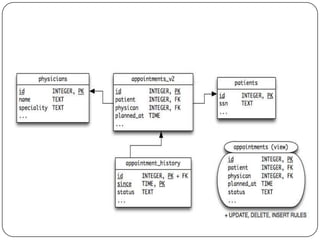
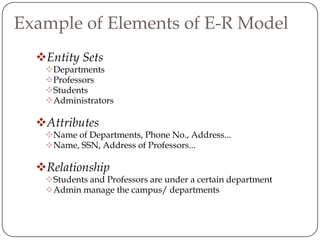
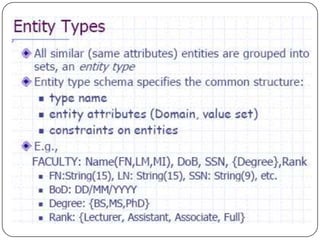
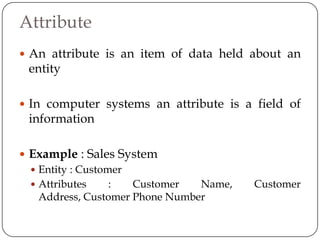
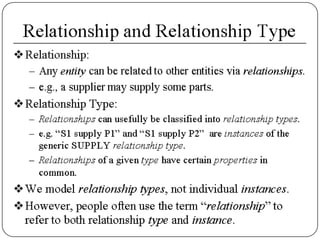
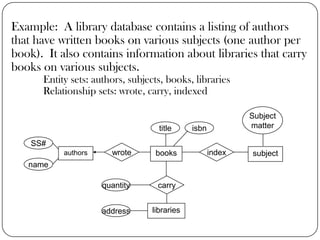
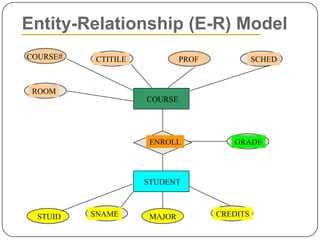
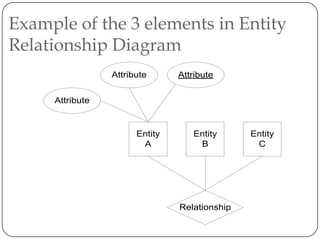
Physical and logical data independence are described. Logical data independence refers to the ability to change the logical schema without impacting external schemas or application programs. Physical data independence is the ability to change the physical schema without affecting the logical schema, such as changing storage structures or devices. Examples of each type of independence are provided. The key elements of an entity-relationship model - entities, attributes, and relationships - are defined. An example E-R diagram showing students, courses, and their relationship is depicted to illustrate these elements.