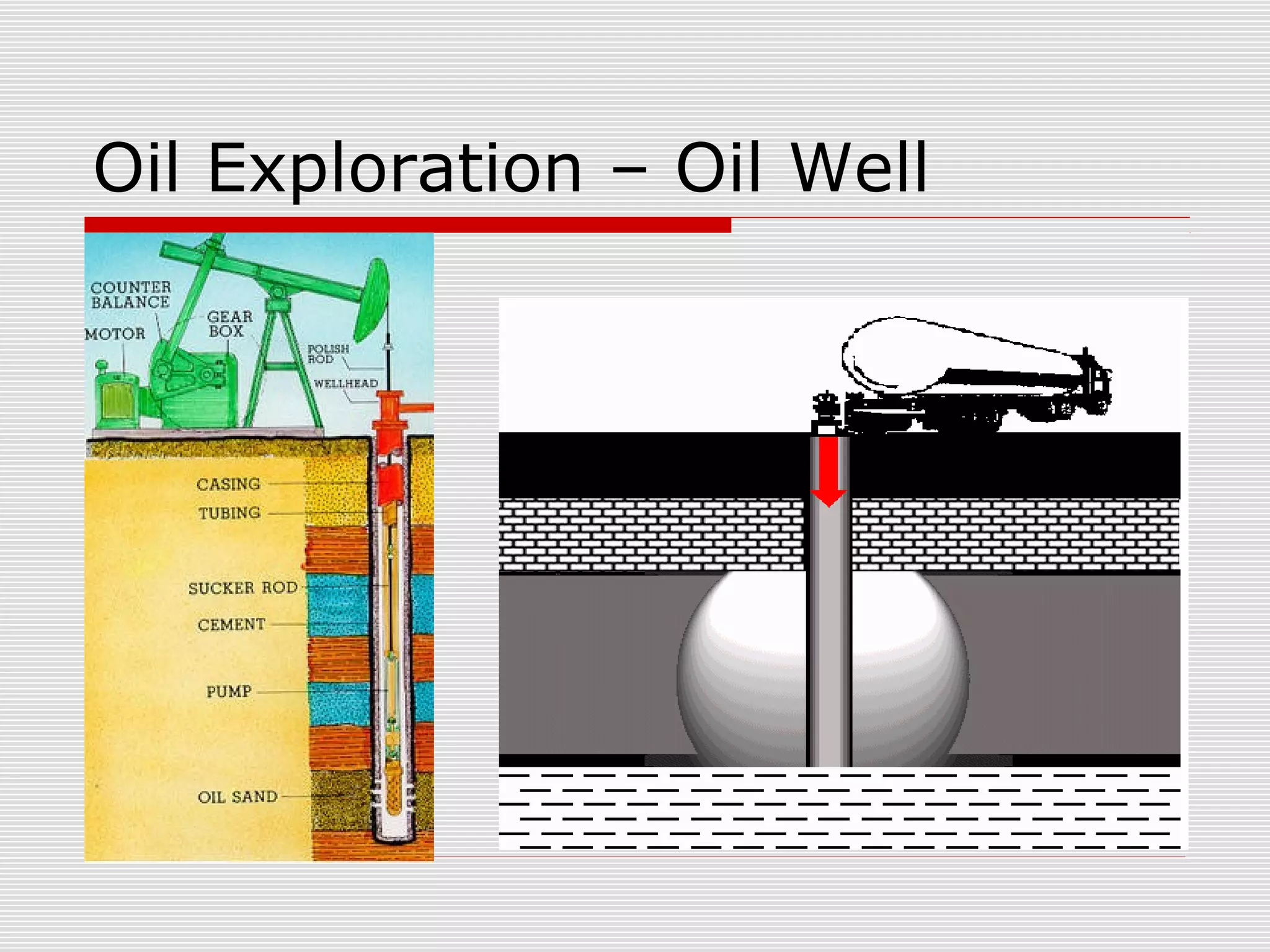
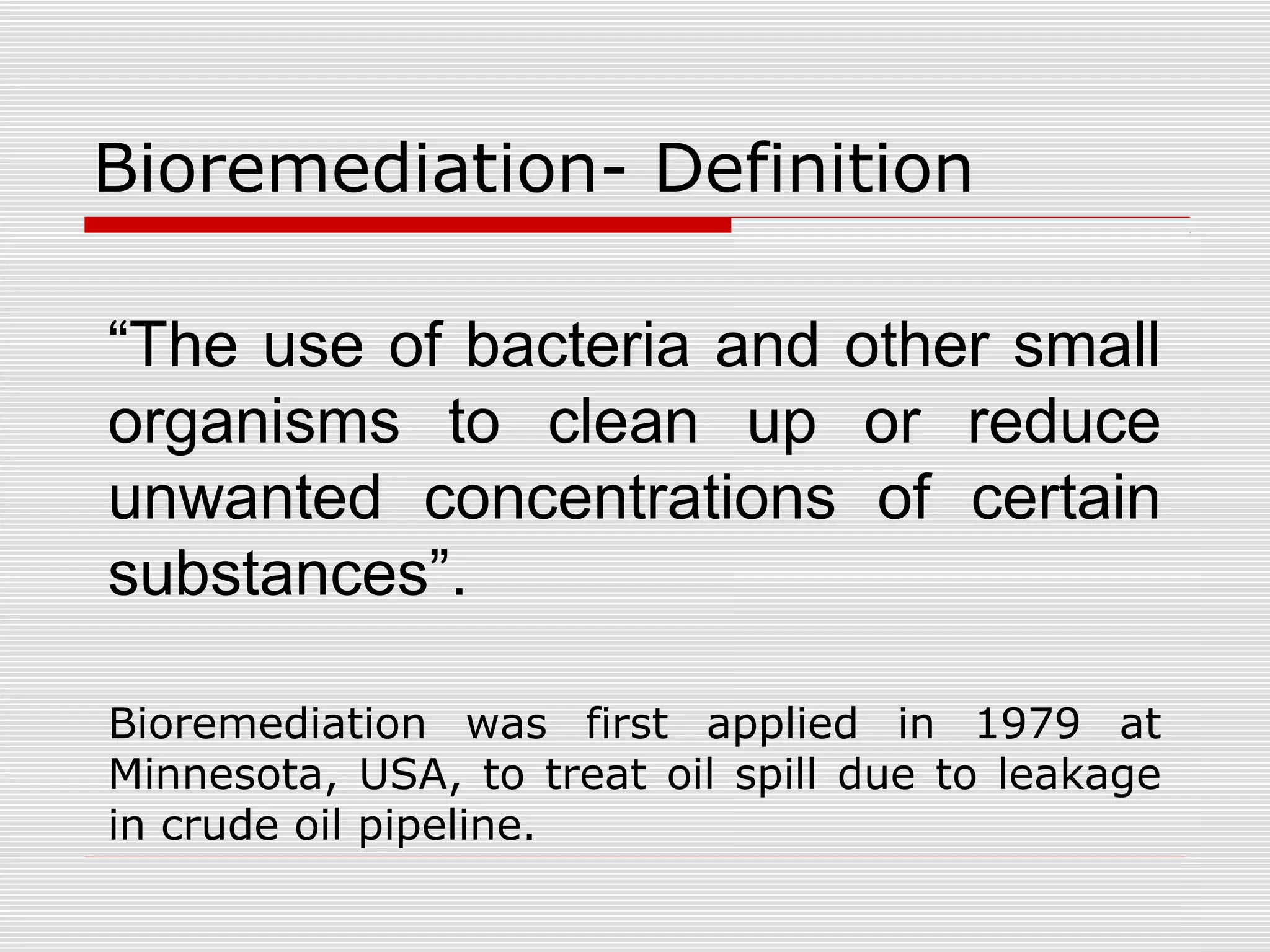
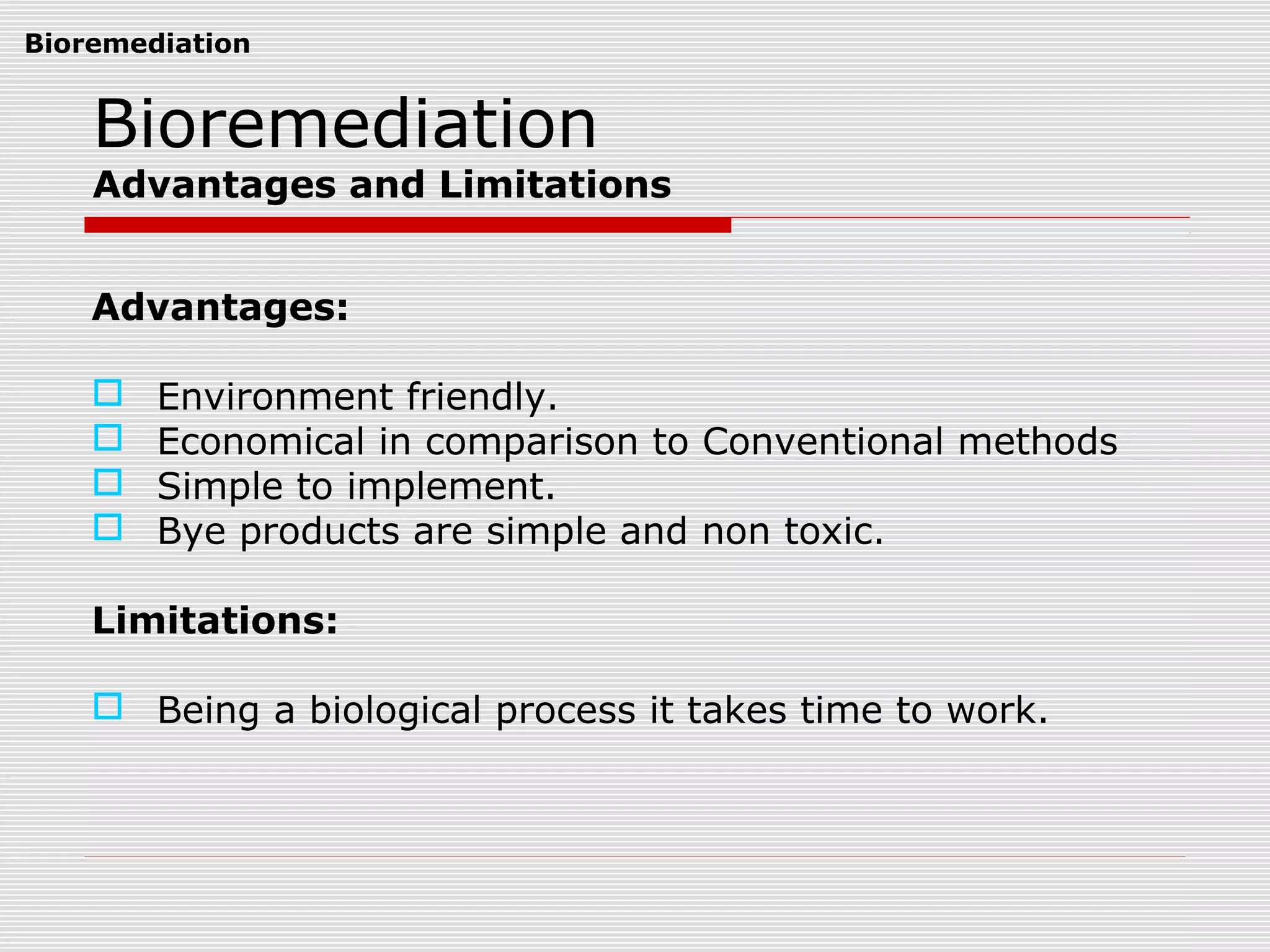
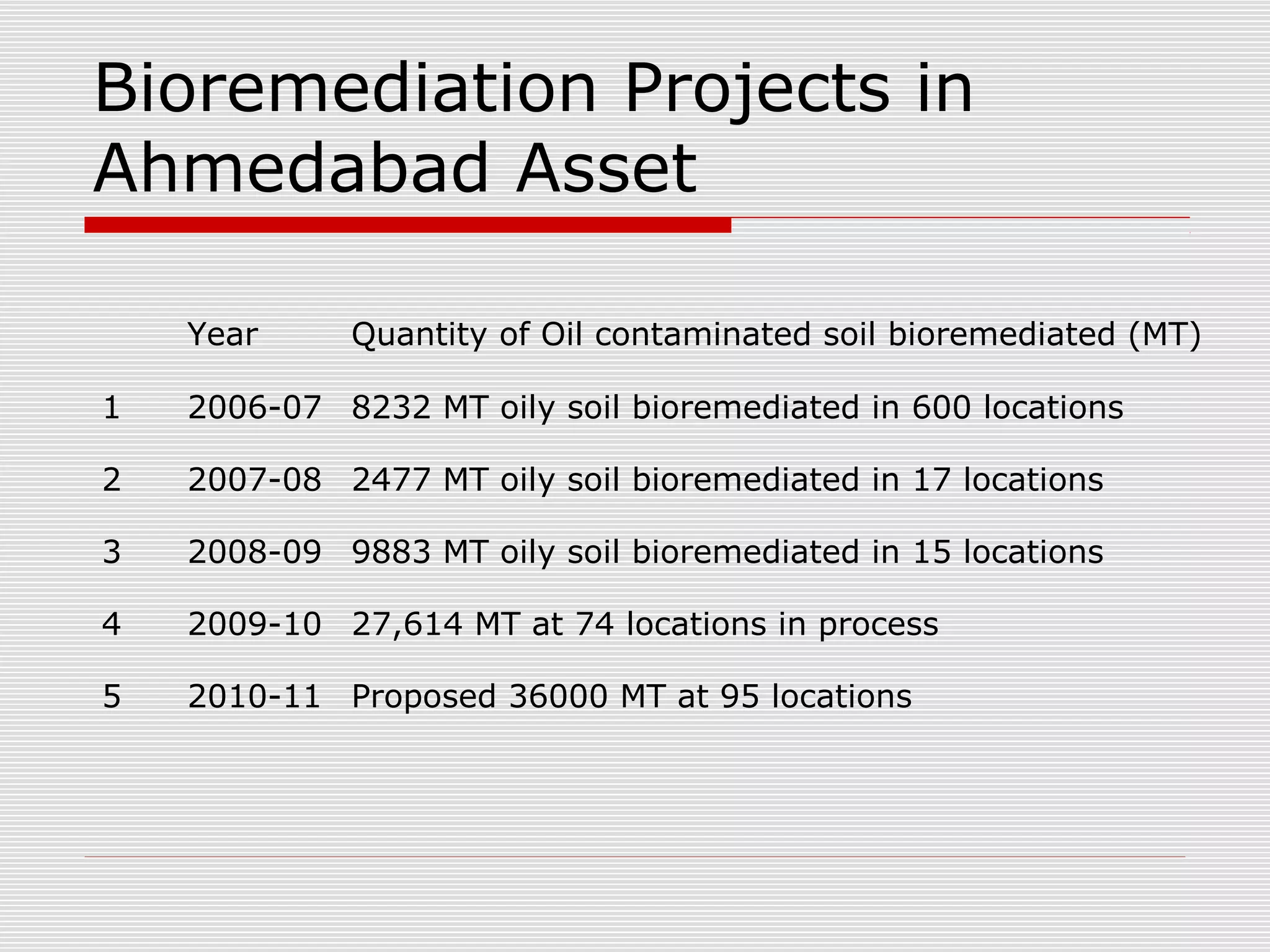
