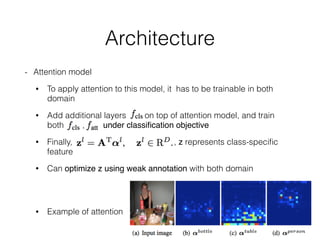
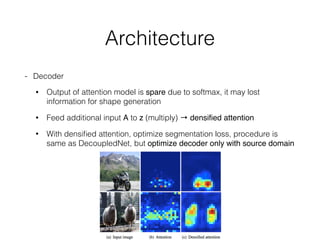
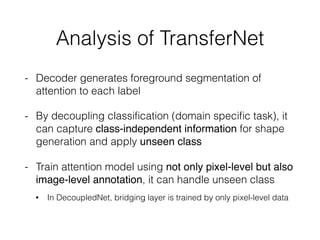
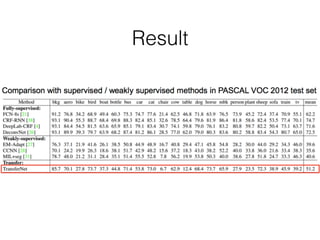
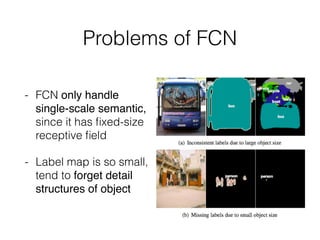
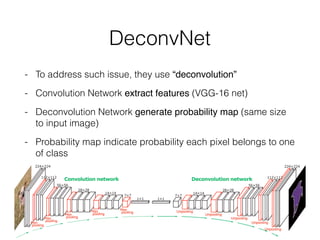
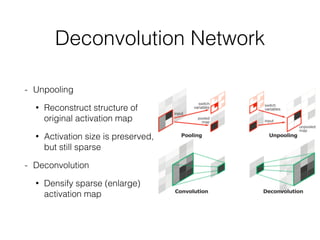
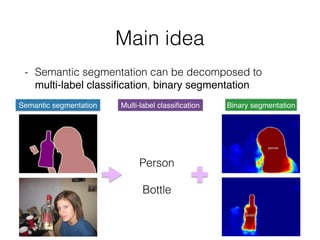
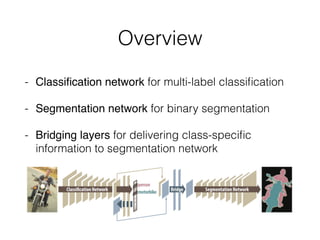
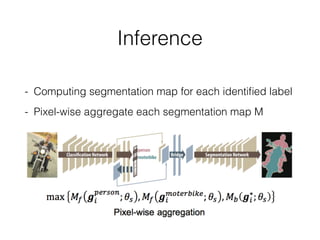
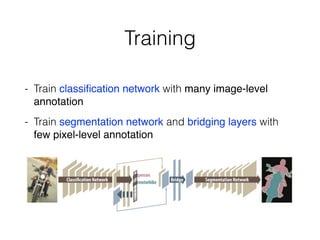
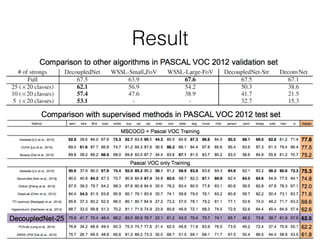
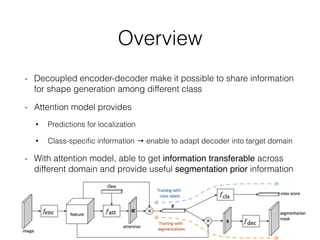
The document discusses three neural network models for semantic segmentation: DeconvNet, DecoupledNet, and TransferNet. DeconvNet uses deconvolution layers to generate dense pixel-wise segmentation maps from convolutional features. DecoupledNet is designed for semi-supervised learning, using separate networks for classification and binary segmentation with bridging layers. TransferNet introduces an attention model to enable transferring a segmentation model trained on one dataset to a different dataset with new classes.


![Semantic Segmentation
- Predict pixel-level label in image
- ct
[Shotton et al . 2007]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/deconvnetdecouplednettransfernetinimagesegmentation-160511060923/85/DeconvNet-DecoupledNet-TransferNet-in-Image-Segmentation-4-320.jpg)










![Architecture
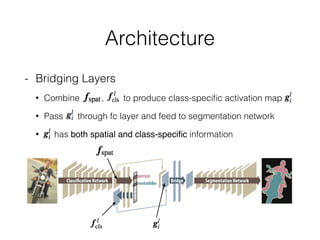
- Saliency Map
1. Produce score vector, set
dscore all 0 but 1 in idx
related to label that want
to track
2. Backprop to arbitrary
layer (pool5 in this paper)
- By saliency map we can get
class-specific information
in each label (class)
Qualitative example of saliency map
[Karen Simonyan et al,. 2014]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/deconvnetdecouplednettransfernetinimagesegmentation-160511060923/85/DeconvNet-DecoupledNet-TransferNet-in-Image-Segmentation-24-320.jpg)






![Architecture
- Encoder
• Extract feature descriptor as
A is obtain from last conv layer to retain spatial information
• M, D is # of hidden unit (20x20), # of channel respectively
- Attention model
• To train weight vector , where represents
relevance of location to each class l
• Formally,
• And extra technique to reduce parameter [R. Memisevic. 2013] did](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/deconvnetdecouplednettransfernetinimagesegmentation-160511060923/85/DeconvNet-DecoupledNet-TransferNet-in-Image-Segmentation-36-320.jpg)