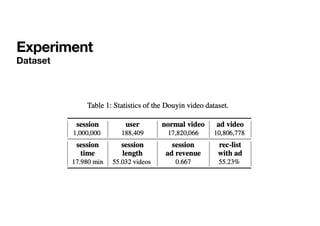
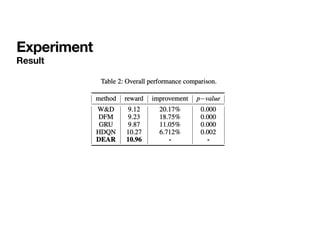
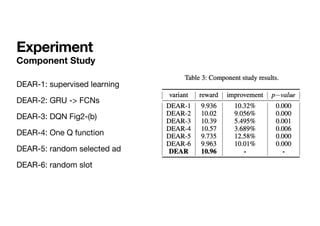
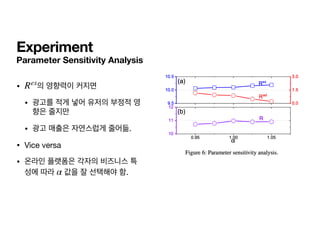
The document presents a deep reinforcement learning (RL) approach called DEAR, aimed at optimizing online advertising impressions within recommendation systems by maximizing revenue while minimizing negative impacts on user experience. It discusses challenges in existing advertising techniques, proposes a Markov decision process-based model, and details the architecture and training of the DEAR framework, including a novel dataset and various experimental metrics. The findings indicate that DEAR significantly improves advertising performance despite some remaining questions about model transparency and dataset design.


















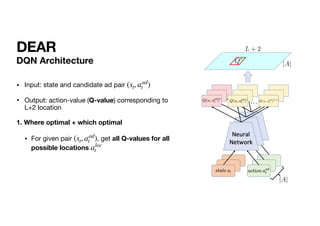
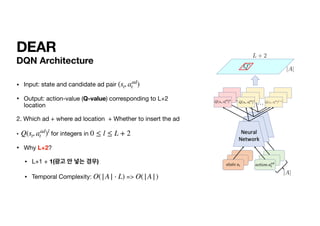

![DEAR
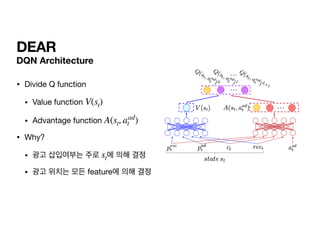
Optimal Action-value function
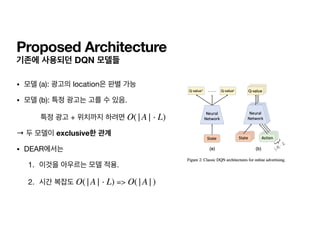
• 앞서 주어진 조건들을 모두 이용하면, optimal policy에 의한 action value function
구할 수 있음.
t+1의 모든 ads, locations에 대해서 조회해보아야 함.
Q*(st, at)
Q*(st, at) =
𝔼
st+1
[rt + γ max
at+1
Q*(st+1, at+1 |st, at)]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dear-210423084549/85/Dear-24-320.jpg)

![DEAR
Optimization
•
•
• target for the current iteration (과거 데이터를 미리 알고 있으므로, 그걸 기반으로 구한 target 값)
• 를 학습할 때에는 target network 를 고정. (Mnih et al. 2013)
•
L(θ) =
𝔼
st,at,rt,st+1
(yt − Q(st, at; θ))2
yt =
𝔼
st+1
[rt + γ max
at+1
Q(st+1, at+1; θT
)|st, at]
L(θ) θT
∇θL(θ) =
𝔼
st,at,rt,st+1
(yt − Q(st, at; θ))∇θQ(st, at; θ)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dear-210423084549/85/Dear-26-320.jpg)