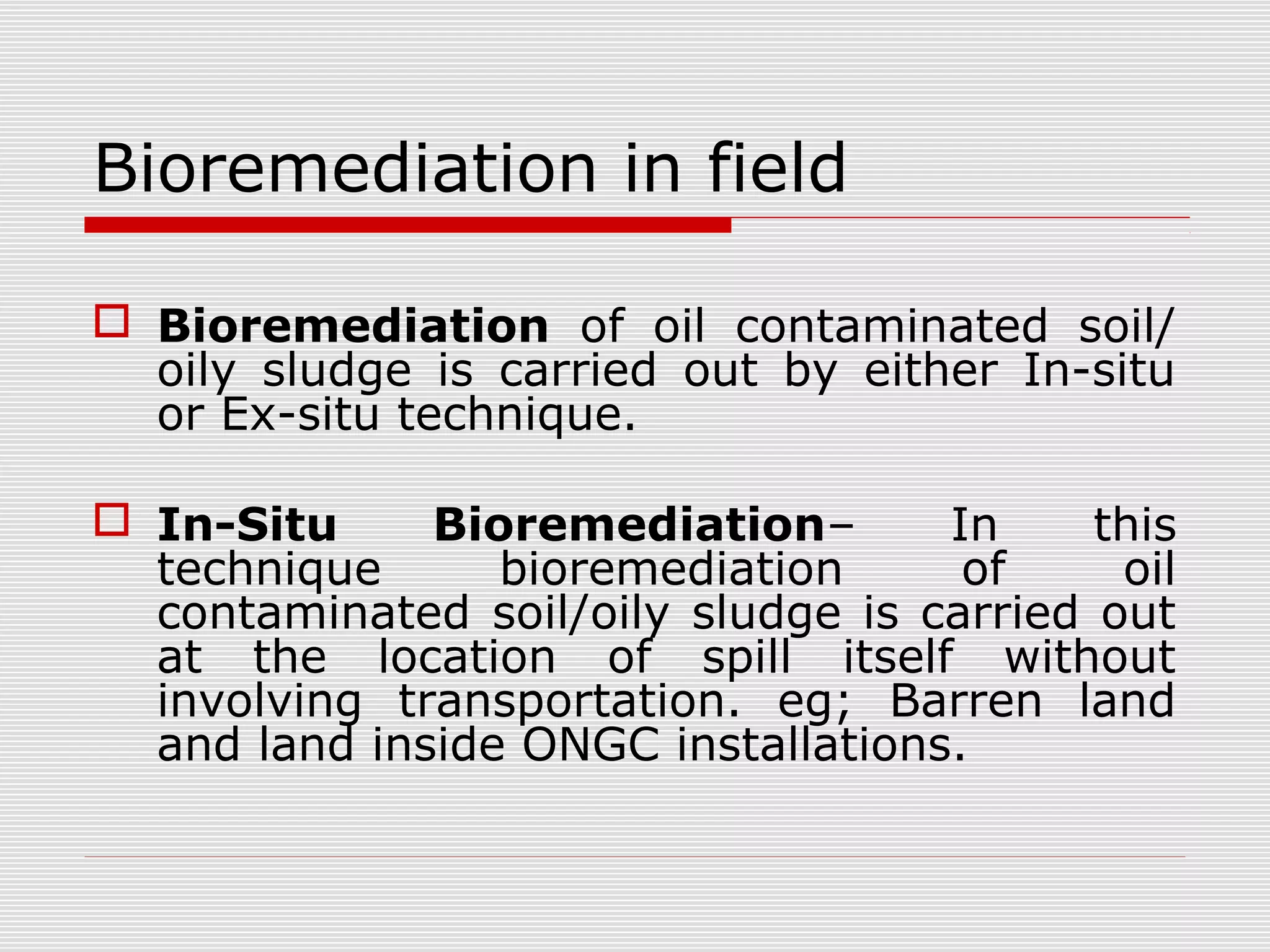
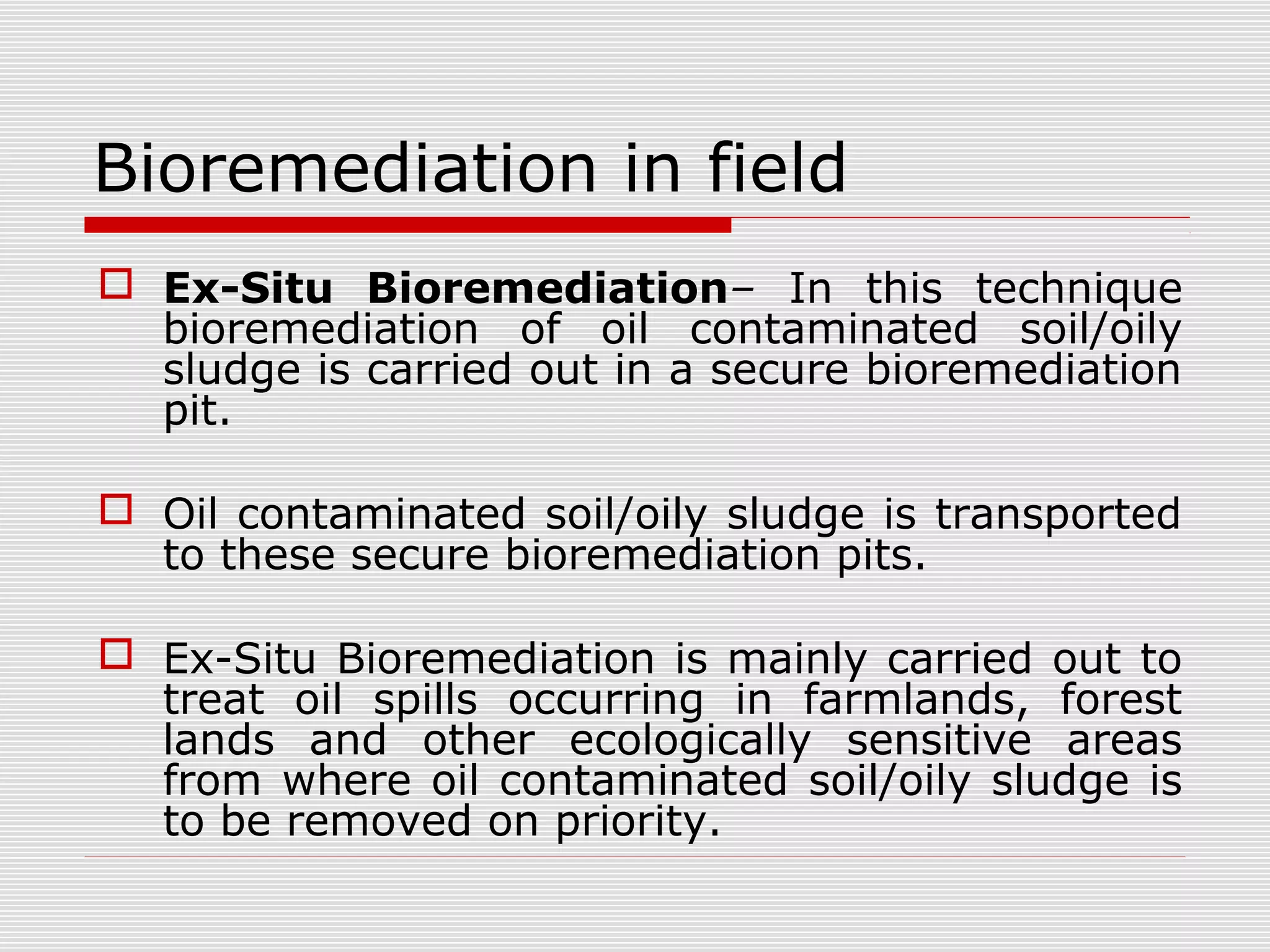
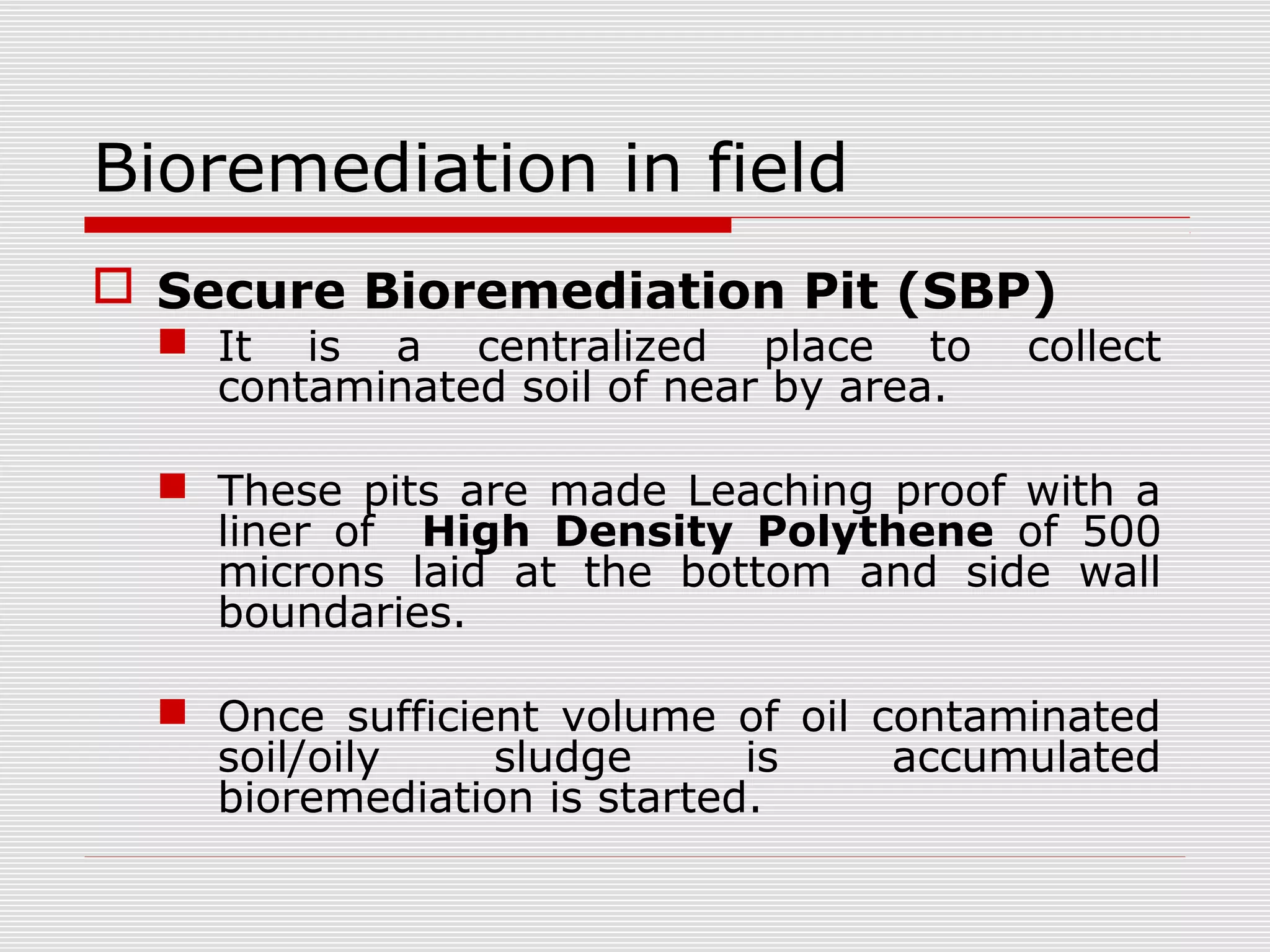
