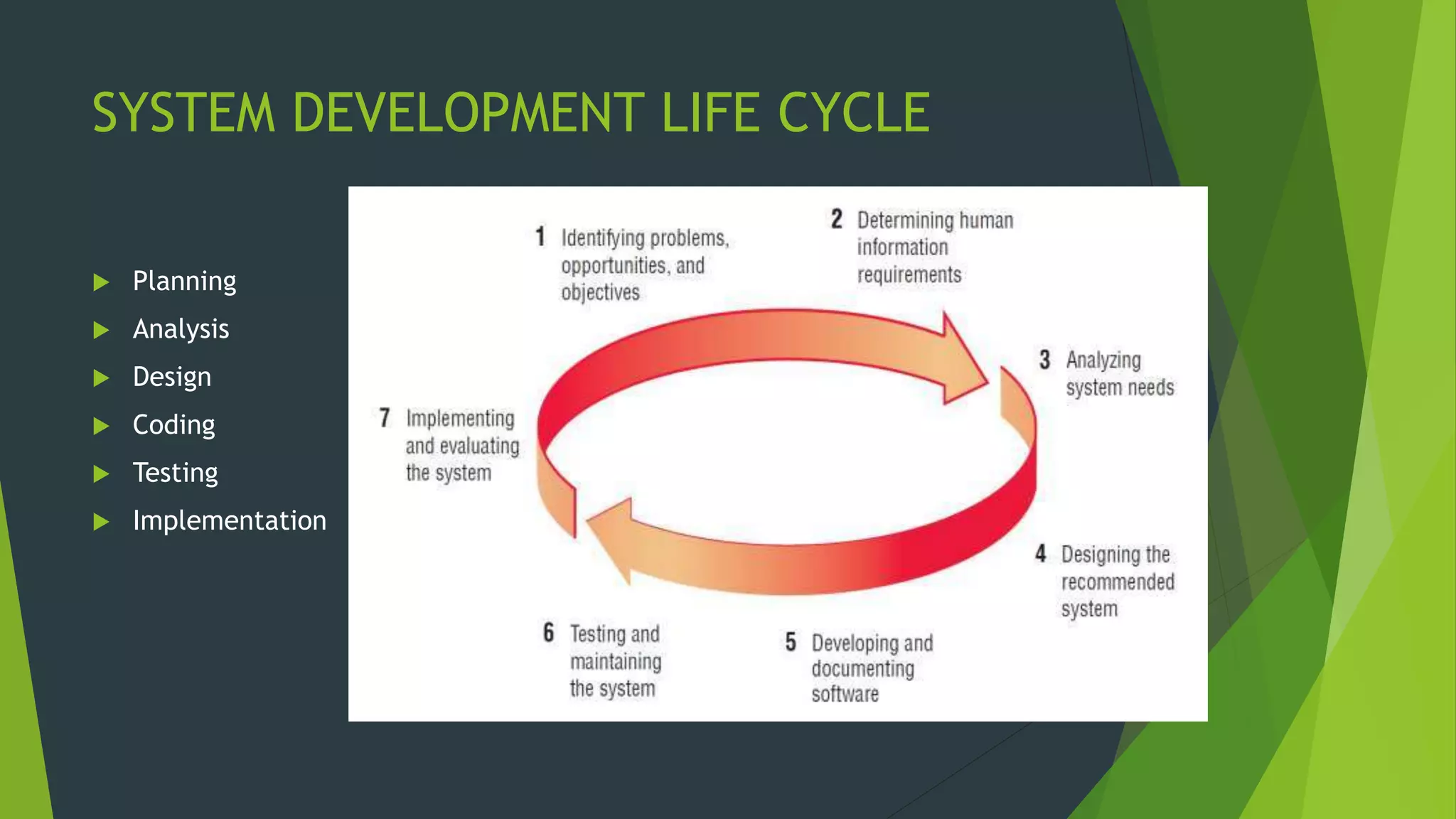
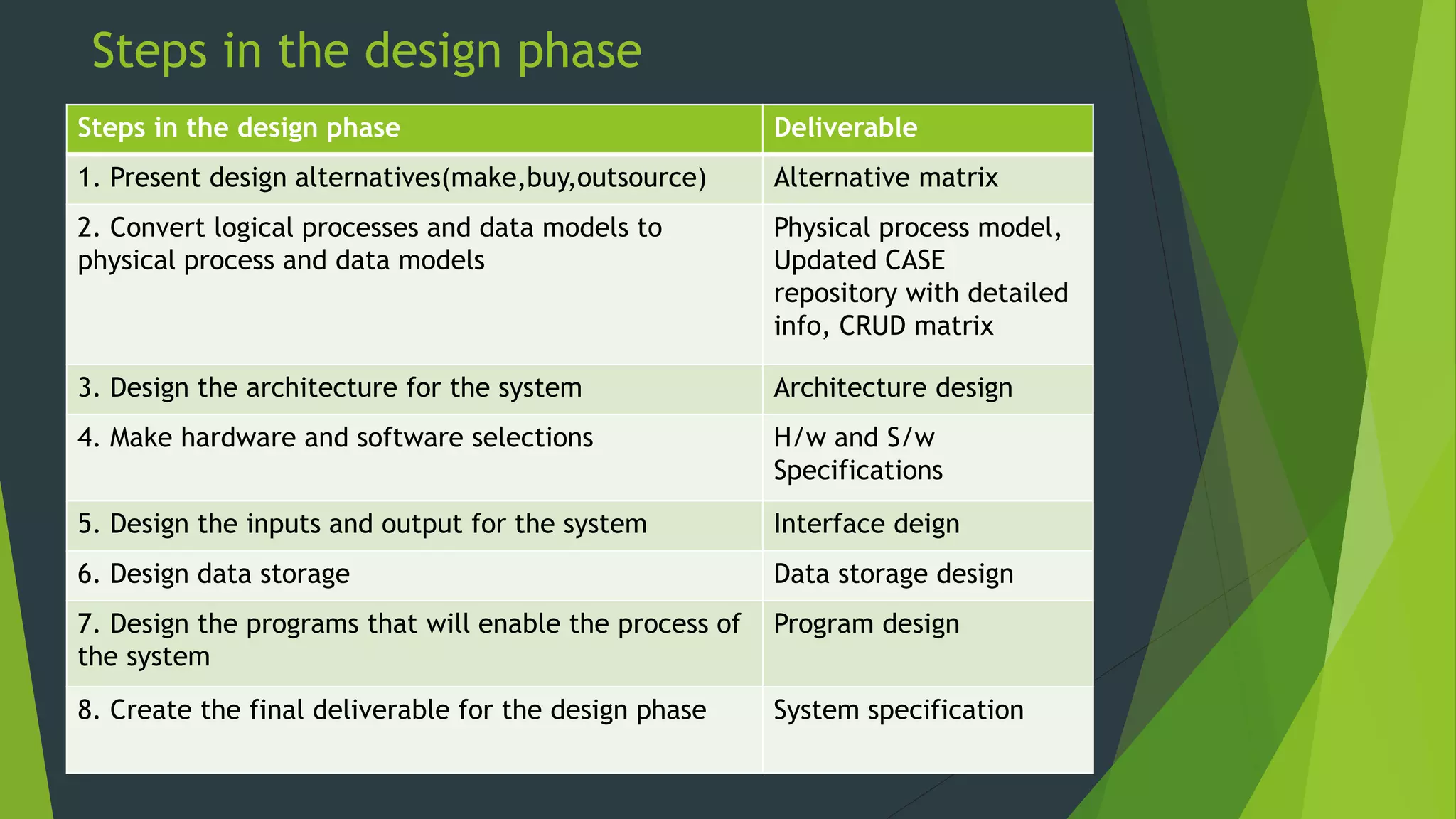
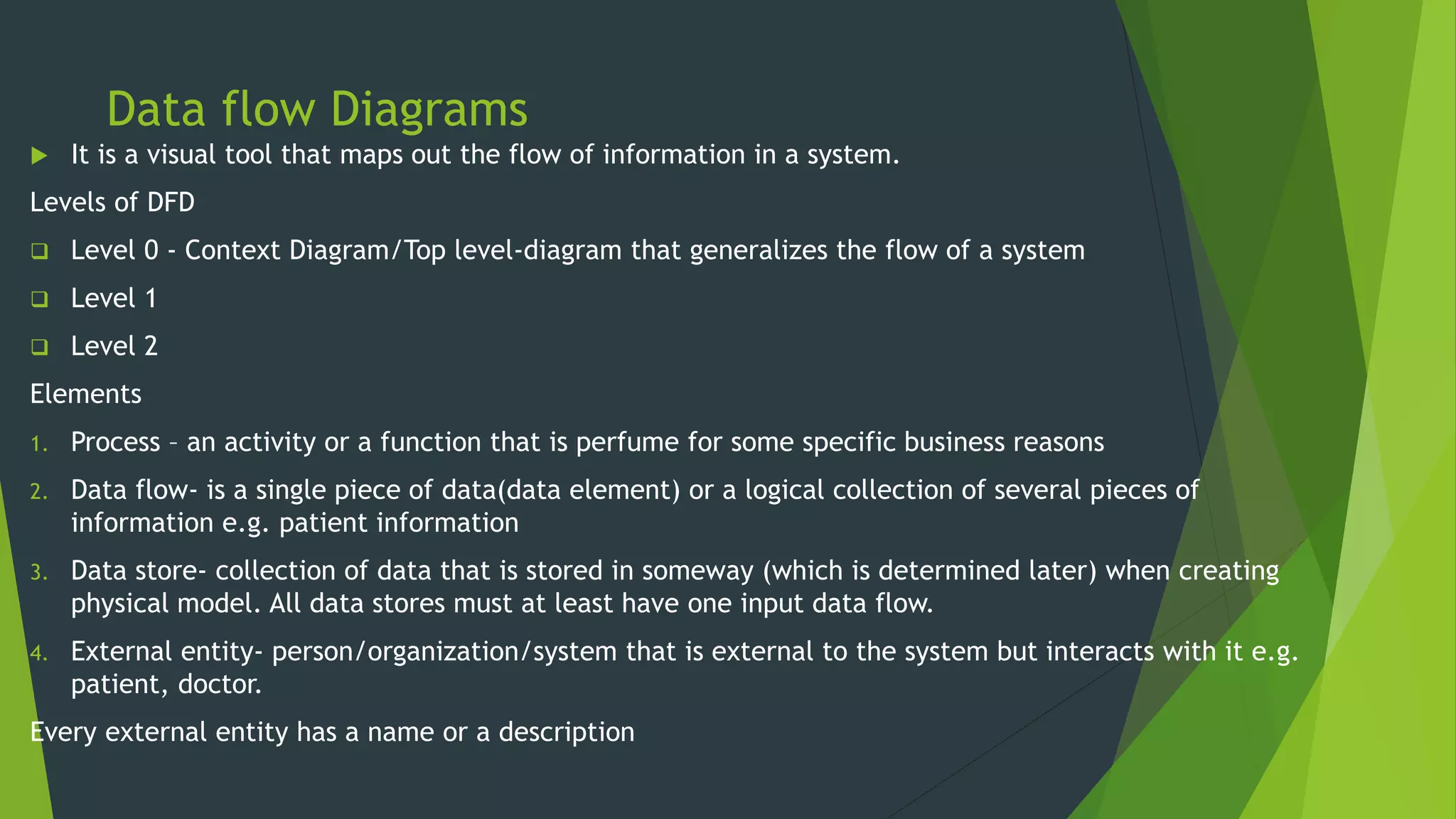
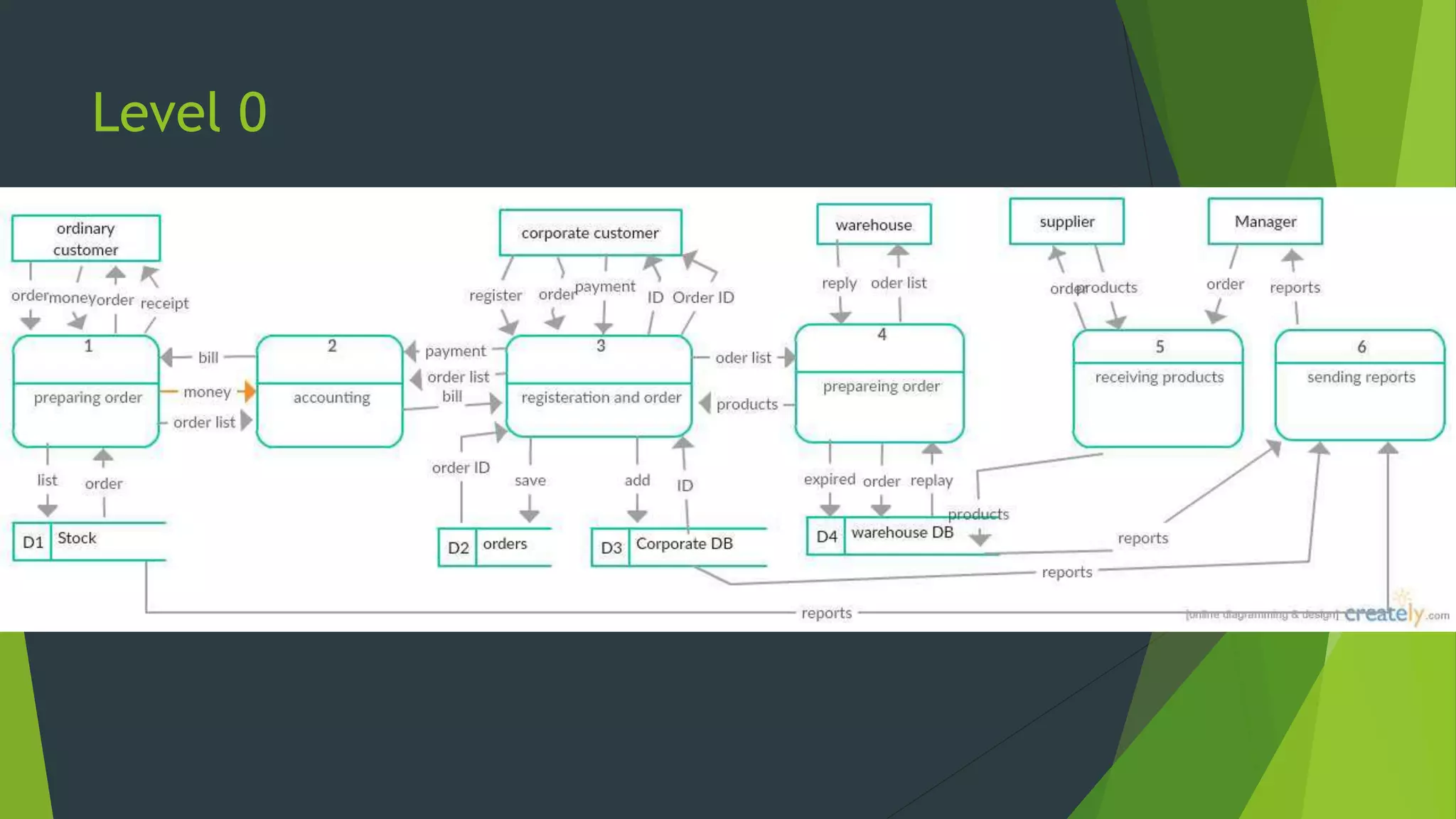
