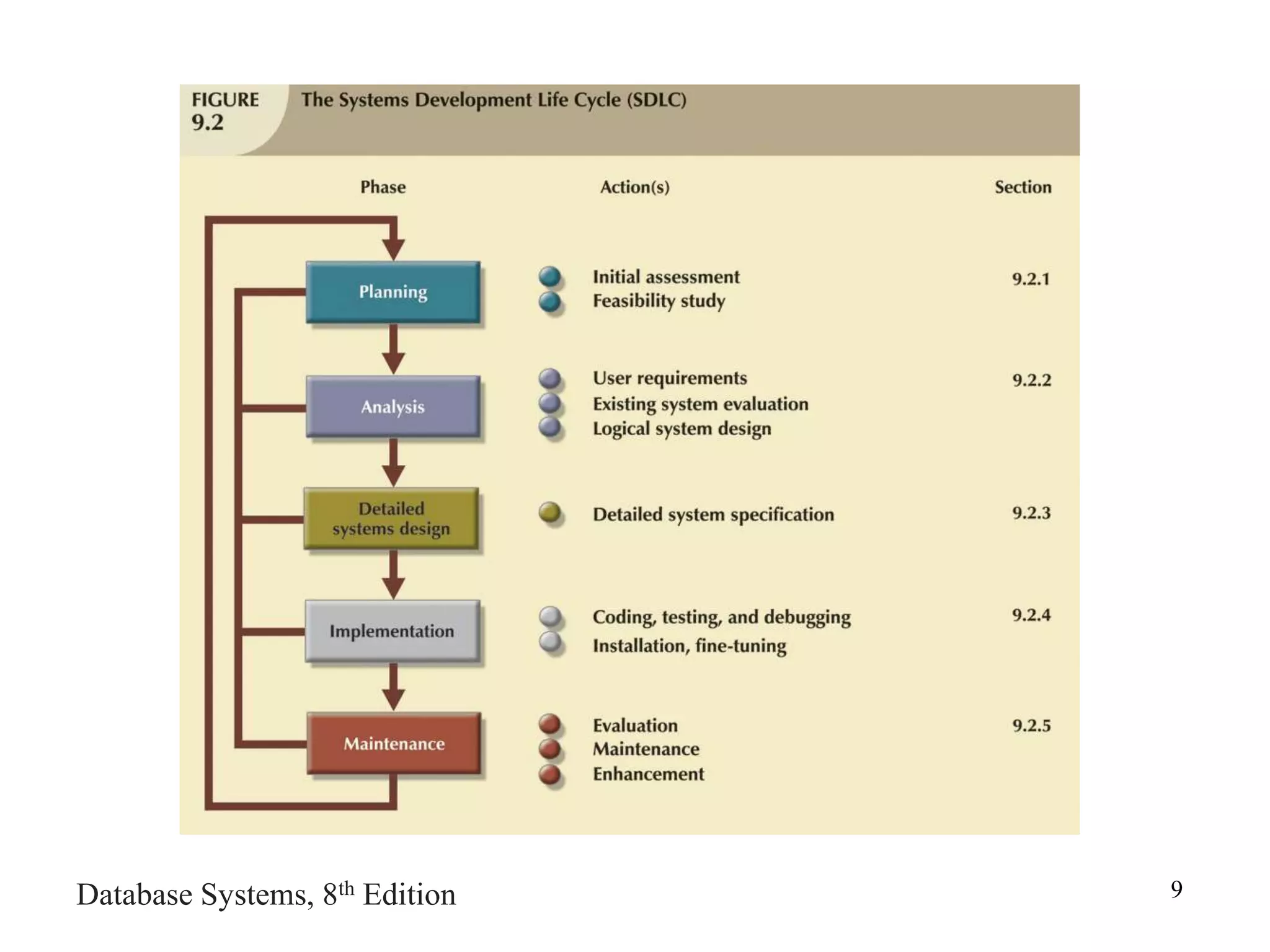
