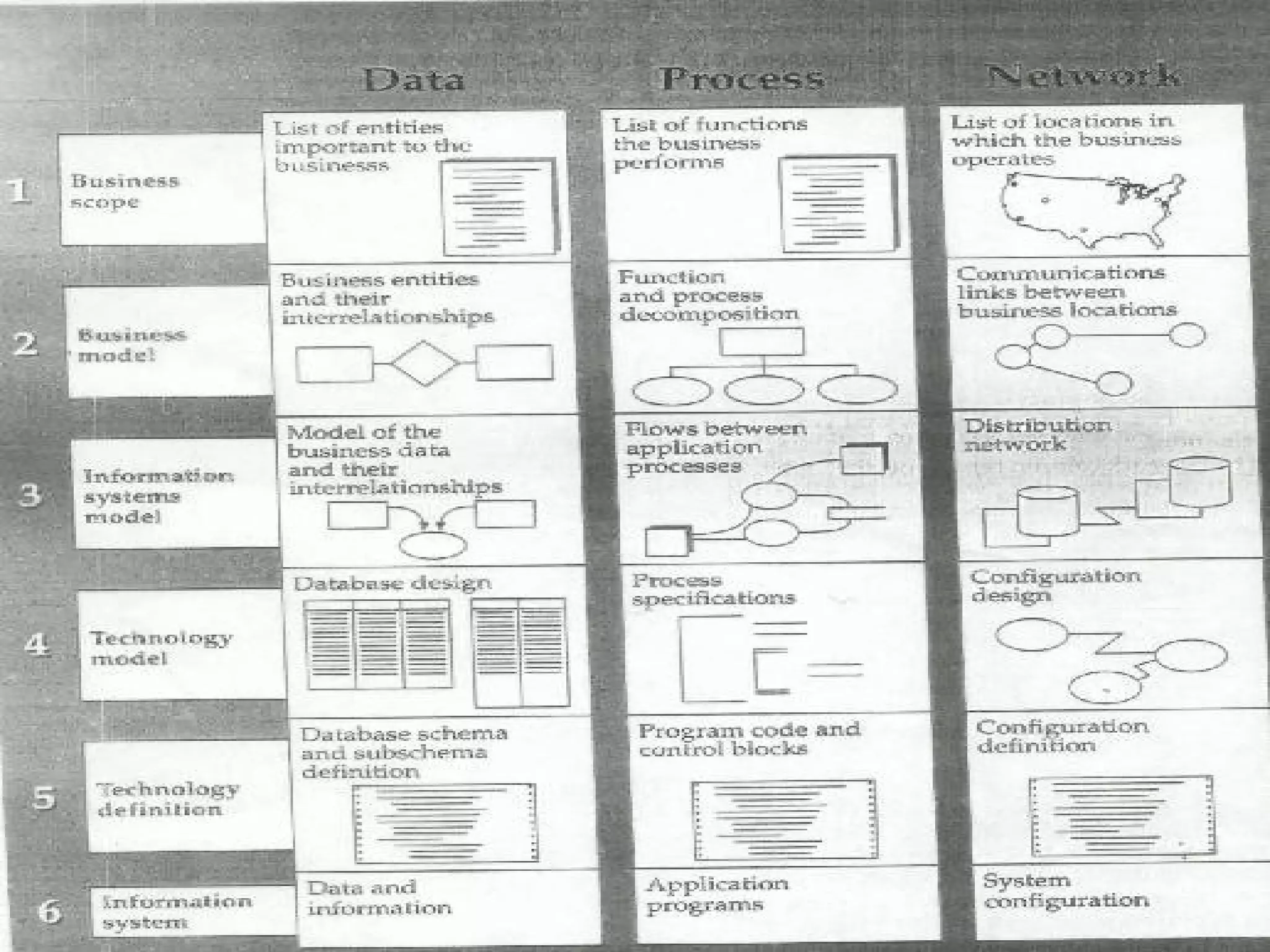
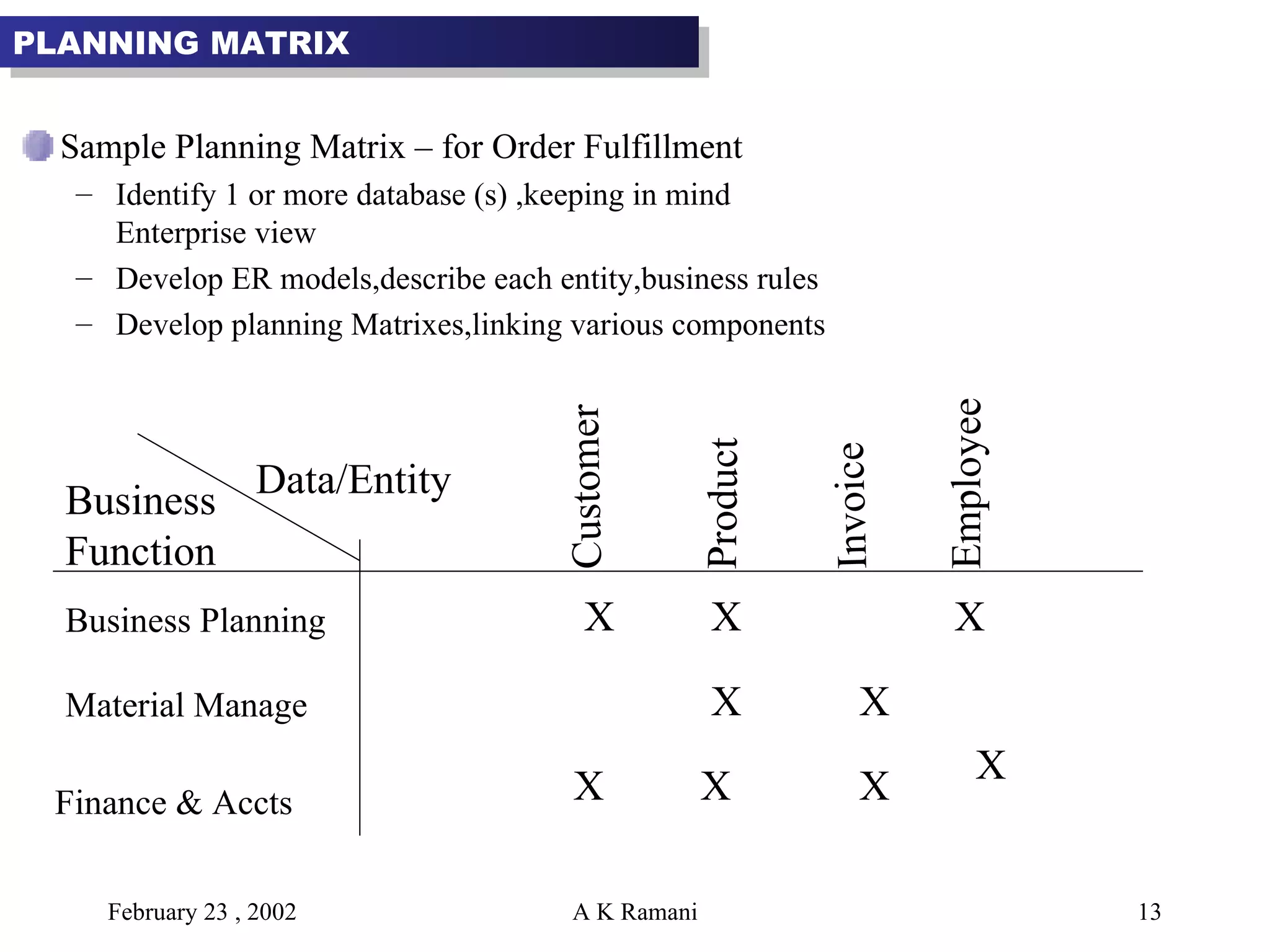
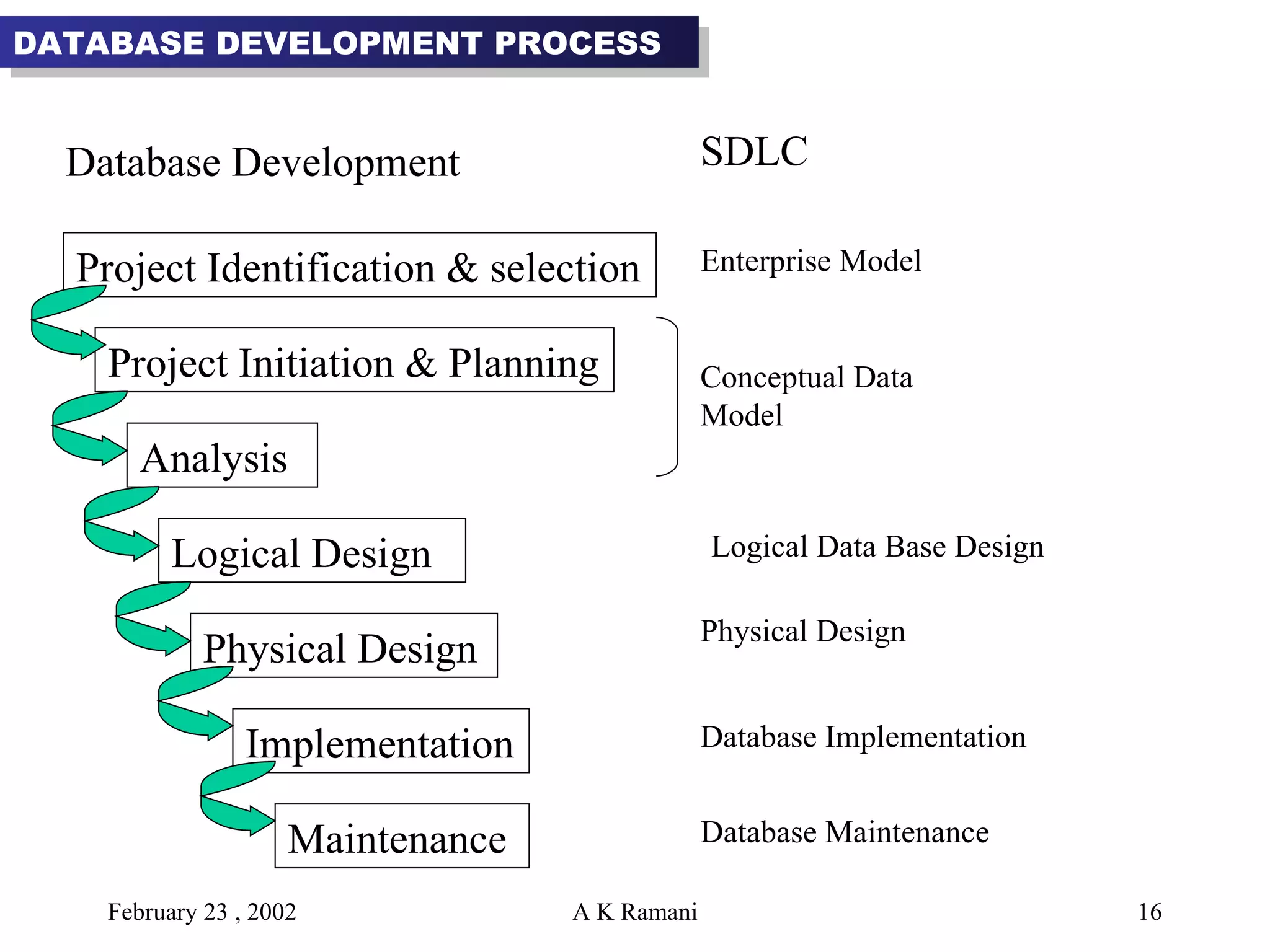