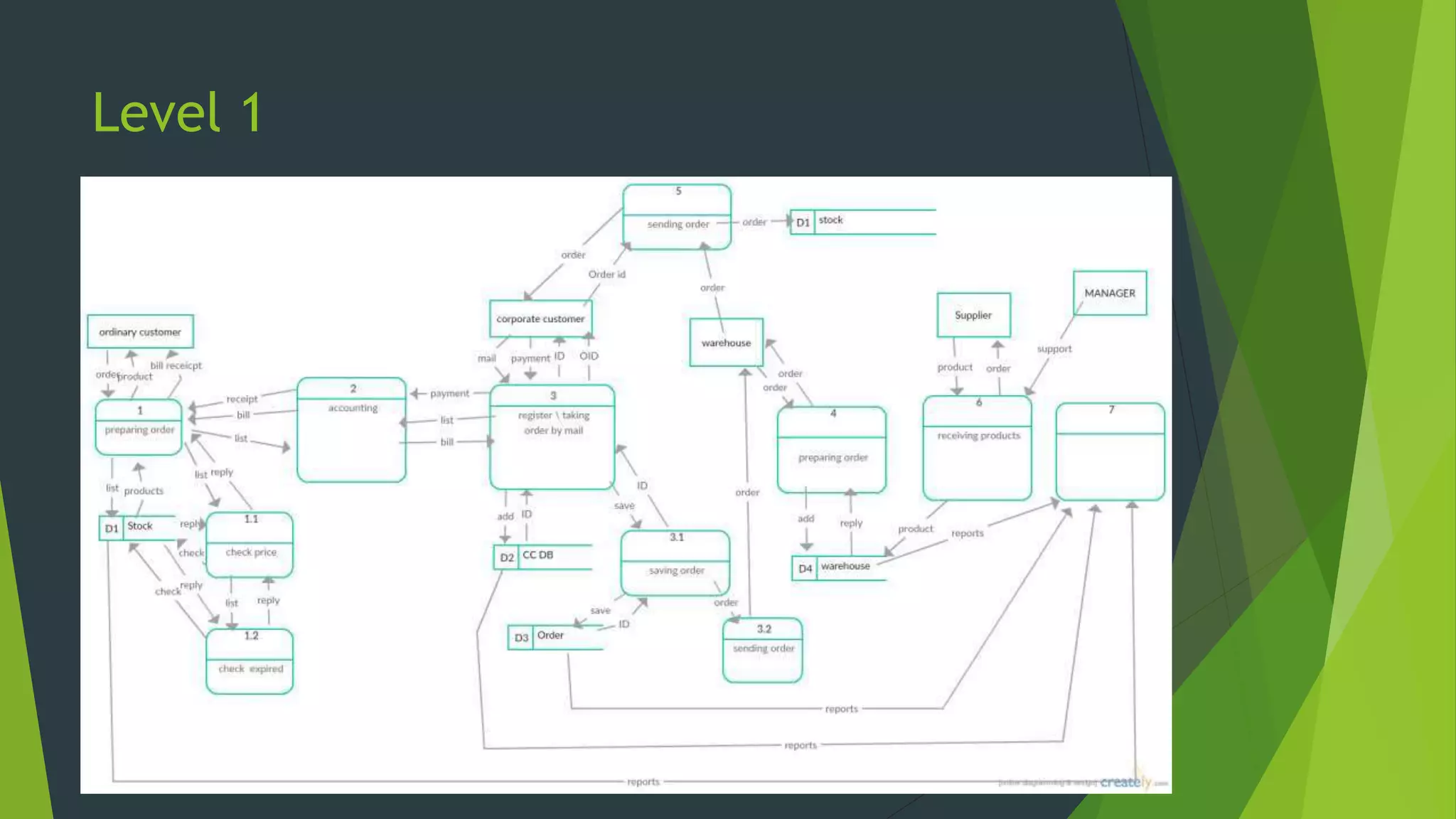
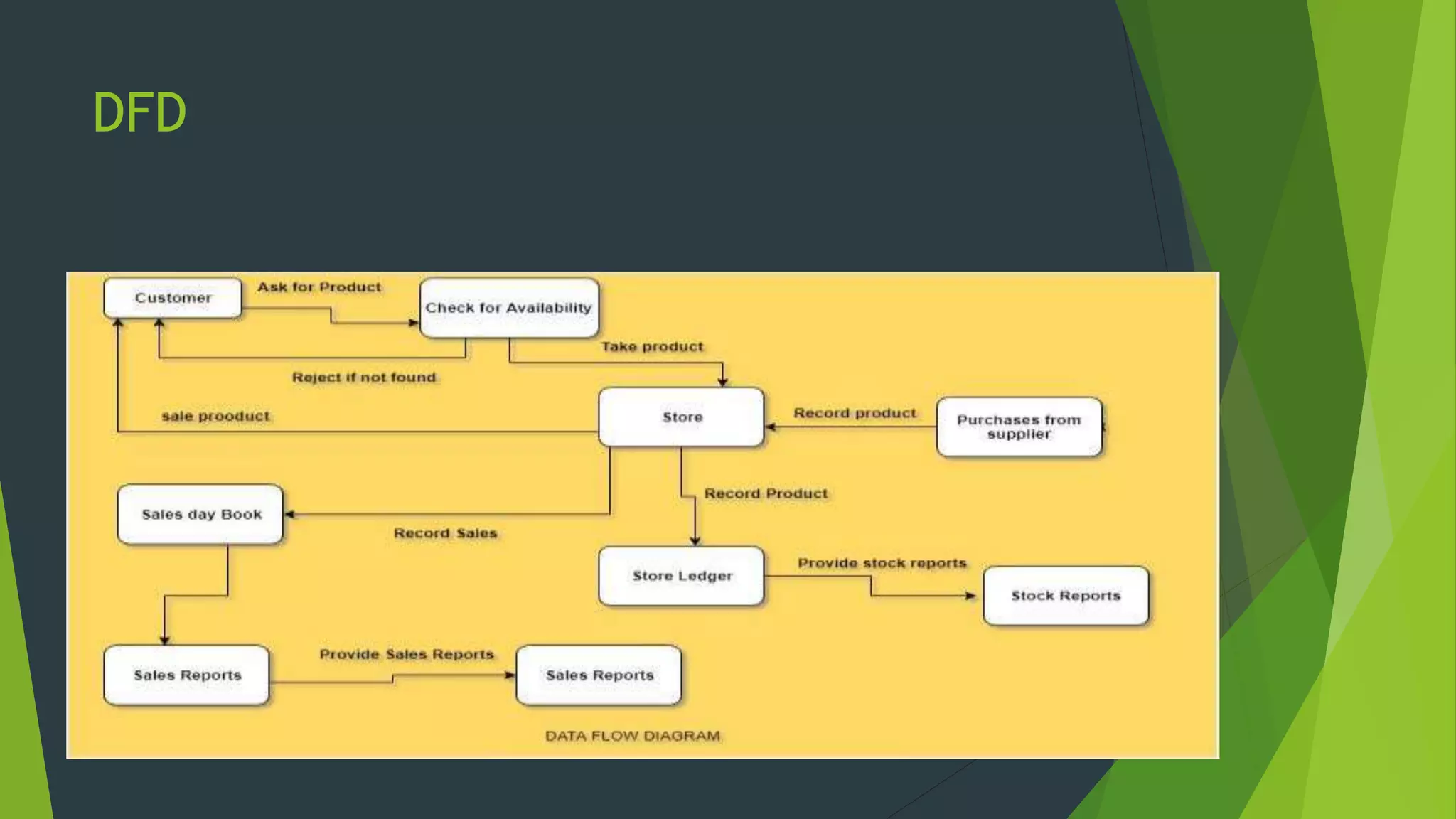
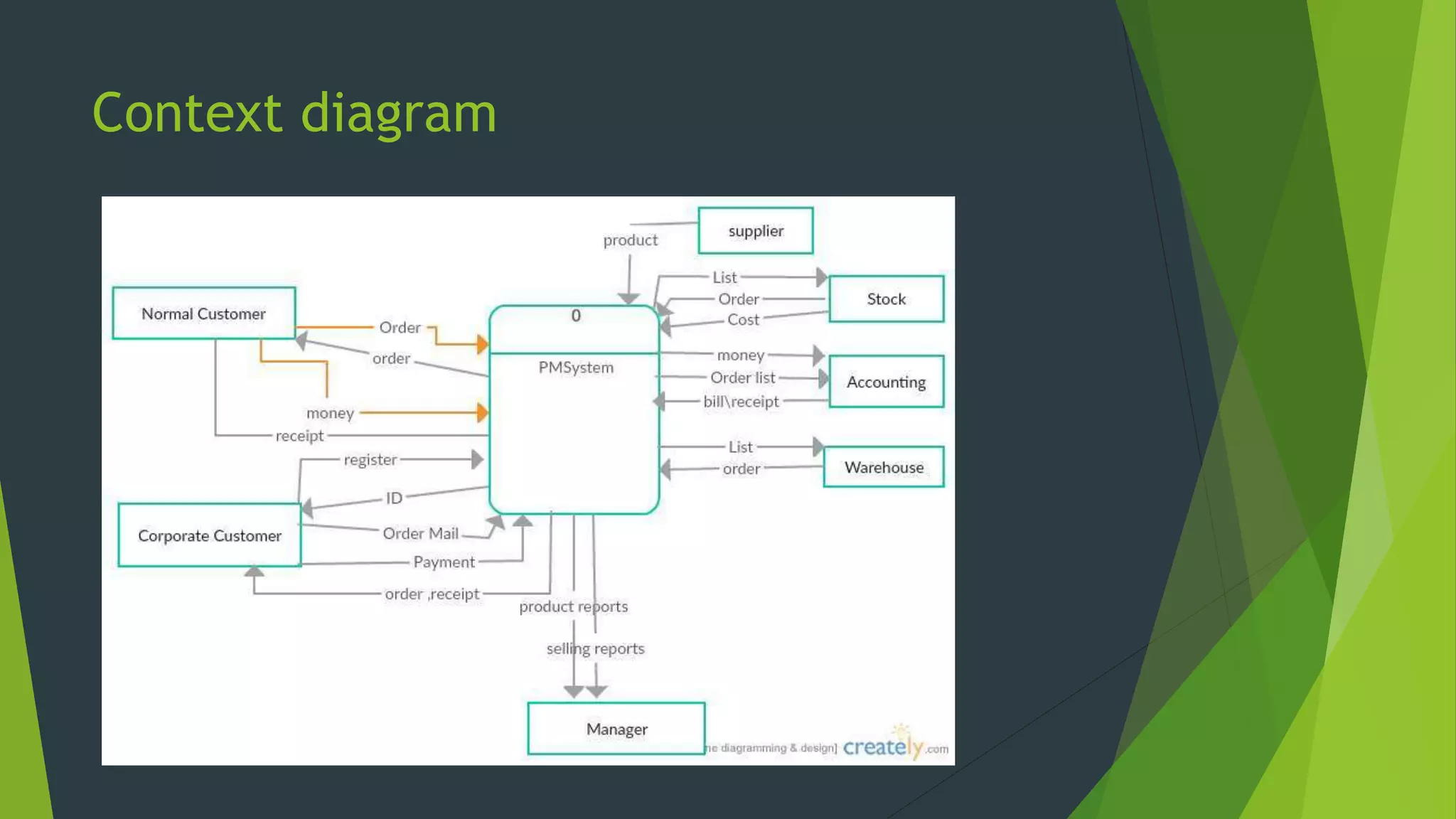
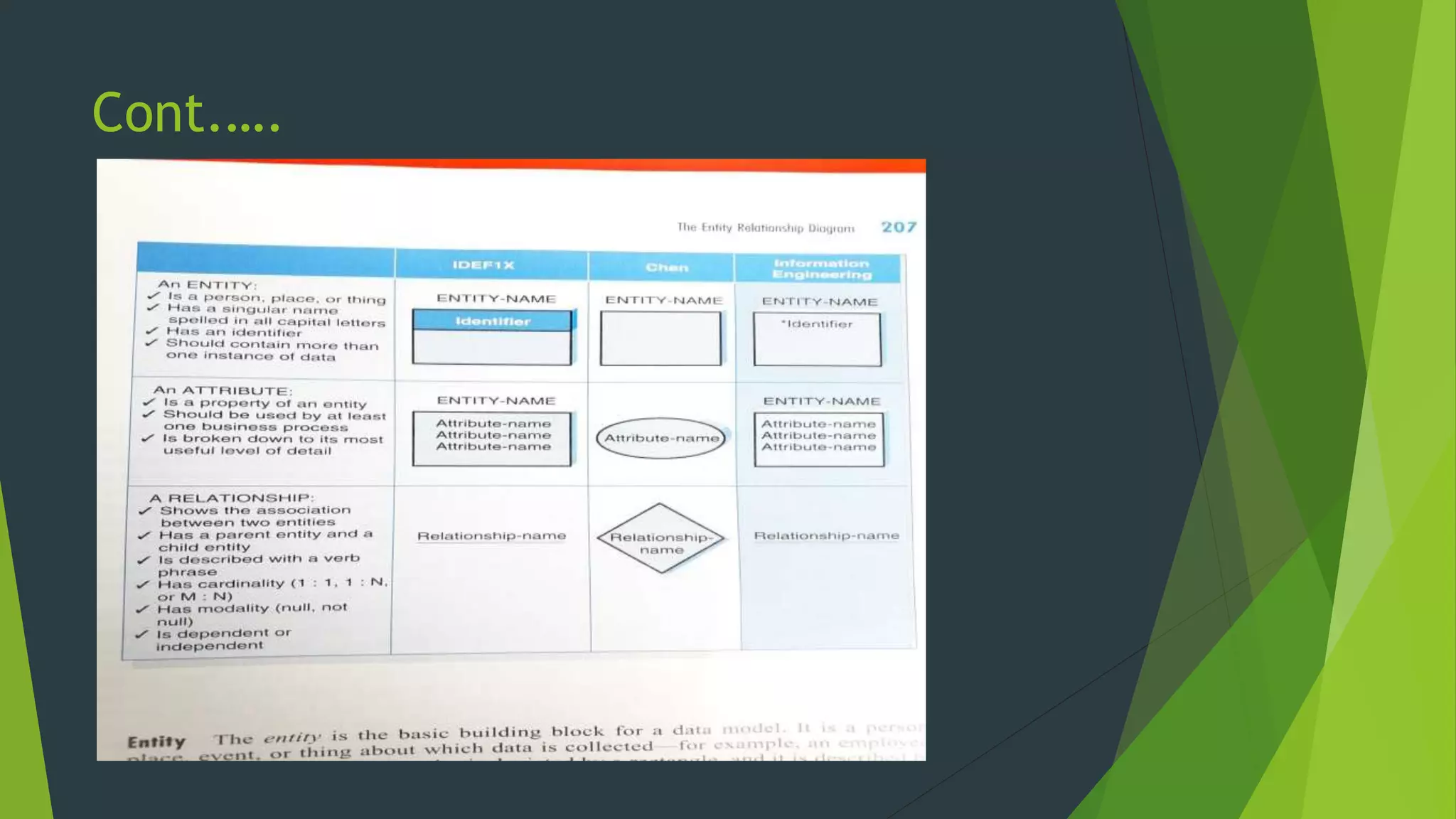
