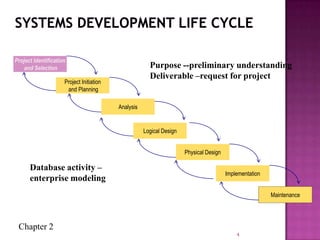
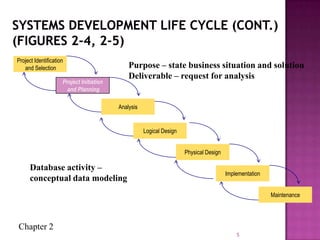
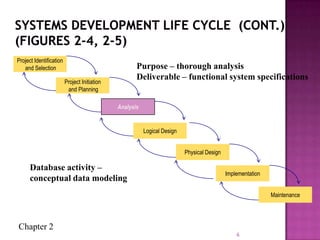
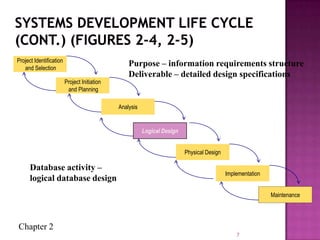
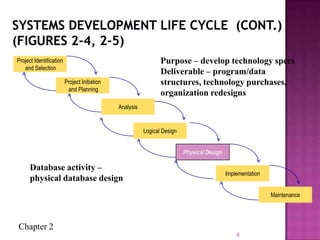
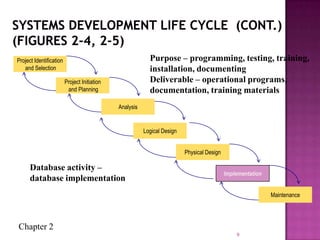
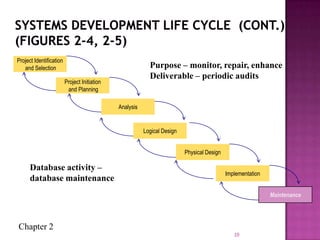
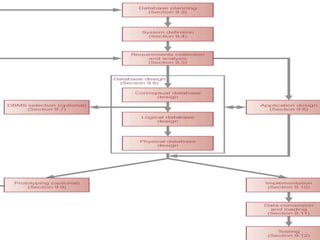
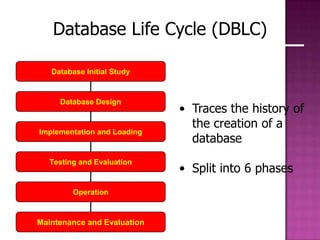
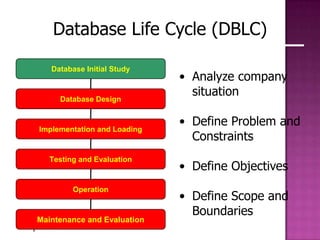
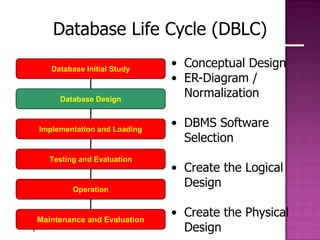
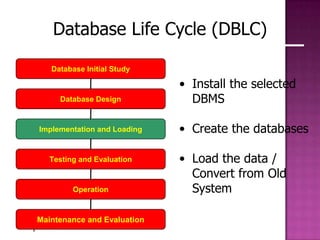
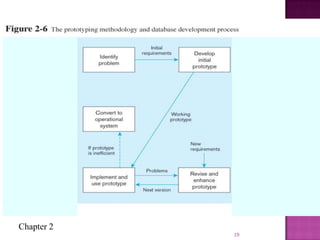
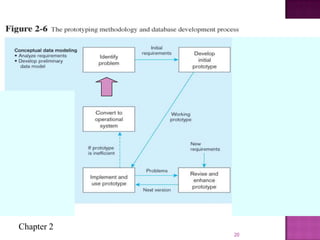
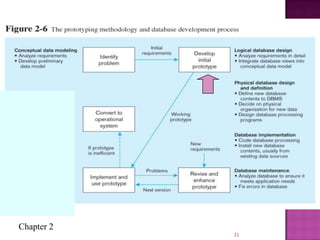
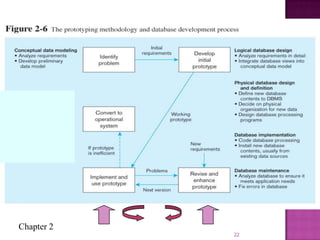
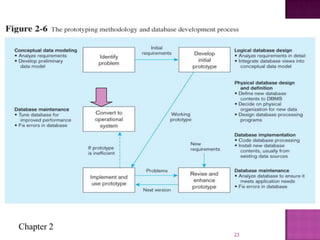
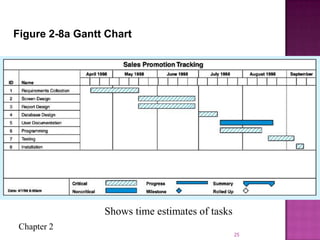
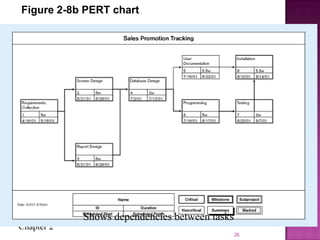
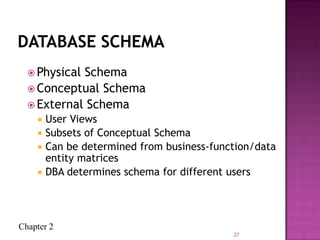
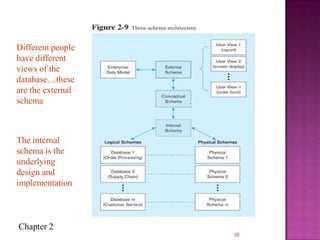
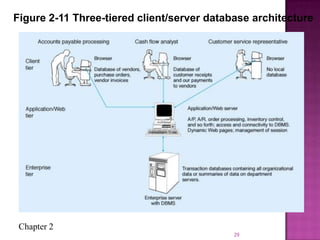
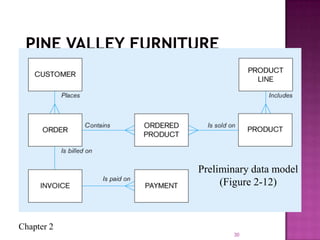
The document discusses the database life cycle and its phases: initial study, design, implementation and loading, testing and evaluation, operation, and maintenance and evaluation. It also discusses database schema, including physical, conceptual, and external schemas. Finally, it discusses project management techniques like Gantt charts and PERT charts that can be used to plan and track database development projects.


![Chapter 2
3
Figure 2-1 Segment from enterprise data model (Pine
Valley Furniture Company) [simplified E-R diagram,
repeat of figure 1.3]
Enterprise data model describes
the high-level entities in an
organization and the
relationship between these
entities](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dblc-130930124144-phpapp02/85/Dblc-3-320.jpg)