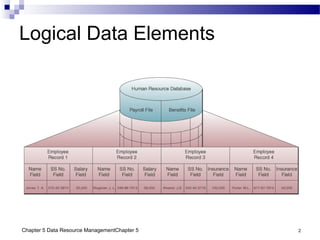
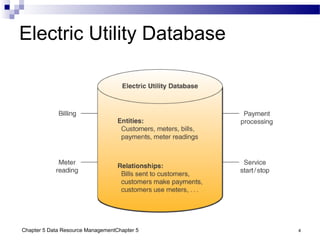
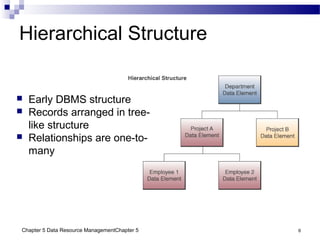
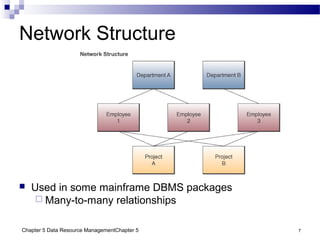
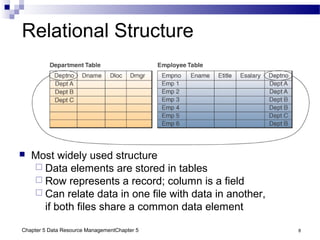
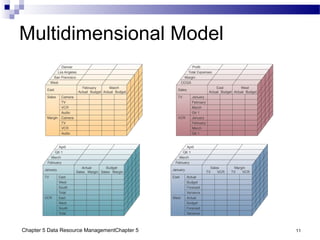
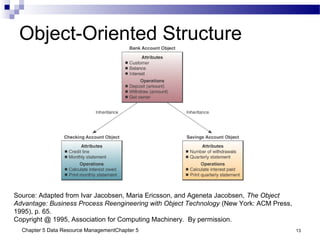
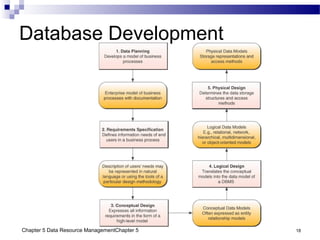
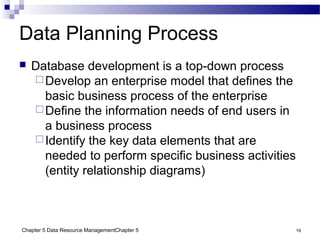
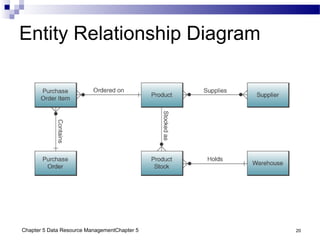
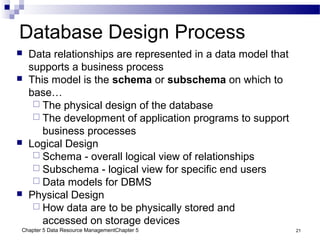
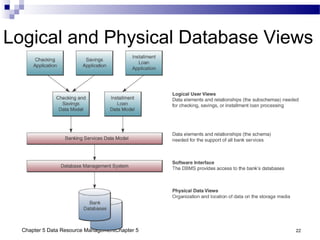
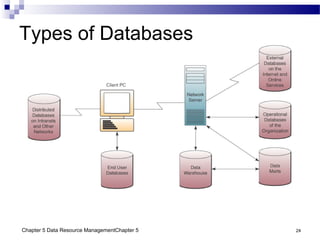
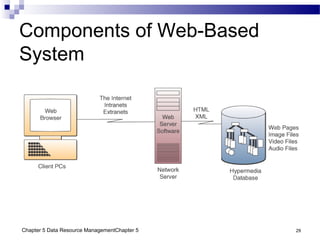
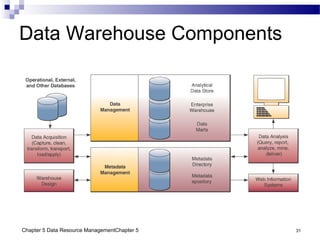
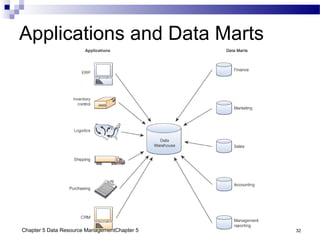
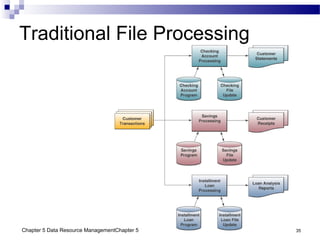
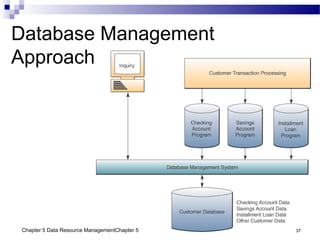
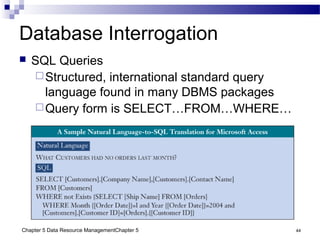
The document discusses different approaches to data resource management. It describes traditional file processing, where data is organized across independent files, leading to issues like data redundancy and lack of integration. The modern approach is database management, which consolidates organizational data into centralized databases managed by a database management system (DBMS). The DBMS allows many applications to access integrated data and maintains data quality. The chapter also covers logical and physical database design, different database structures, and types of databases like operational, distributed, external, and data warehouses.