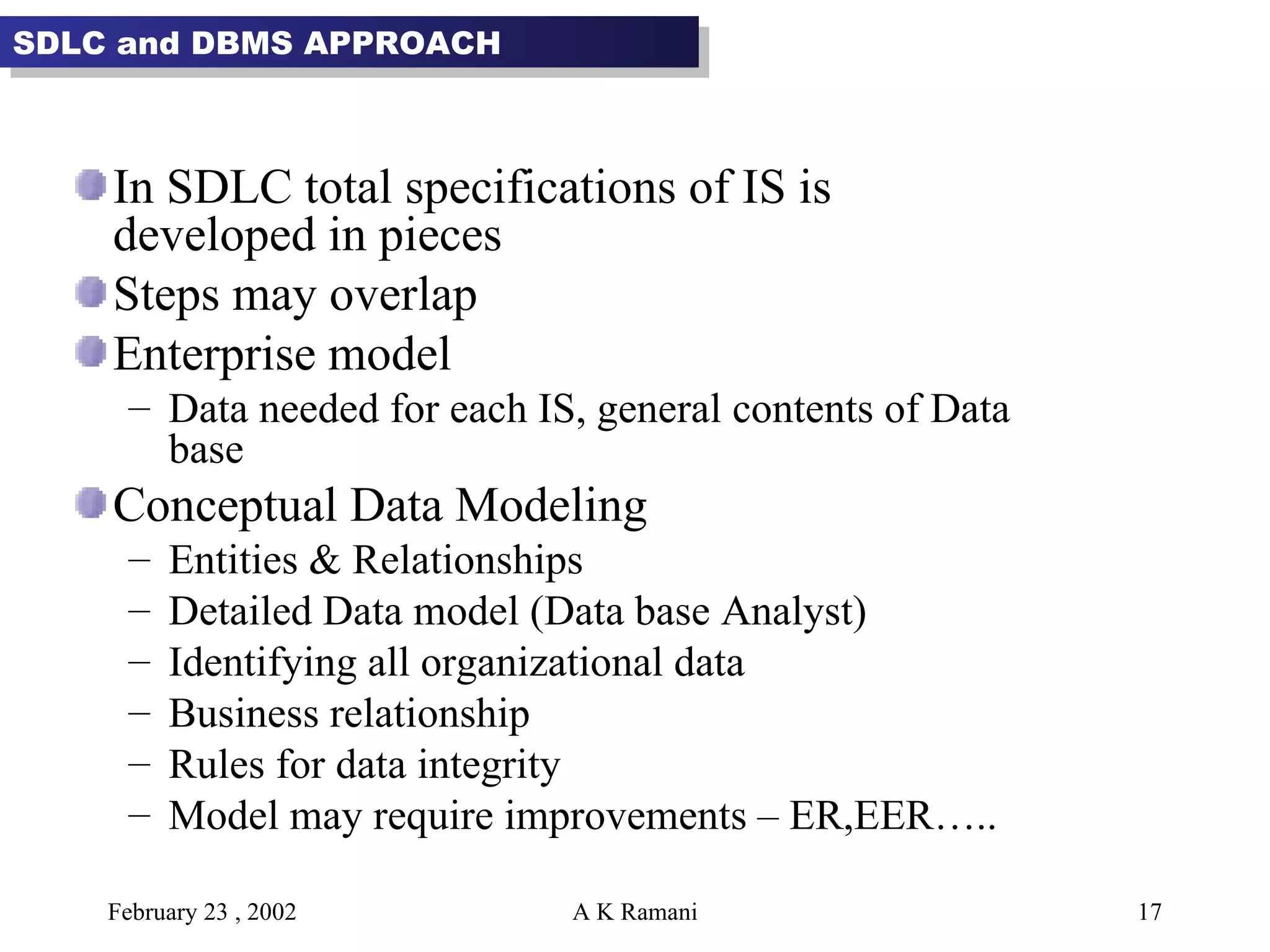
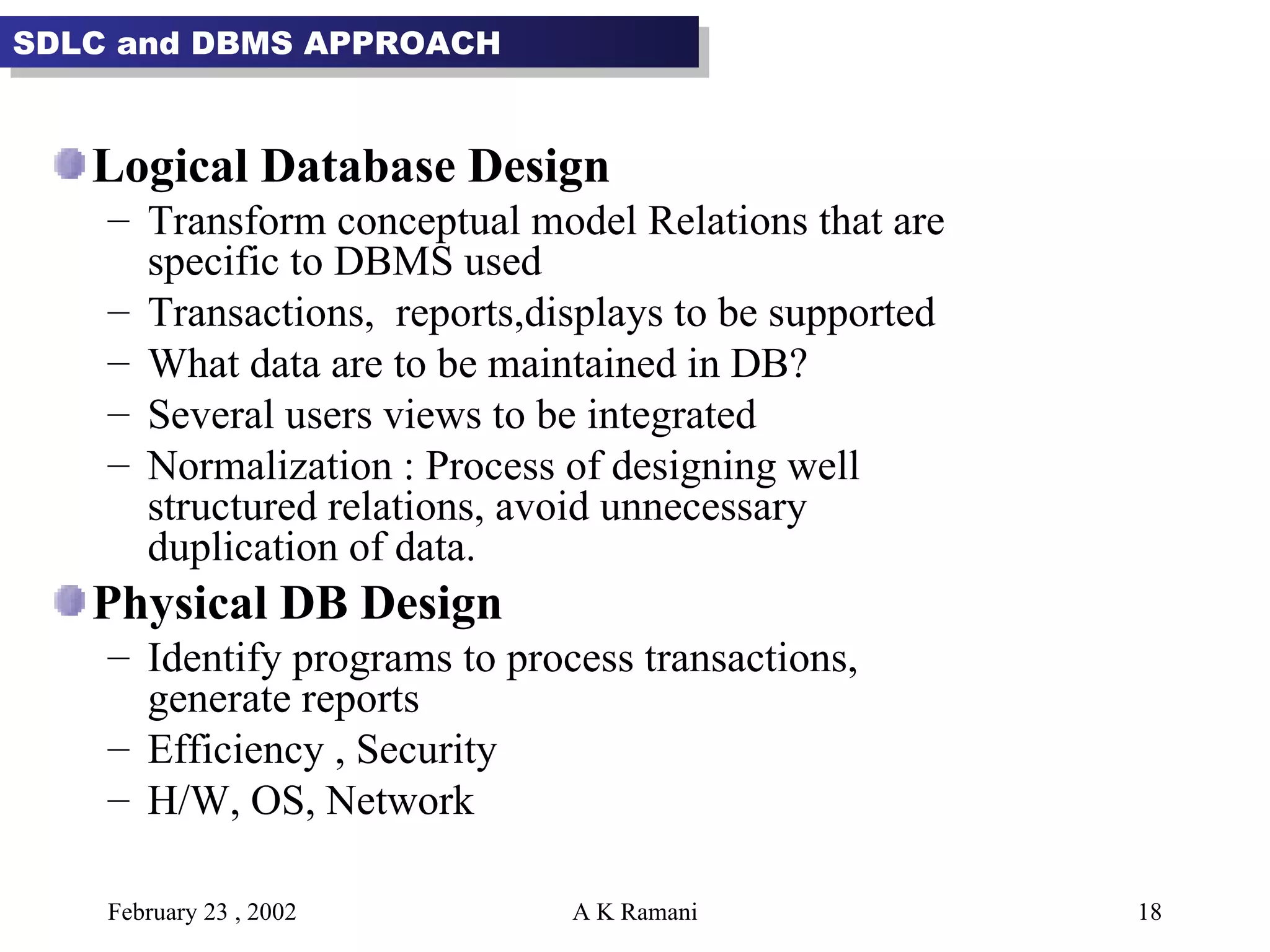
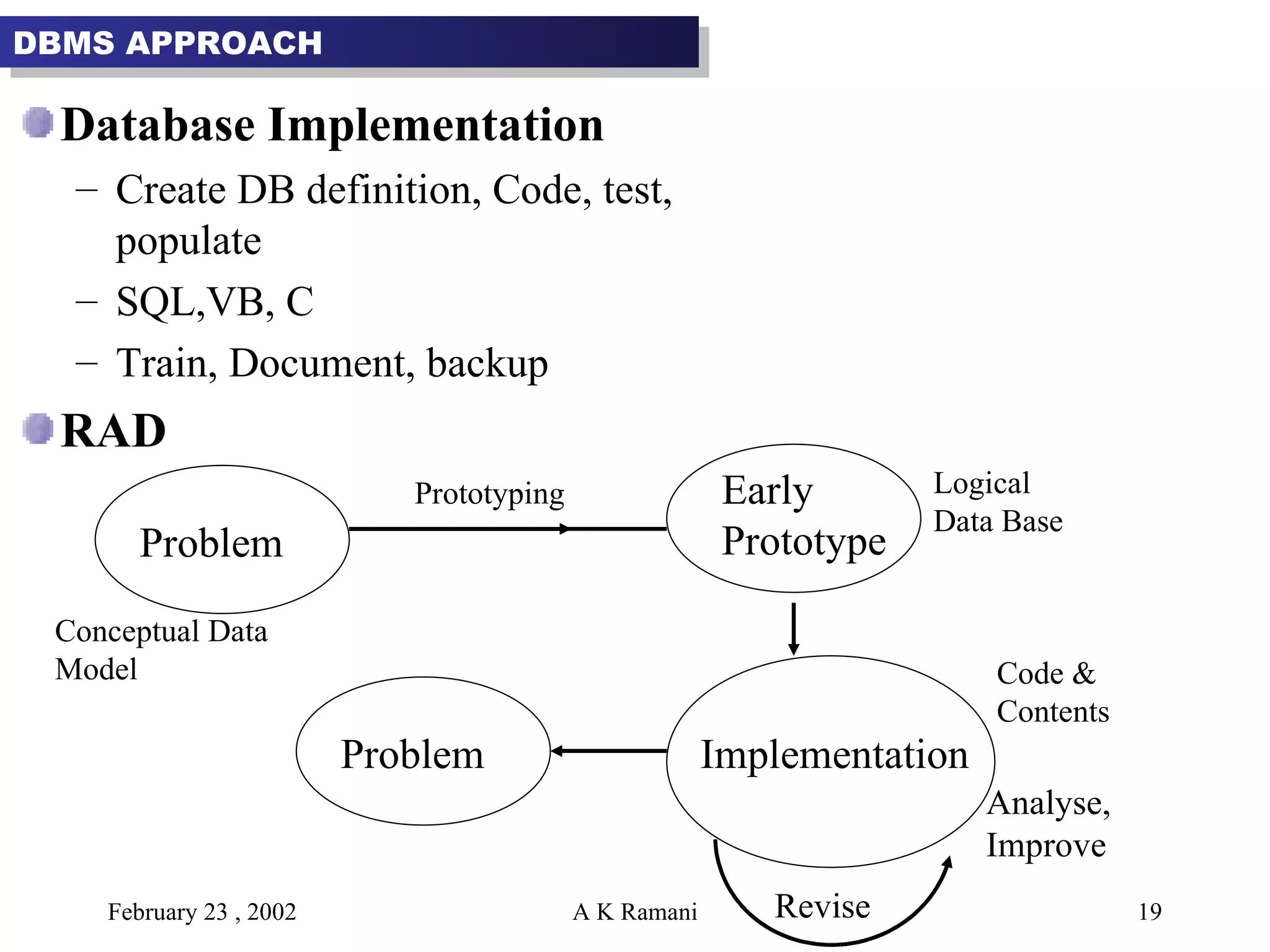