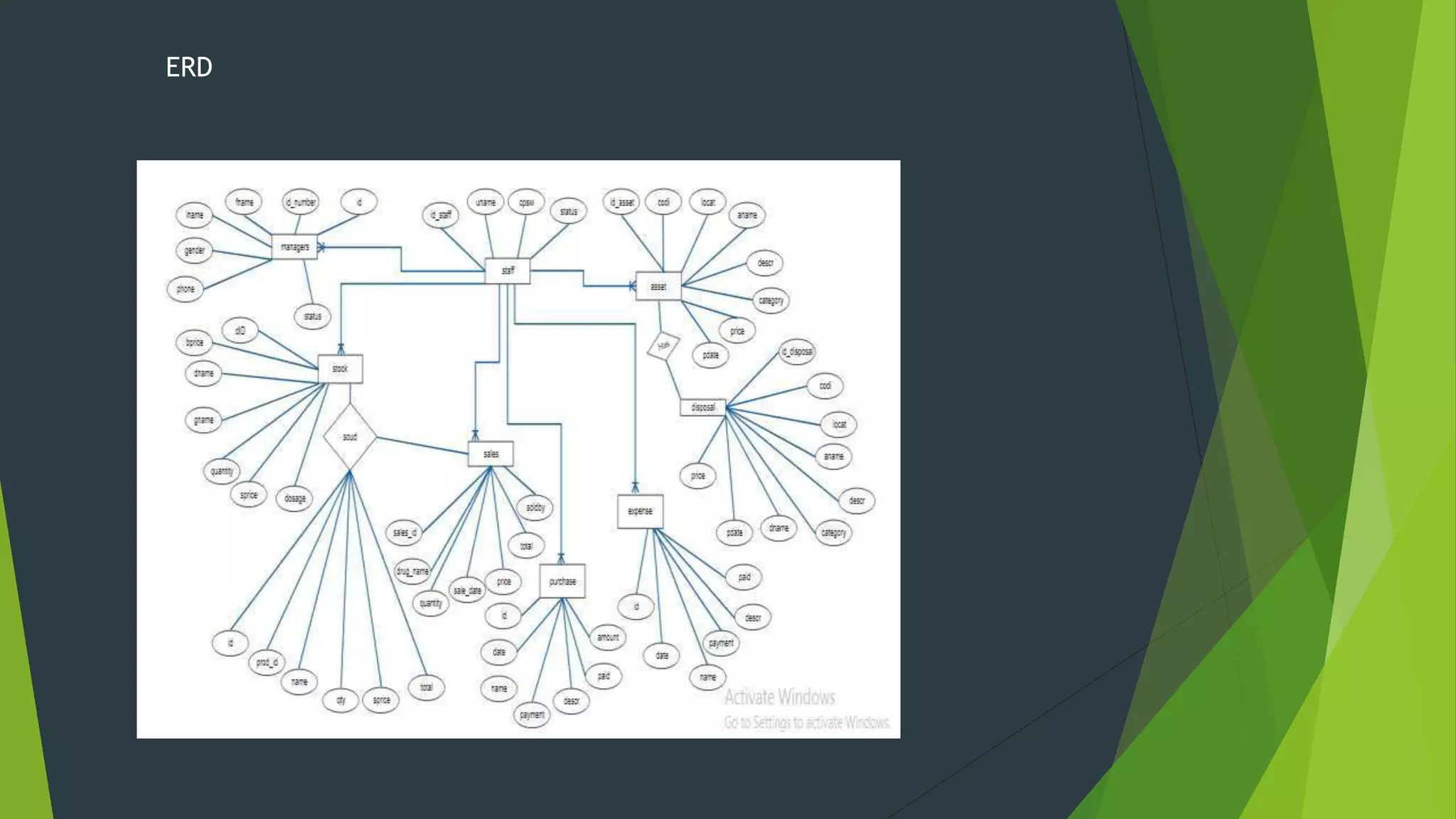
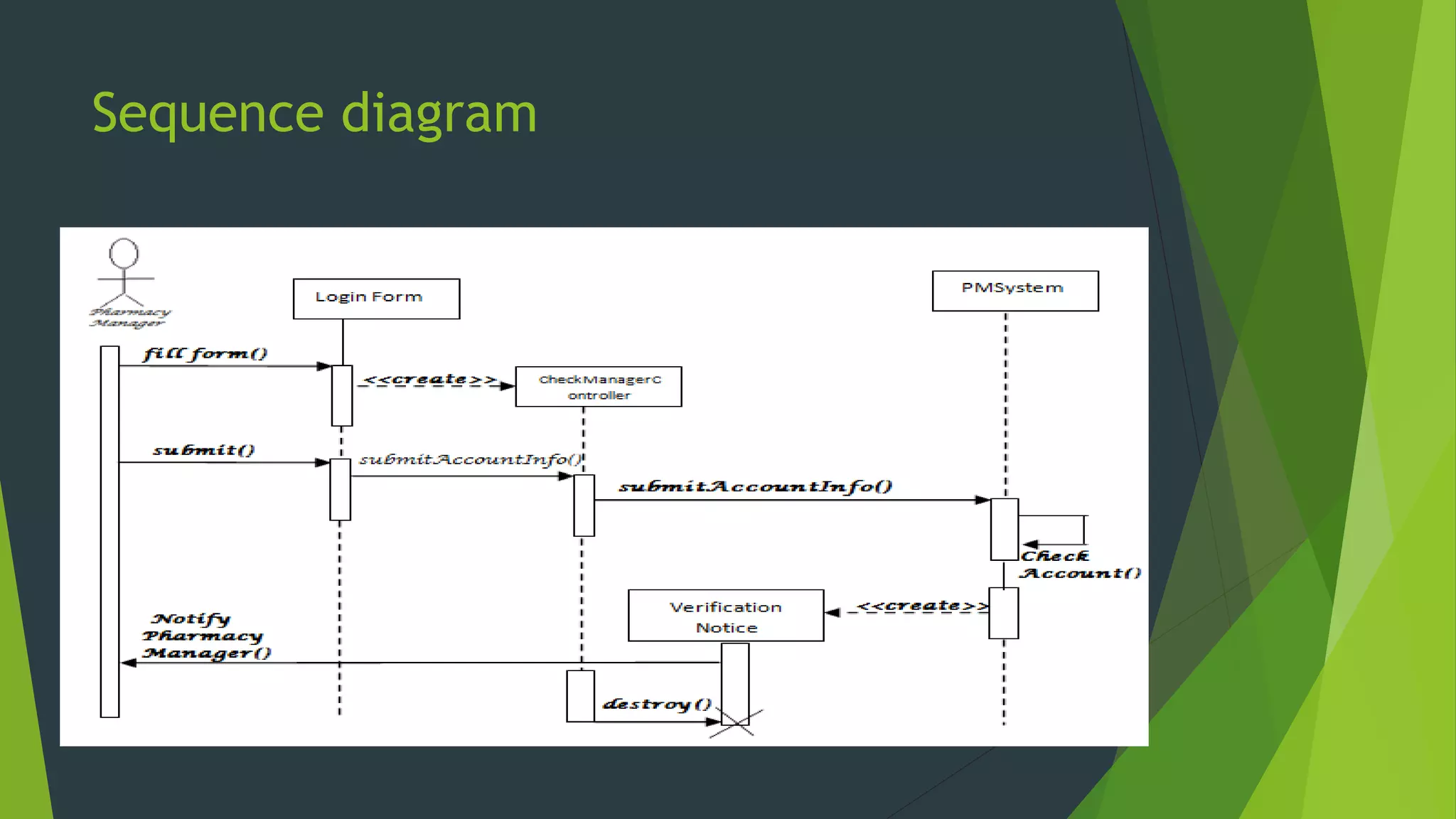
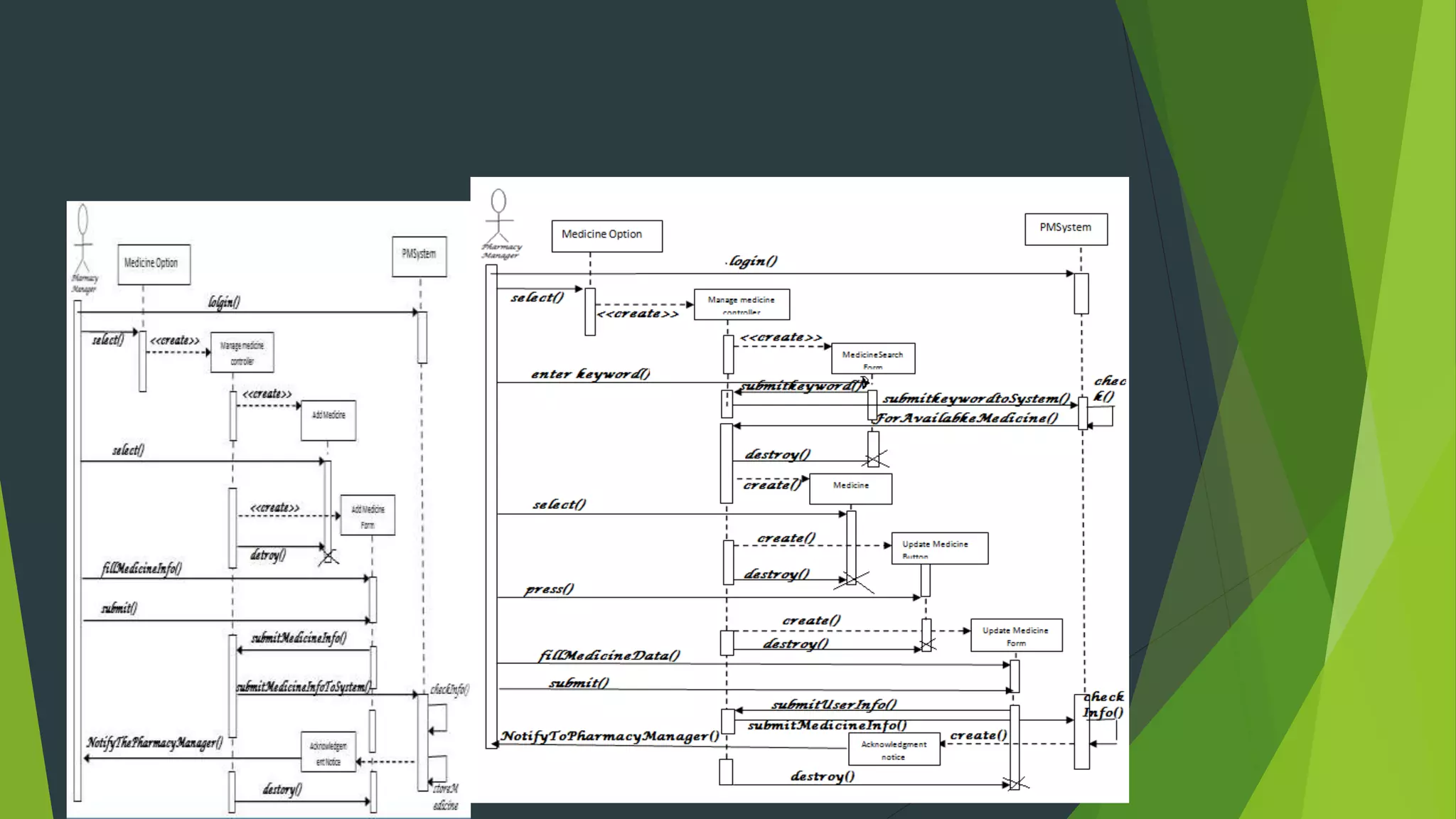