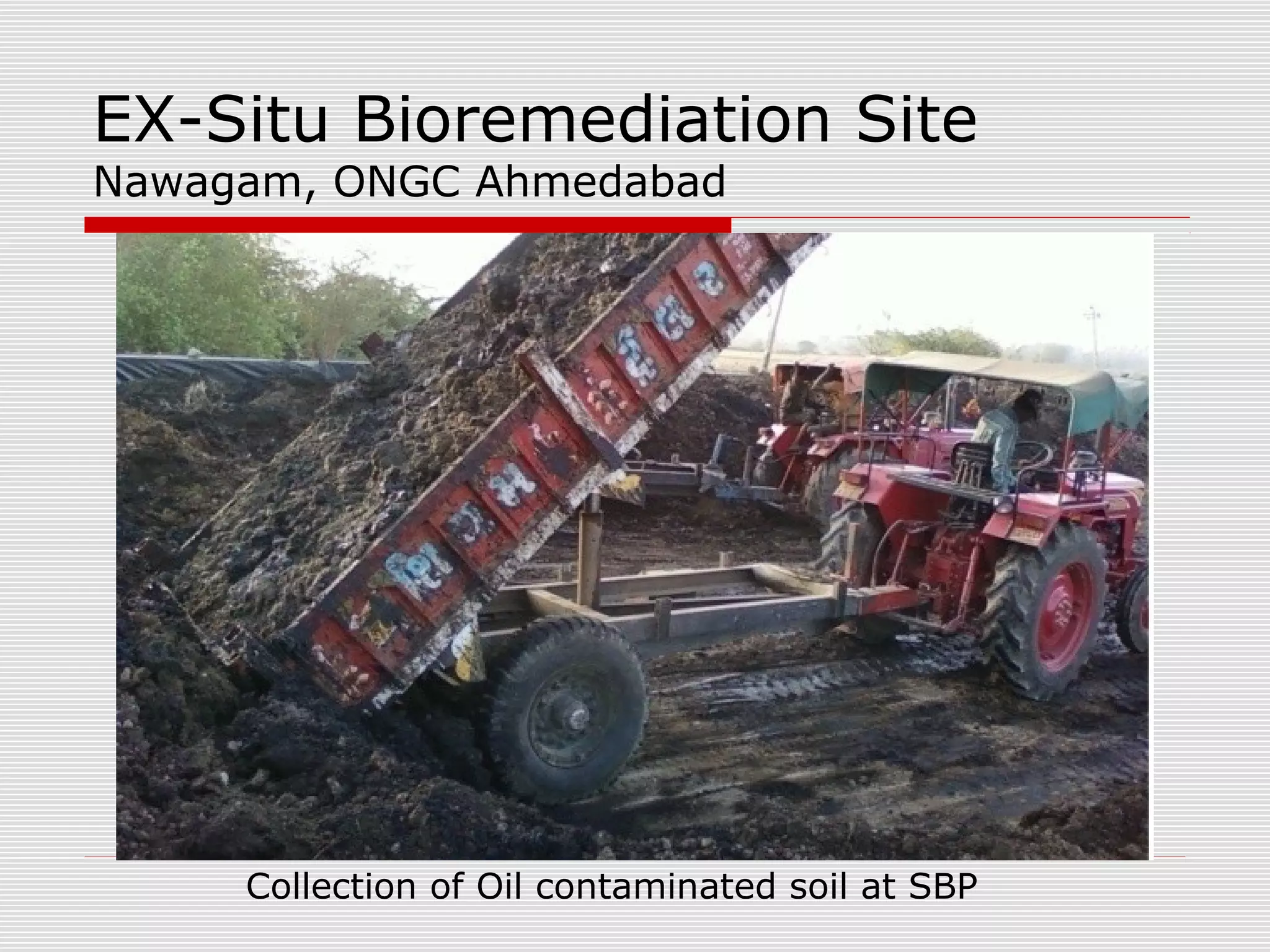
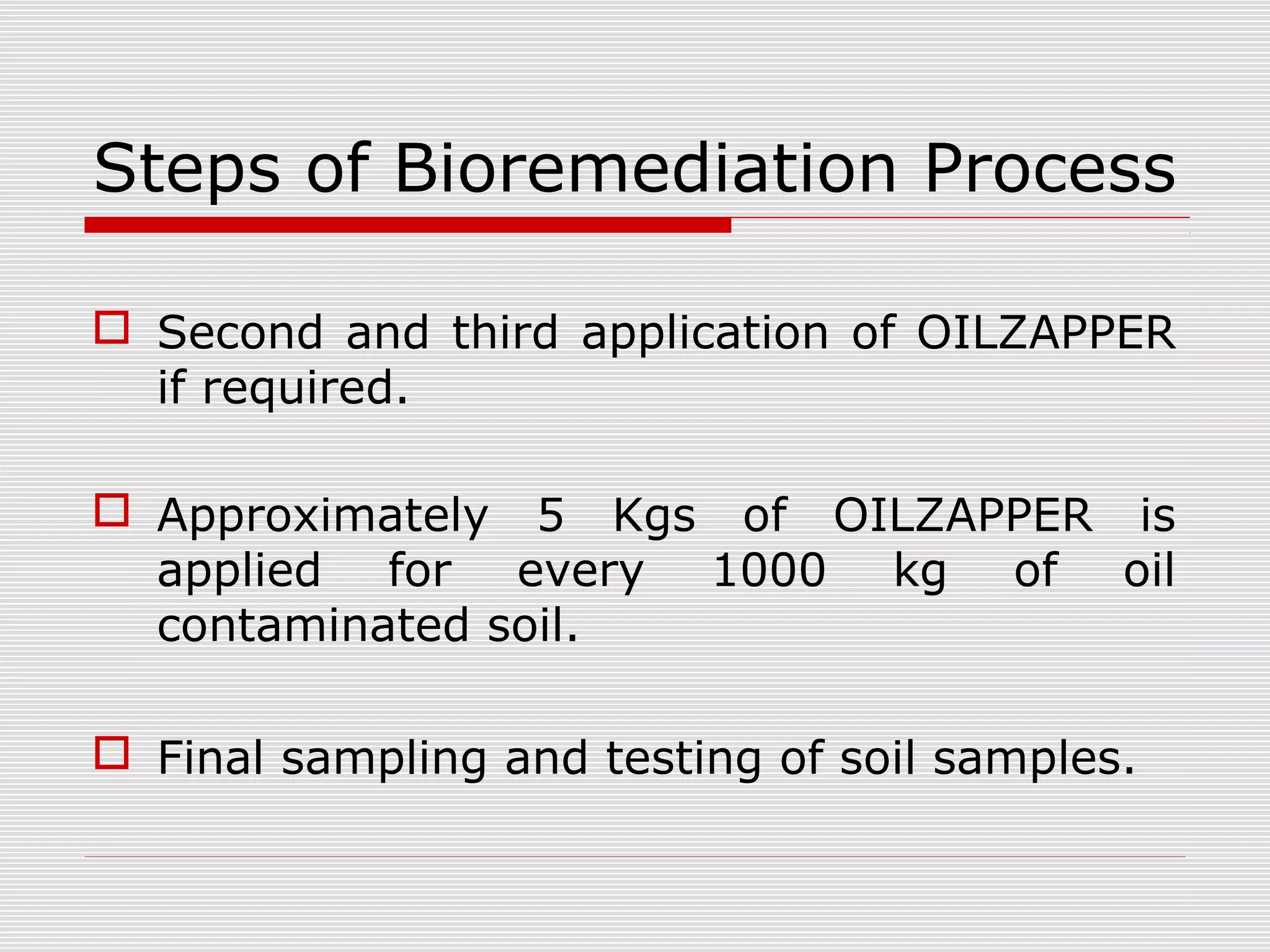
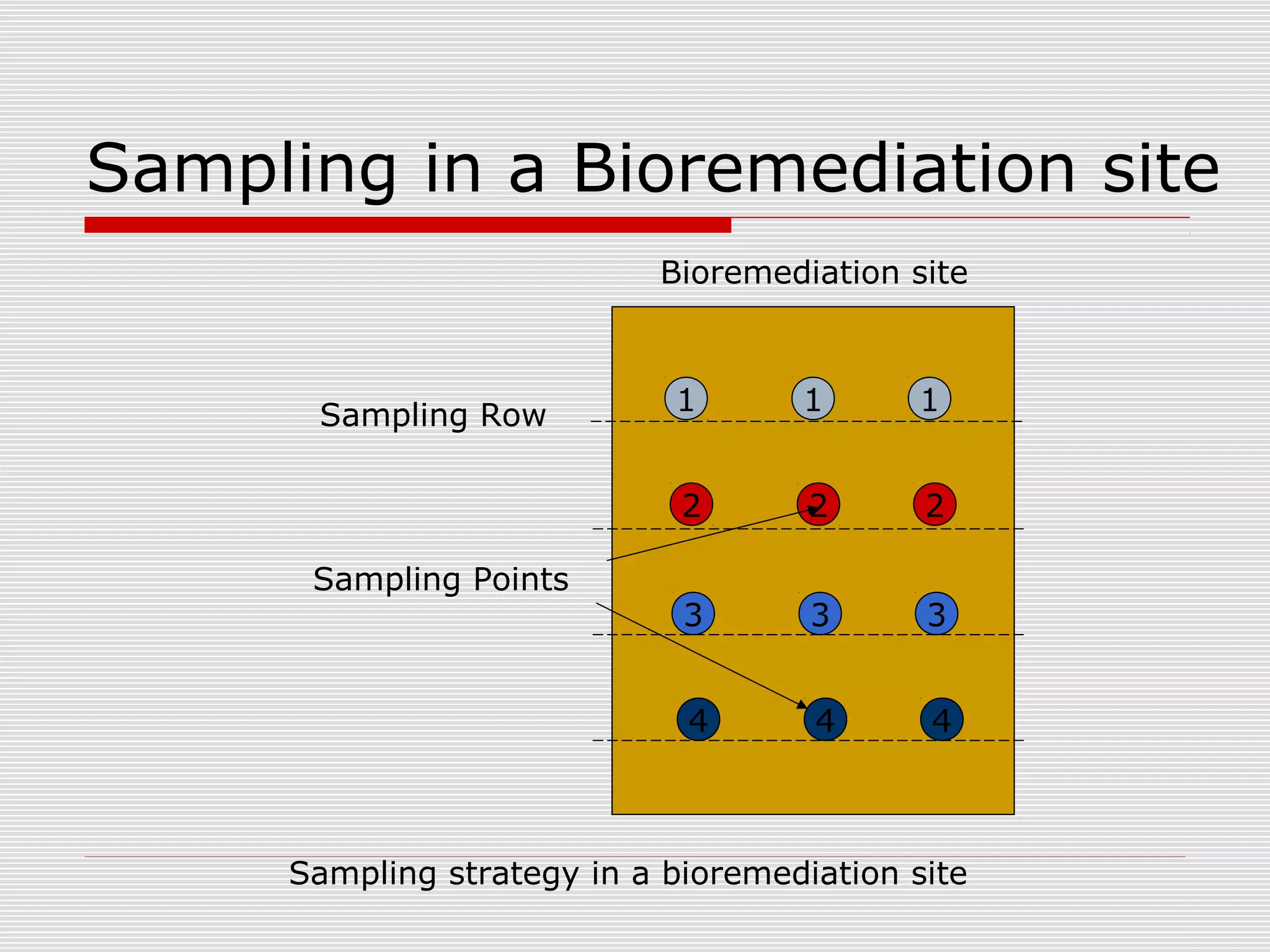
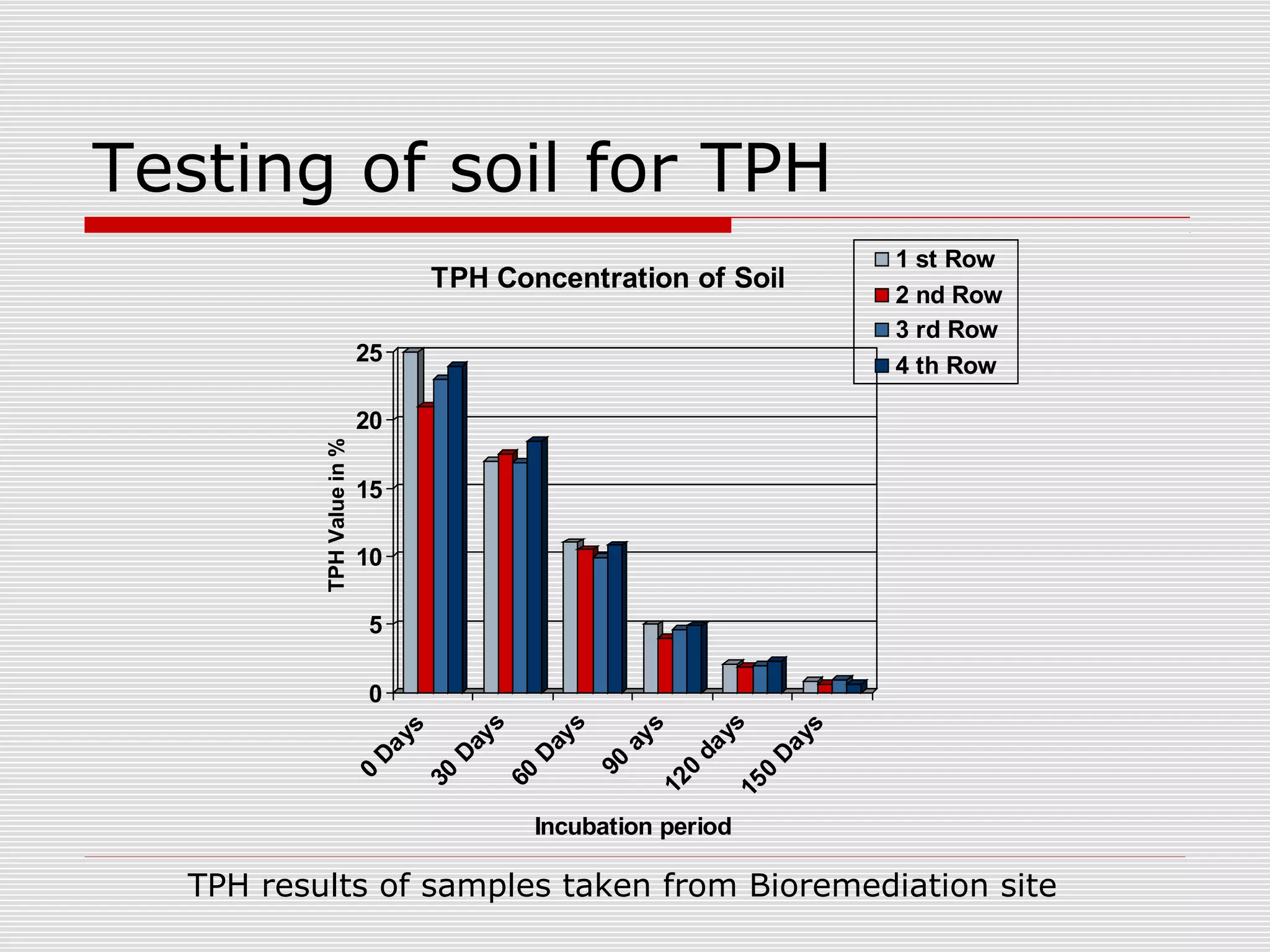