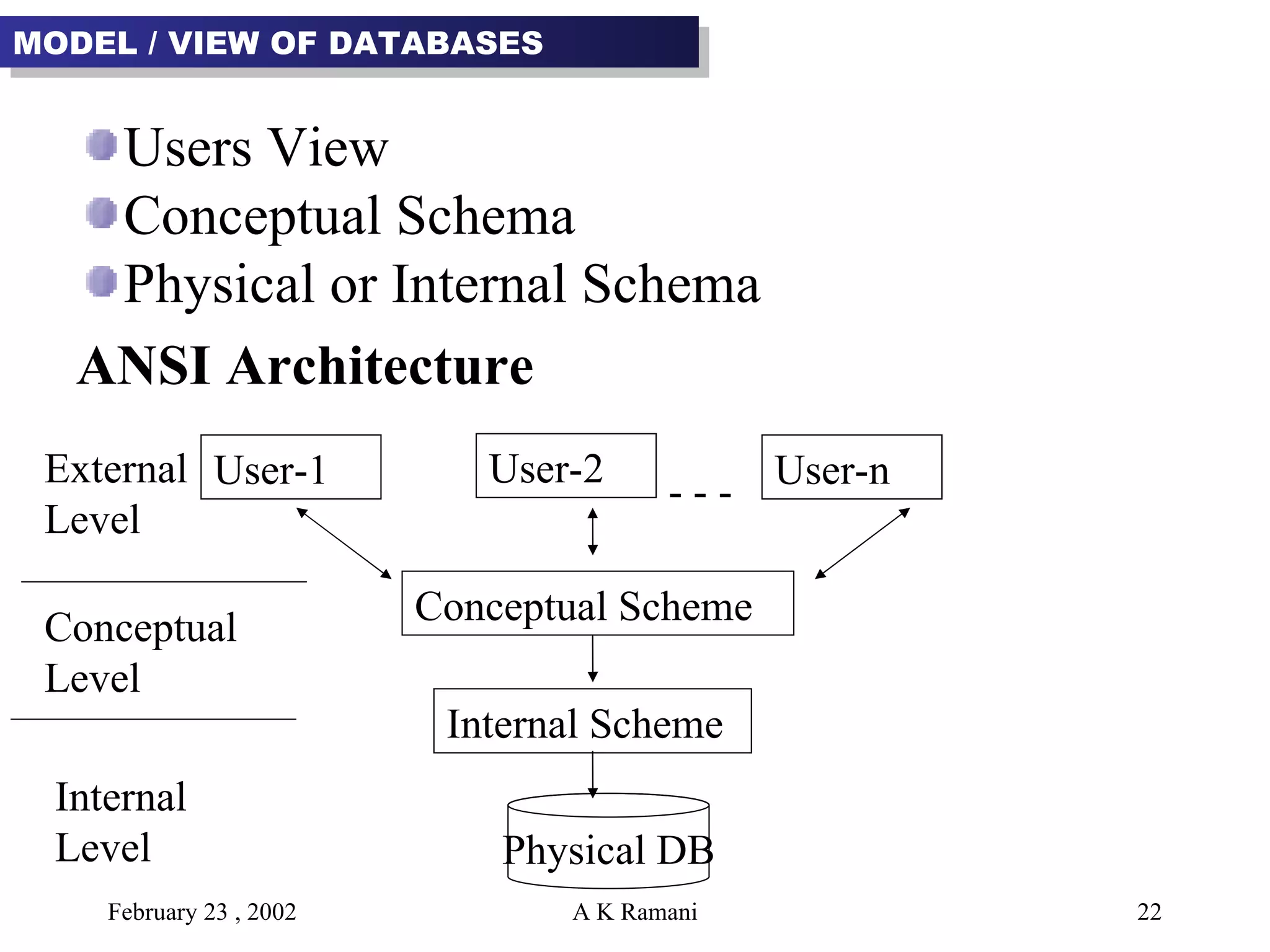
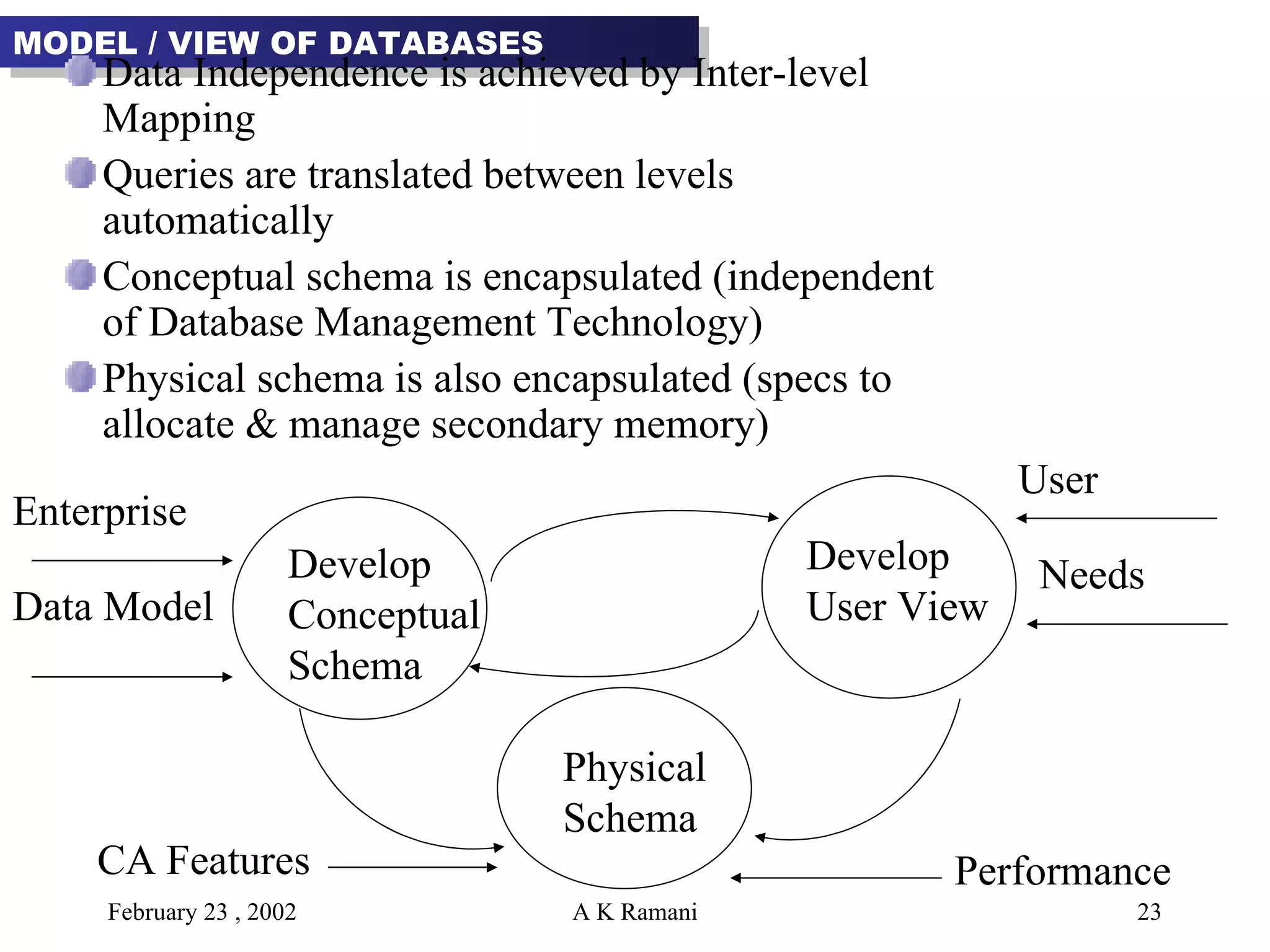
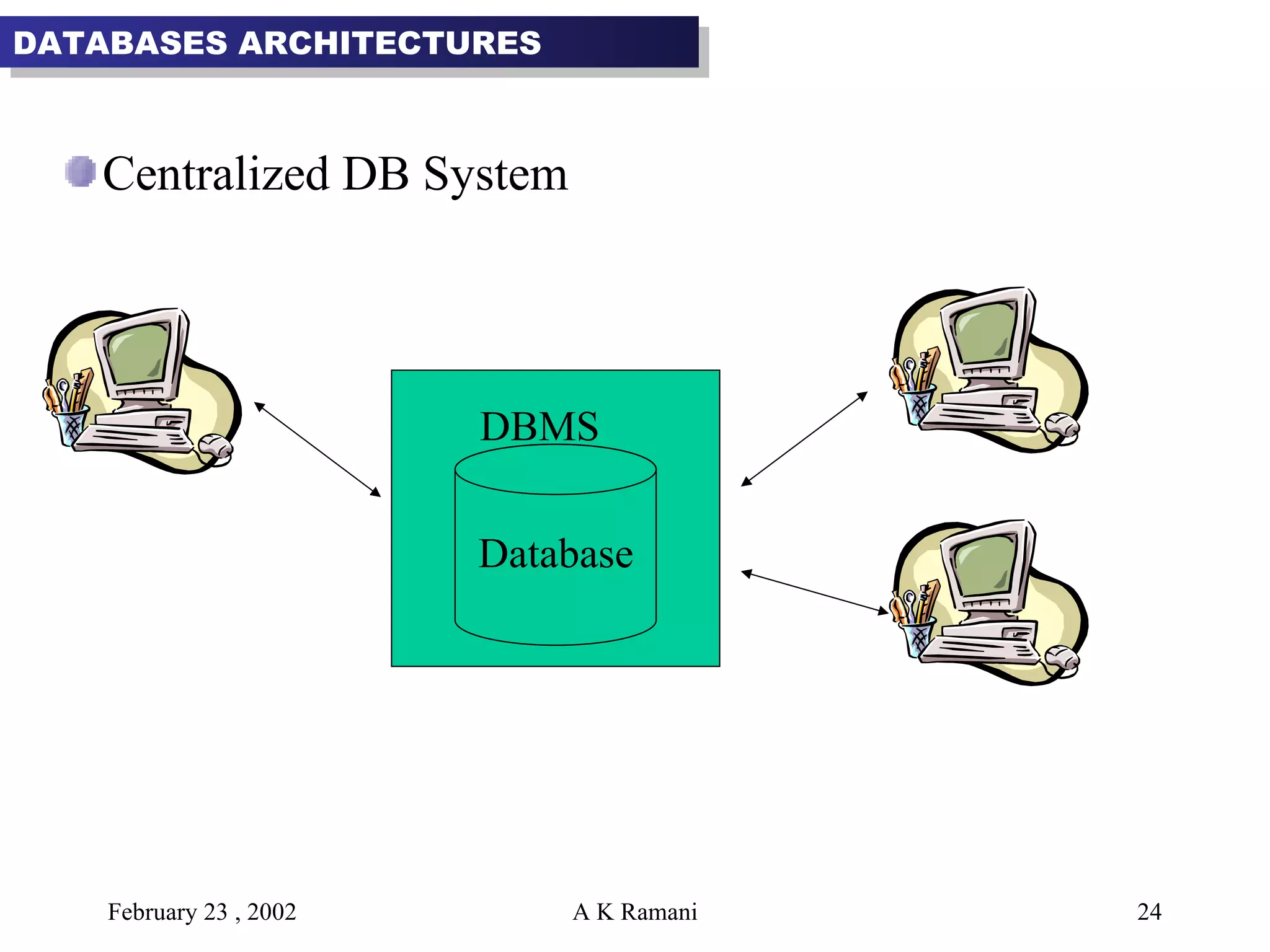