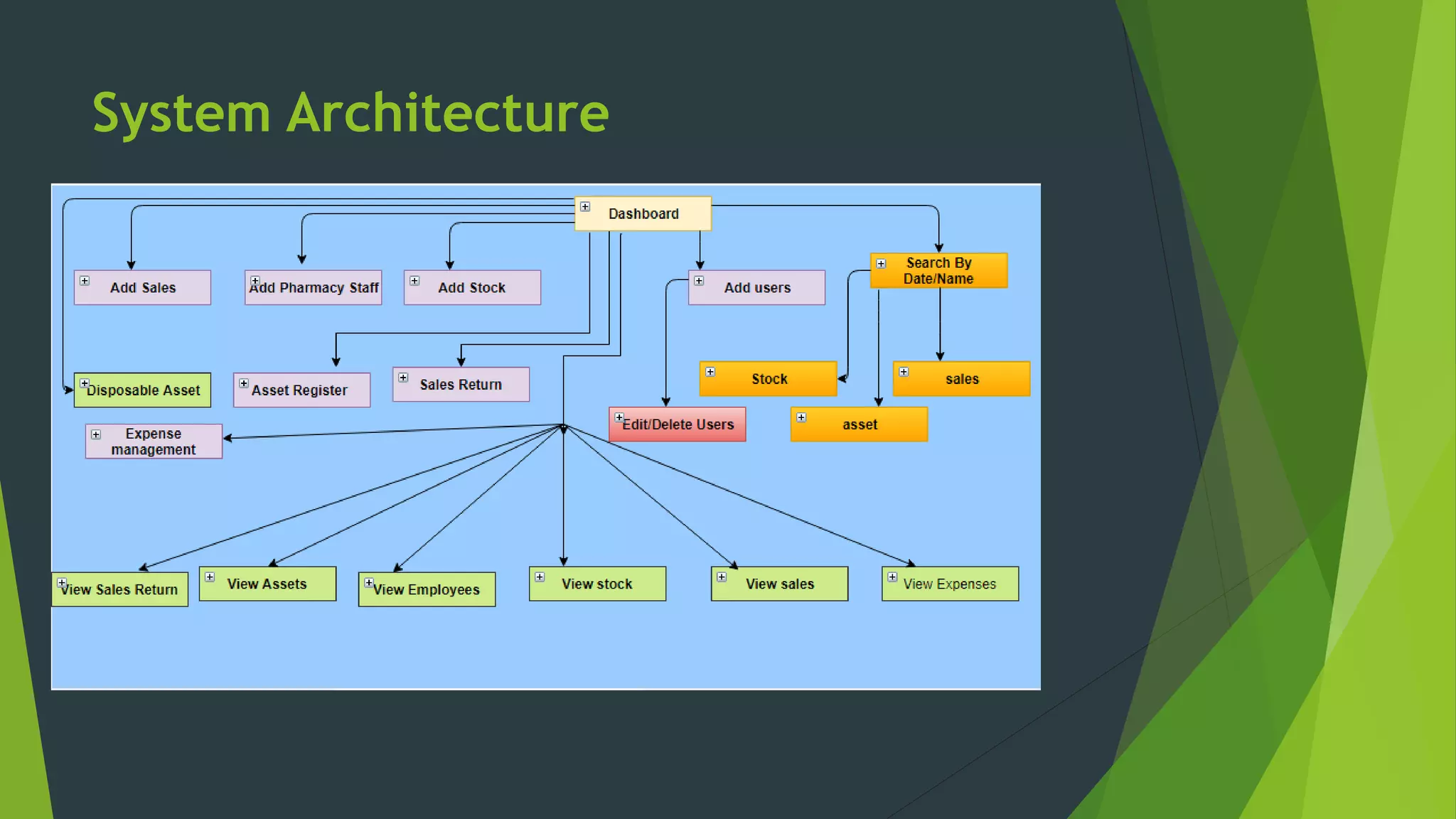
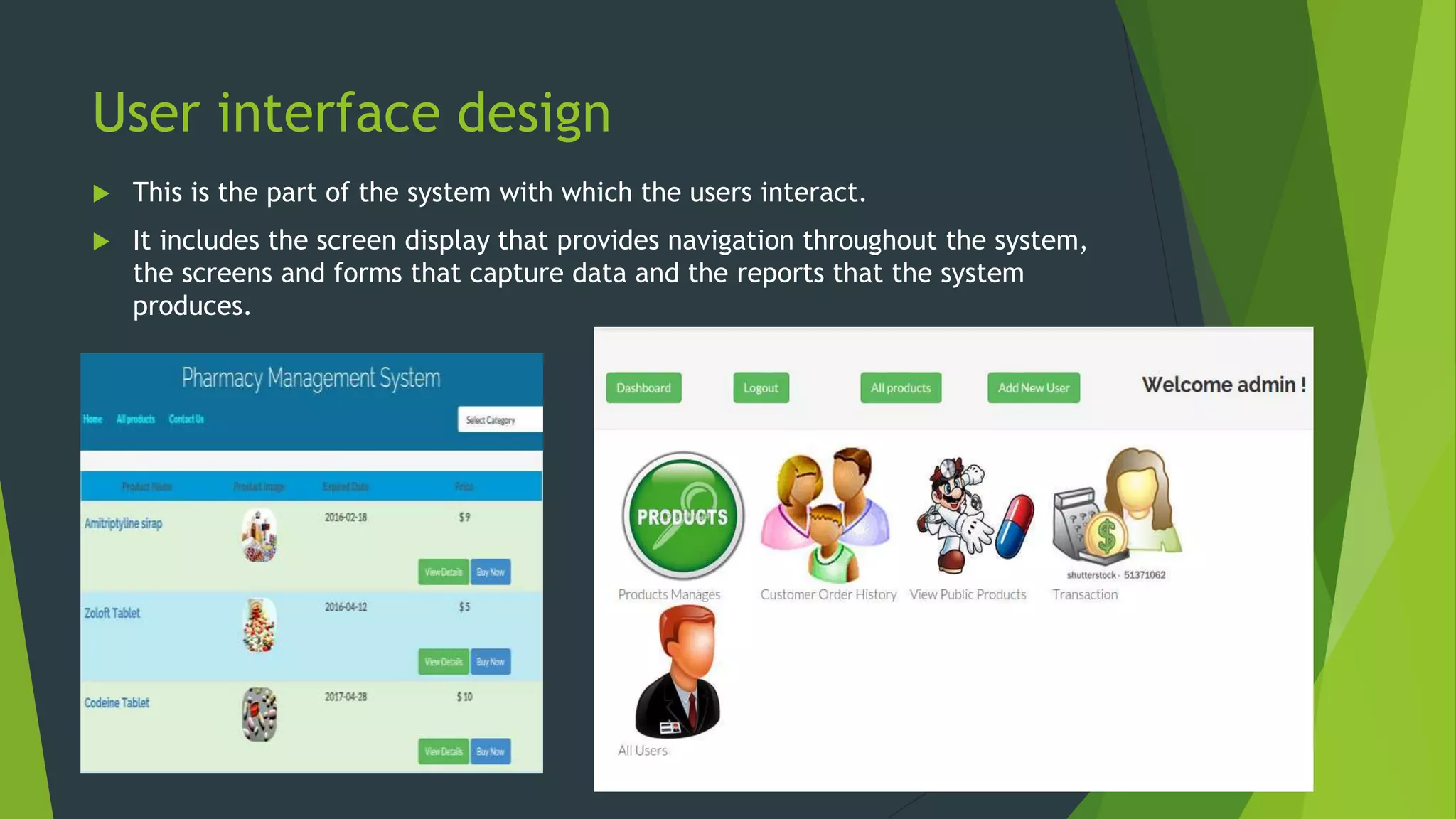
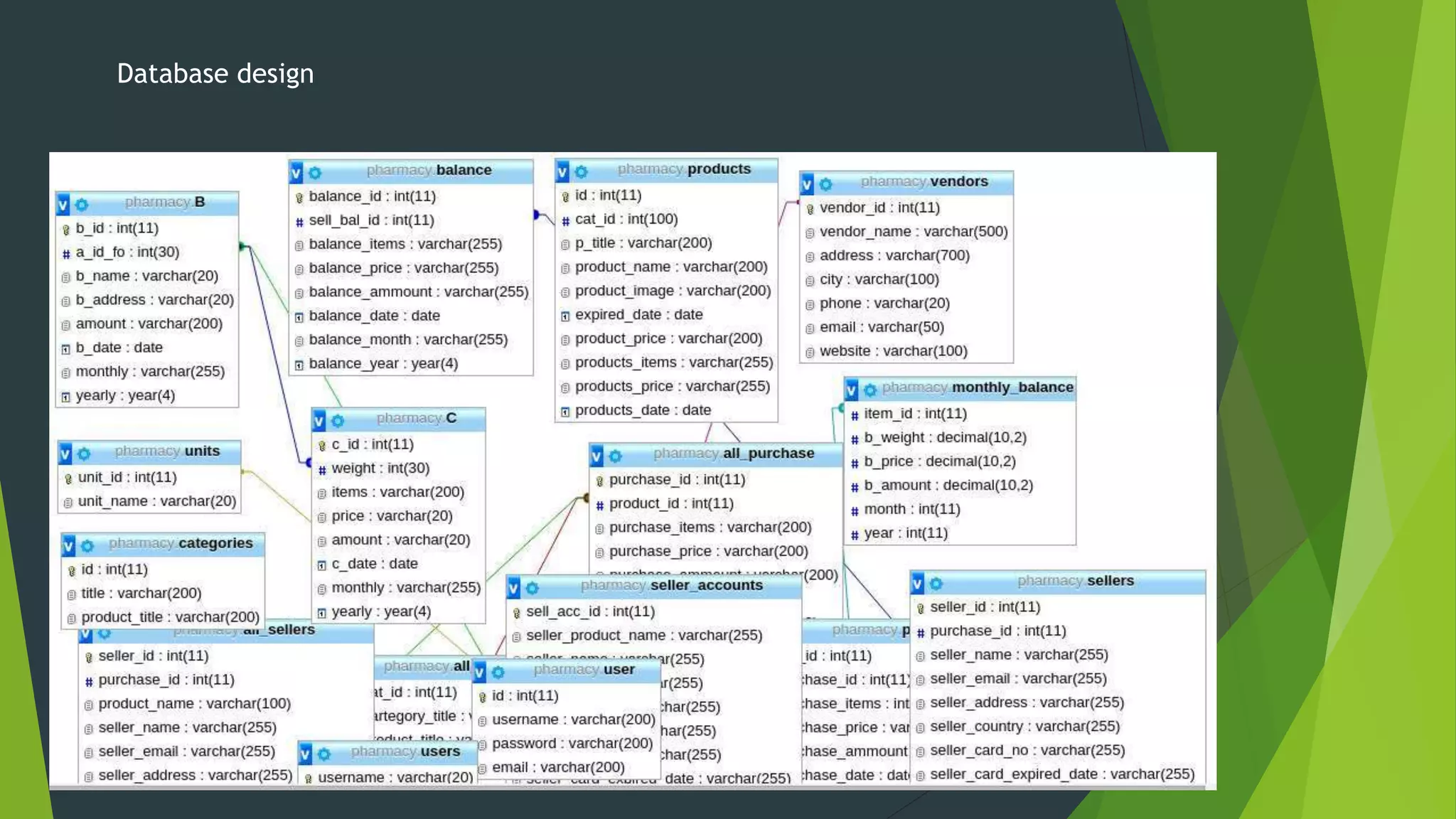
The document discusses the design phase of the system development life cycle. It describes the objectives and steps of the design phase, which include presenting design alternatives, converting logical models to physical models, designing the system architecture, making hardware and software selections, and designing inputs, outputs, data storage, and programs. Common design strategies like custom development, packaged systems, and outsourcing are also covered. The document then explains various system design methods and the stages of system design, including logical, physical, and program design. Finally, it discusses avoiding common design mistakes.