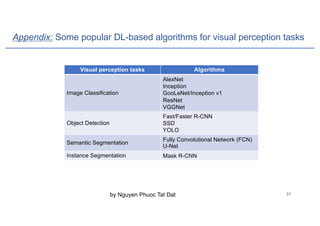
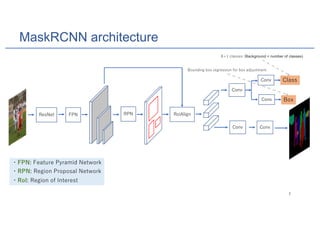
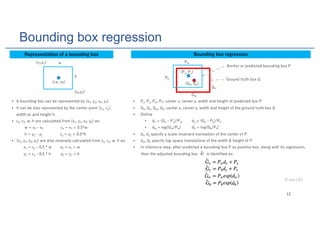
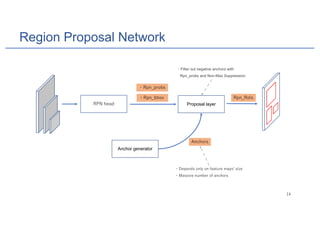
Mask R-CNN is an algorithm for instance segmentation that builds upon Faster R-CNN by adding a branch for predicting masks in parallel with bounding boxes. It uses a Feature Pyramid Network to extract features at multiple scales, and RoIAlign instead of RoIPool for better alignment between masks and their corresponding regions. The architecture consists of a Region Proposal Network for generating candidate object boxes, followed by two branches - one for classification and box regression, and another for predicting masks with a fully convolutional network using per-pixel sigmoid activations and binary cross-entropy loss. Mask R-CNN achieves state-of-the-art performance on standard instance segmentation benchmarks.














![RoIAlign
1024
1024
540
540
Input image
Object
64
1024/16 = 64
540/16 = 33.75
33.75
Feature map
RoI
16X less
33.75 / 7 = 4.82 each bin
7x7
Small feature map
(for each RoI)
RoI
Use bilinear interpolation to
calculate exact value at each bin
No quantization
(From [1])
FCN](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/maskrcnn-181001023652/85/Mask-RCNN-for-Instance-Segmentation-23-320.jpg)
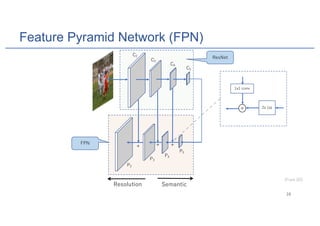
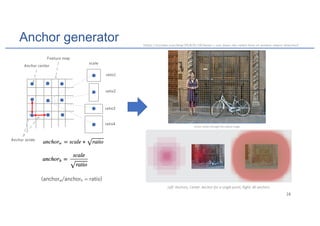
![Identify Feature Pyramid level for RoIs
Resize
P2
P3
P4
P5
w, h: width & height of a RoI
224: canonical ImageNet pre-training size
k0: target level of the RoI whose w*h = 2242
(here, k0 = 5)
Target level k of a RoI is identified by:
Crop the RoIs on
their feature map
Intuitions:
Features of large RoIs from smaller feature map (high semantic level)
Features of small RoIs from larger feature map (low semantic level)
RoIs
(From [6])](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/maskrcnn-181001023652/85/Mask-RCNN-for-Instance-Segmentation-24-320.jpg)

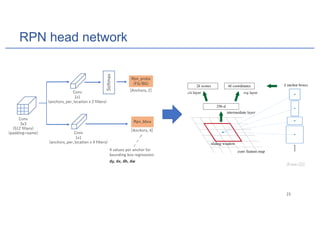
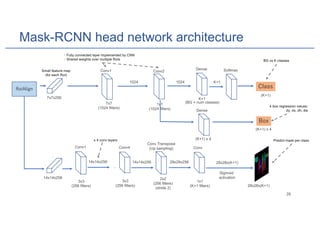
![Mask-RCNN head network
• A classifier to identify the class for each RoI: K classes + background
• A regressor to predict the 4 values dy, dx, dh, dw for each RoI
• Fully Convolutional Network (FCN) [5] to predict mask per class
• Represent a mask as m x m matrix
• For each RoI, try to predict mask for each class
• Use sigmoid to predict how probability for each pixel
• Use binary loss to train the network](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/maskrcnn-181001023652/85/Mask-RCNN-for-Instance-Segmentation-26-320.jpg)




![Mask-RCNN on COCO data
(From [1])](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/maskrcnn-181001023652/85/Mask-RCNN-for-Instance-Segmentation-32-320.jpg)
![Evolution of R-CNN
= Faster R-CNN [2] + Fully Convolutional Network [5]
RoIPool RoIAlign Per-pixel softmax Per-pixel sigmoid
Mask R-CNN [1]
Faster R-CNN = Fast R-CNN [3] +
Fast R-CNN = R-CNN [4] + ConvNet on whole input image first, then apply RoIPooling layer
R-CNN [1]
Region proposal on input image + +
+=
+
+](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/maskrcnn-181001023652/85/Mask-RCNN-for-Instance-Segmentation-33-320.jpg)

![References
[1] Kaiming He, Georgia Gkioxari, Piotr Dollár, and Ross Girshick. Mask R-CNN. IEEE
International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), 2017.
[2] S. Ren, K. He, R. Girshick, and J. Sun. Faster R-CNN: Towards real-time object detection
with region proposal networks. In NIPS, 2015.
[3] R. Girshick. Fast R-CNN. In ICCV, 2015.
[4] R. Girshick, J. Donahue, T. Darrell, and J. Malik. Rich feature hierarchies for accurate object
detection and semantic segmentation. In CVPR, 2014
[5] J. Long, E. Shelhamer, and T. Darrell. Fully convolutional networks for semantic
segmentation. In CVPR, 2015.
[6] T.Y. Lin, P. Dollár, R. Girshick, K. He, B. Hariharan, and S. Belongie. Feature pyramid
networks for object detection. In CVPR, 2017
by Nguyen Phuoc Tat Dat](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/maskrcnn-181001023652/85/Mask-RCNN-for-Instance-Segmentation-35-320.jpg)