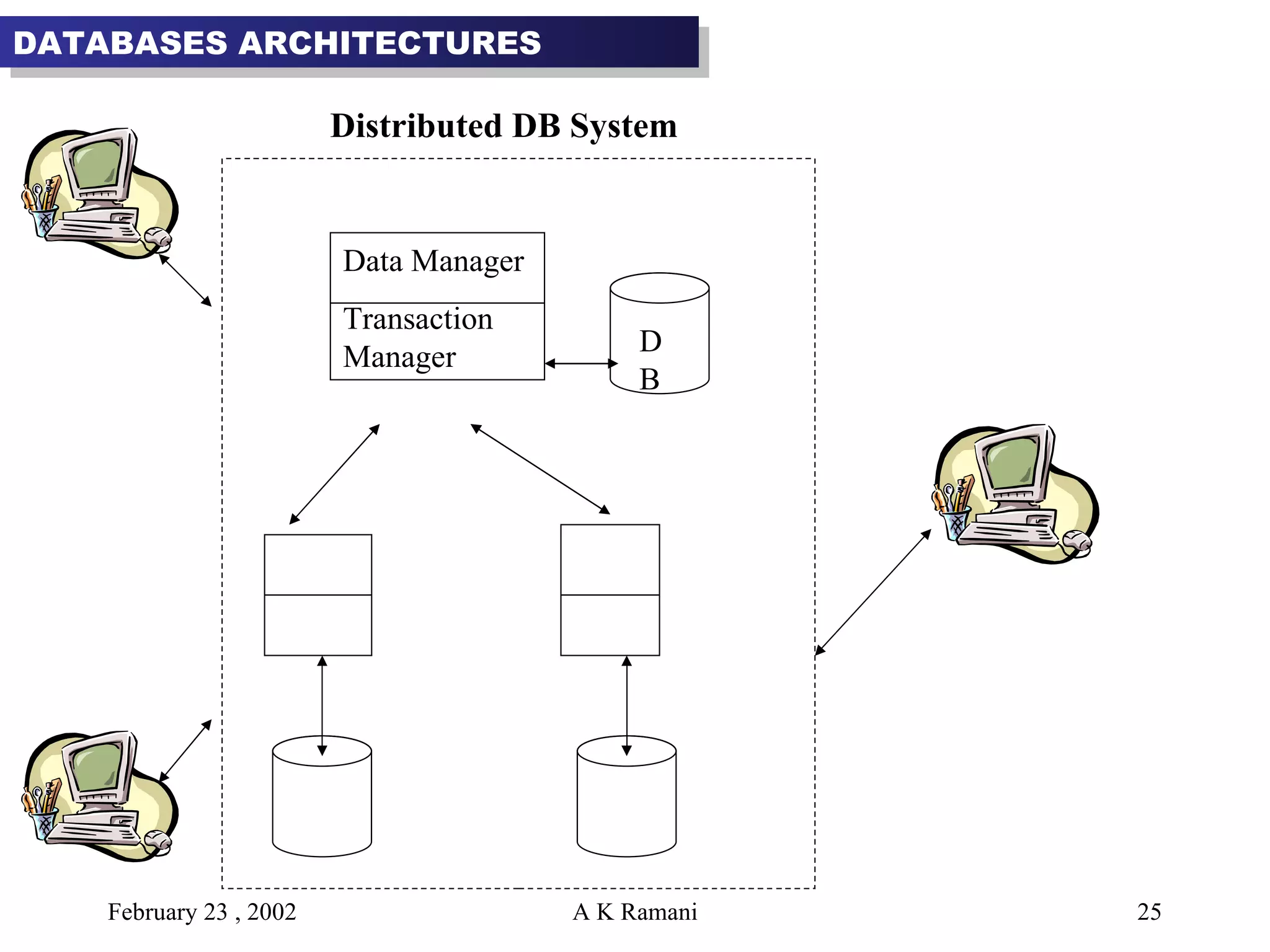
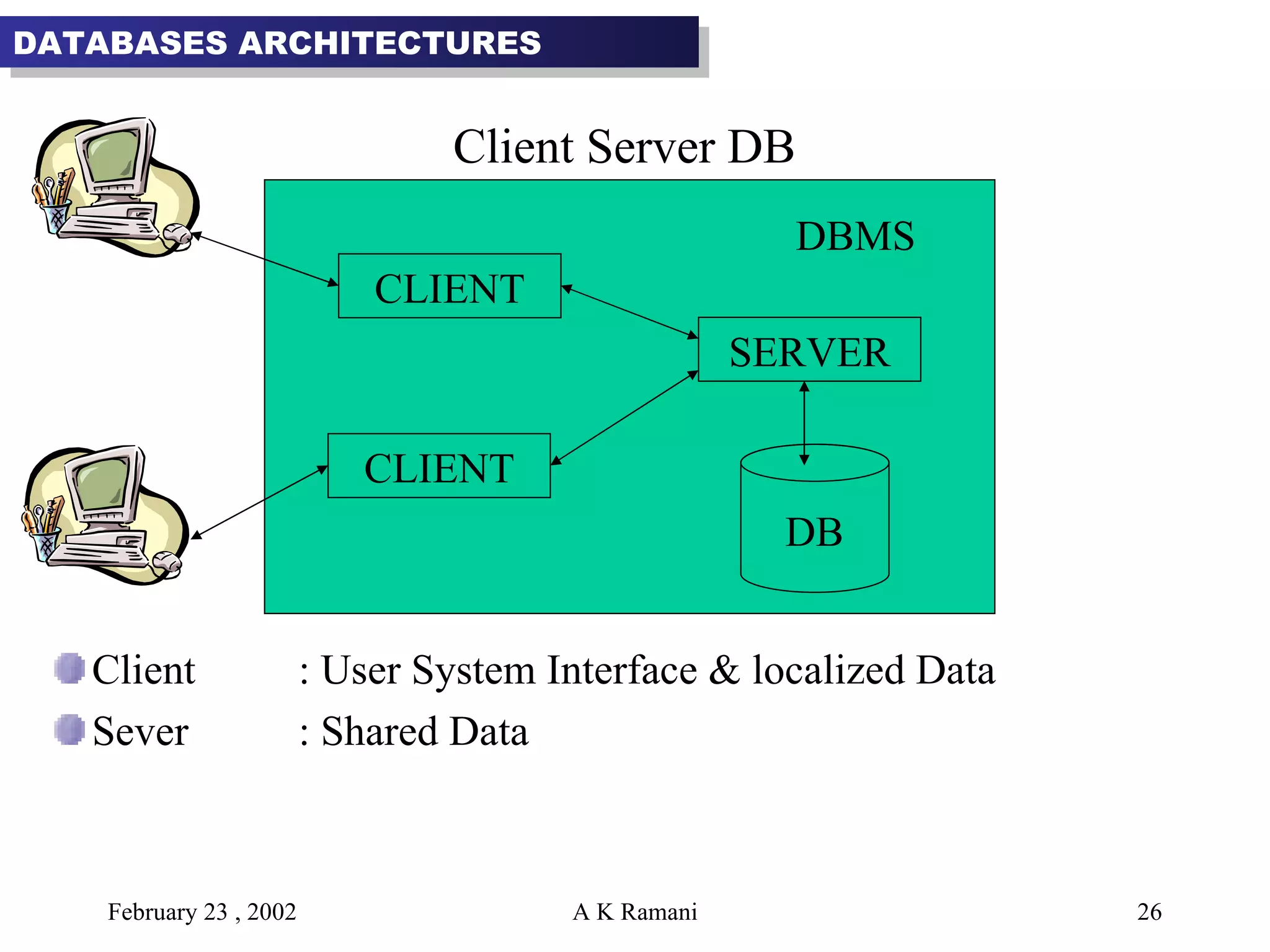
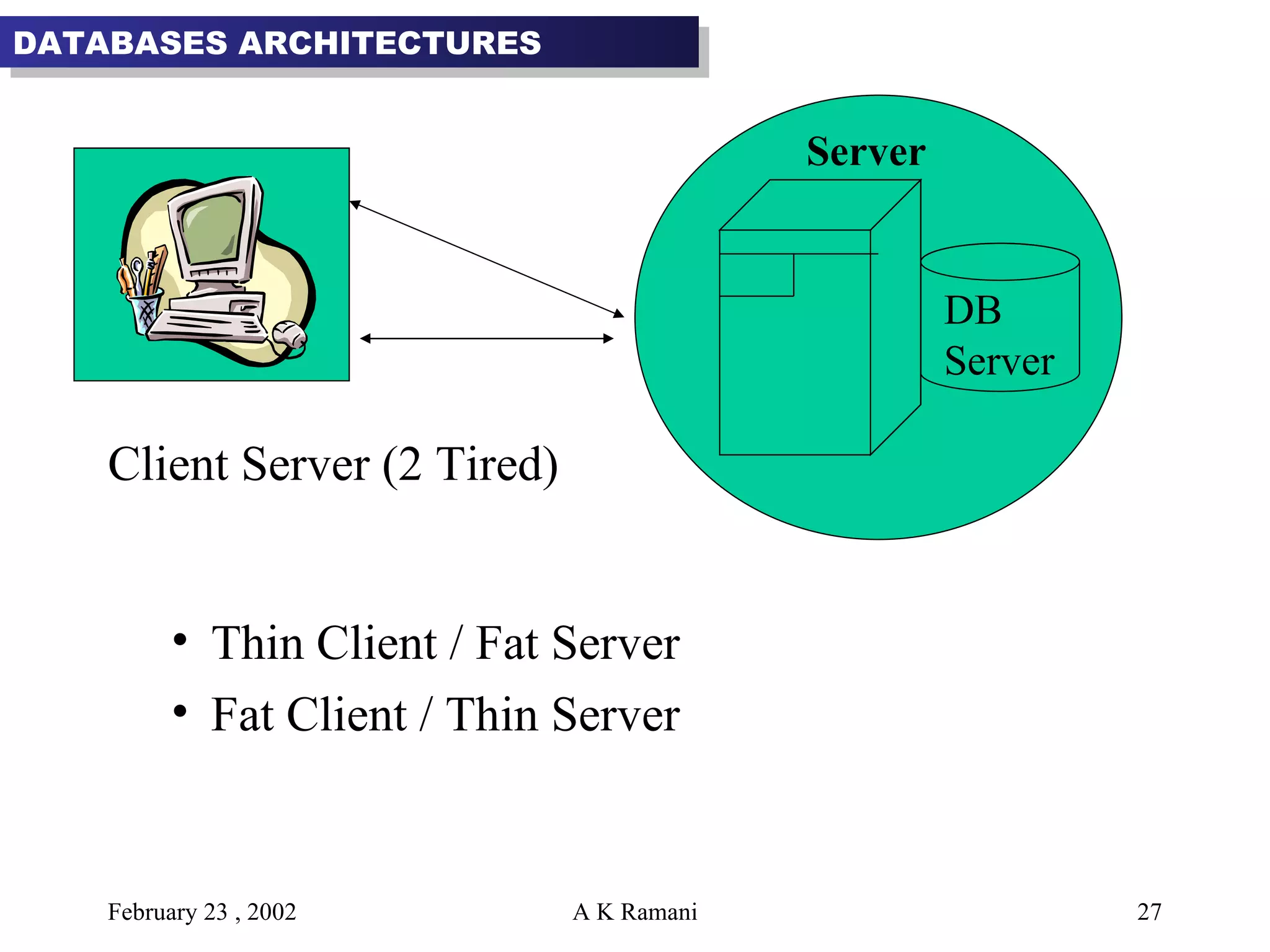