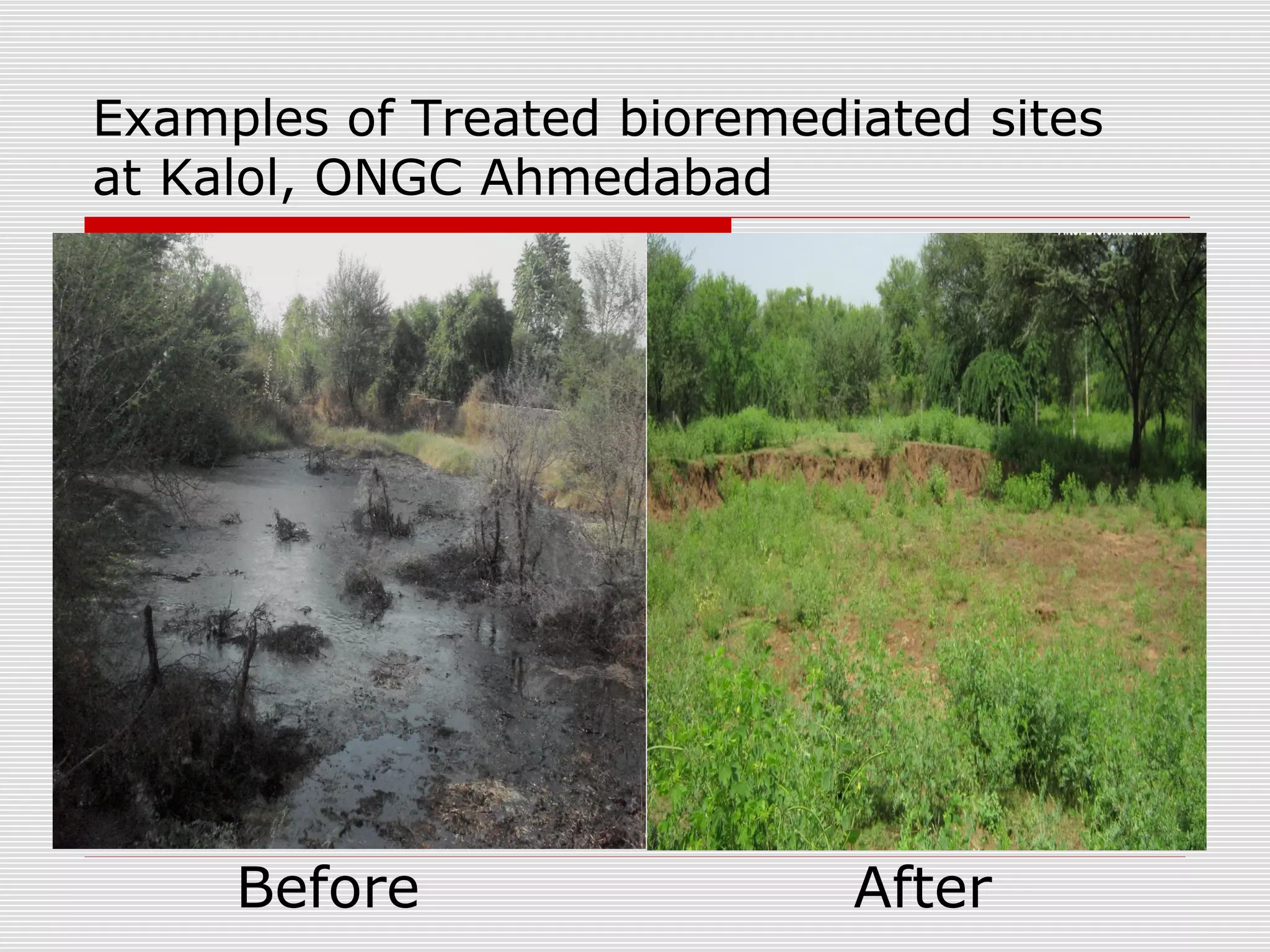
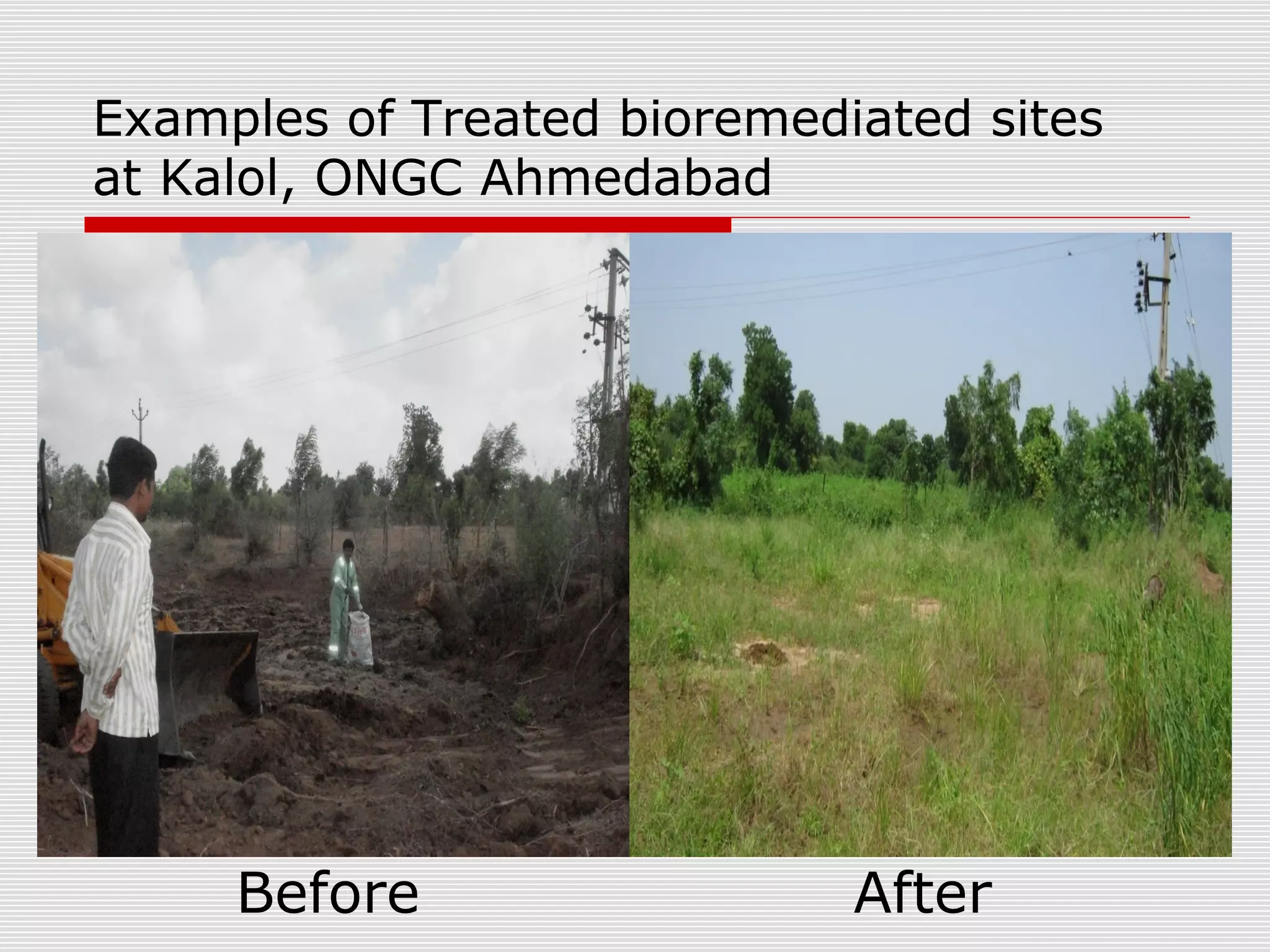
The document discusses bioremediation of oil spills by ONGC Ltd. in Ahmedabad, India. It notes that ONGC has bioremediated over 50,000 metric tons of oil contaminated soil across 63 installations within a 70 km radius of Ahmedabad since 2006. Both in-situ and ex-situ bioremediation techniques are used, with the latter involving transportation of contaminated soil to secure bioremediation pits for treatment. The indigenous bacterial consortium Oilzapper, developed by TERI, is applied to degrade the oil in the contaminated soil through a monitored bioremediation process, with soil sampling done to test the reduction in total petroleum hydrocarbons over time.