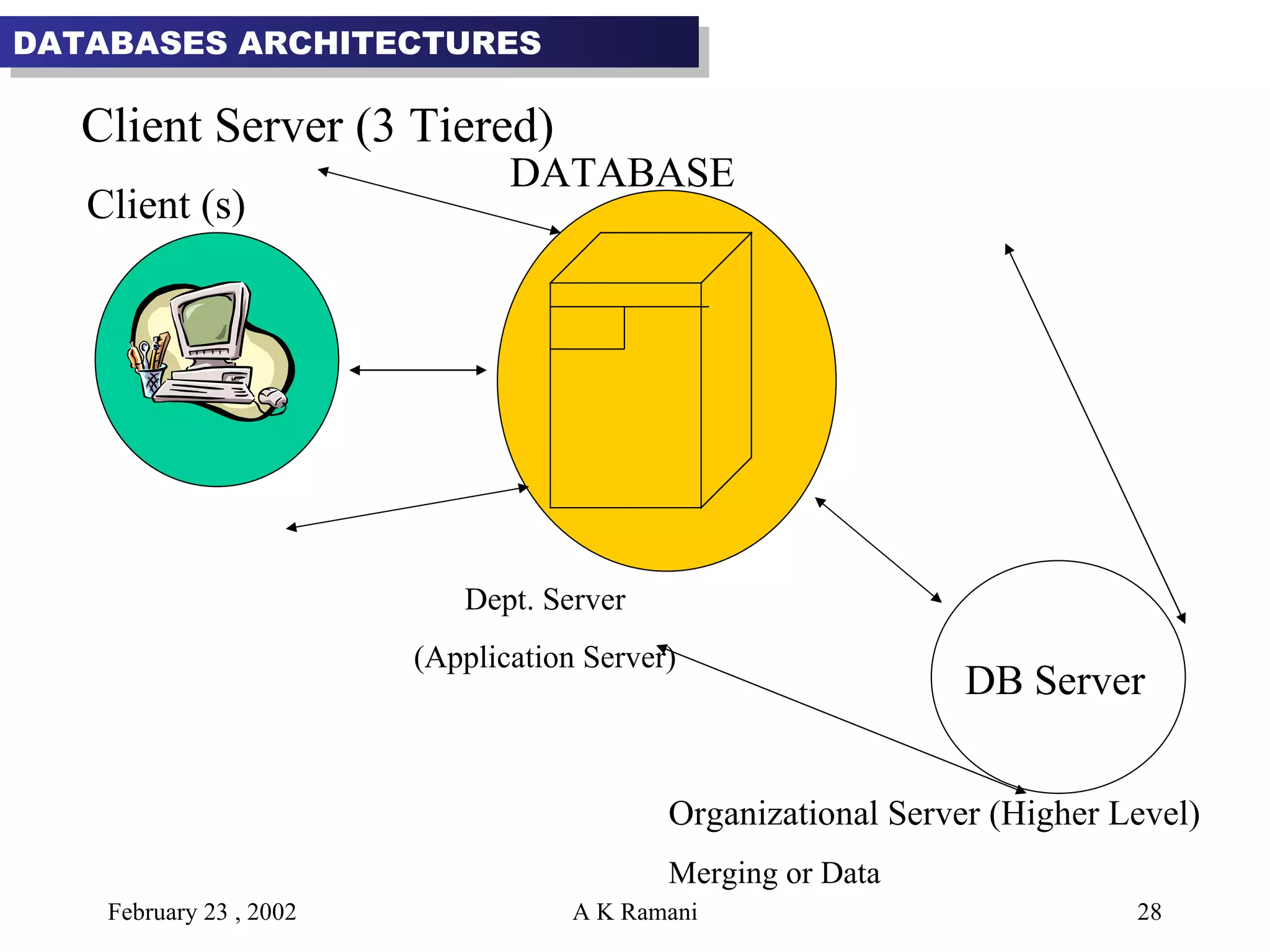
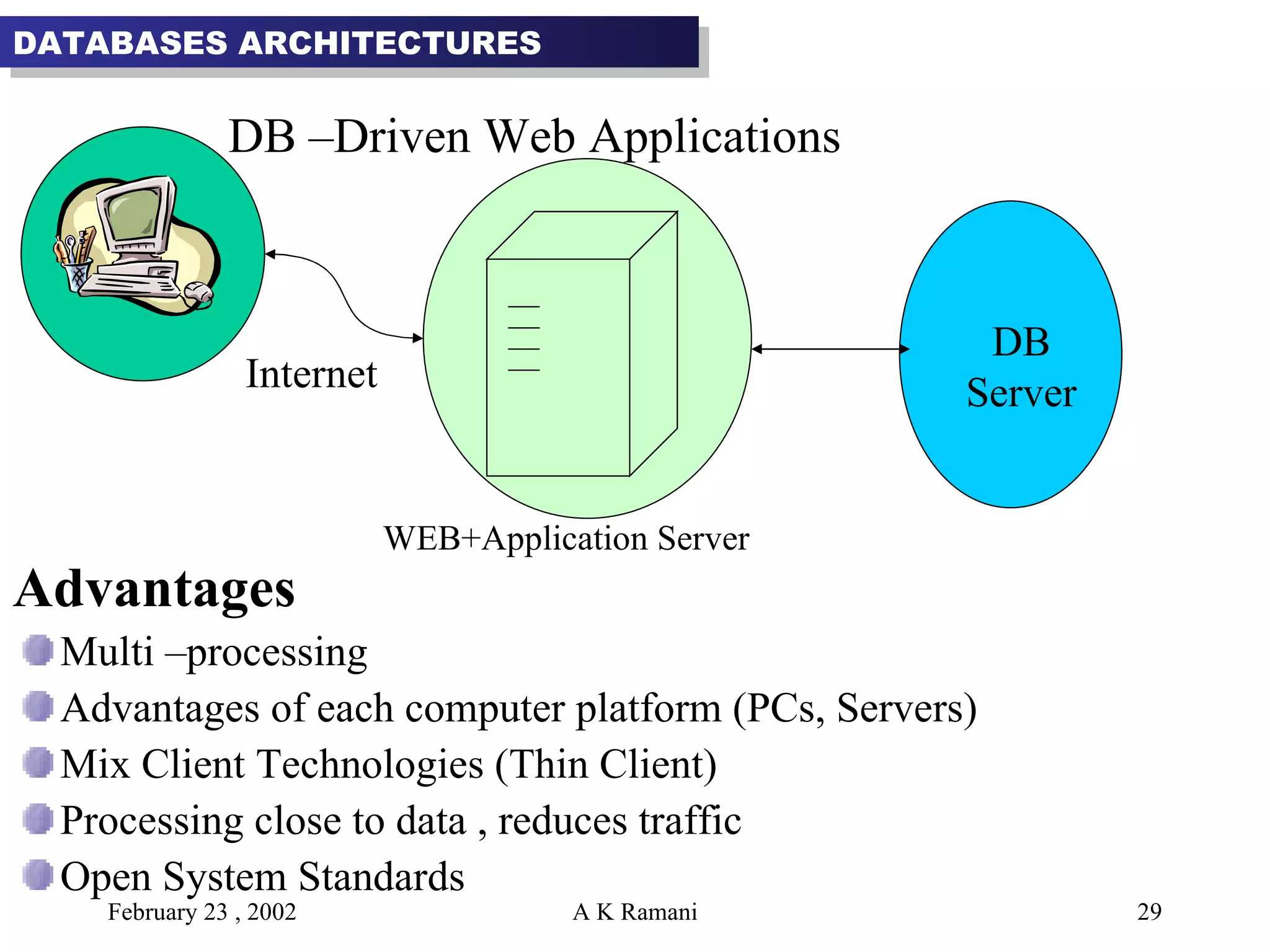
The document outlines the general steps in database development which include enterprise data modeling (EDM) and developing an information systems architecture (ISA). Key steps include reviewing current systems, analyzing business requirements, planning the database project, and considering how the ISA can grow and be flexible. The development process also involves conceptual and logical data modeling, physical database design, and implementation.