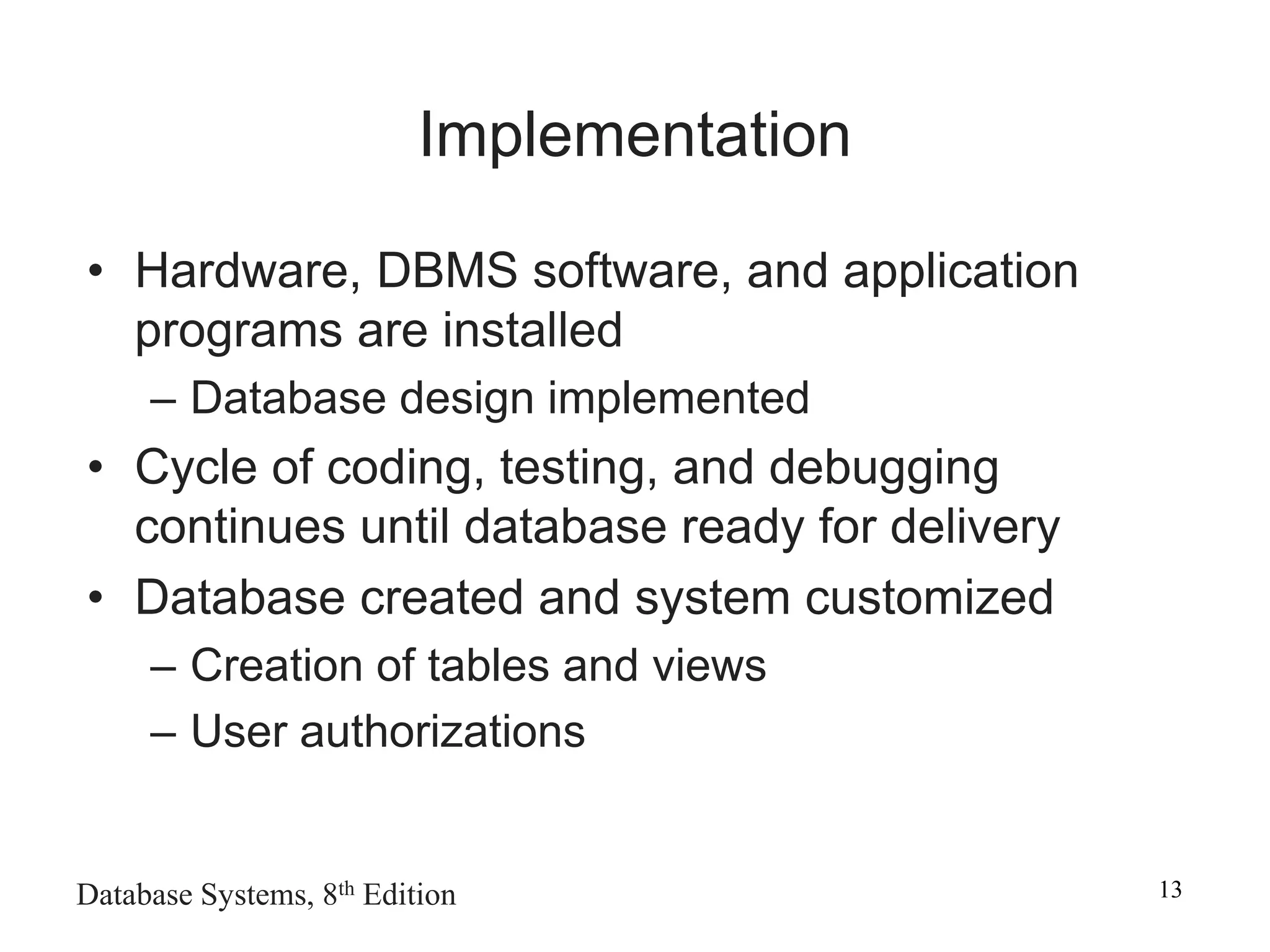
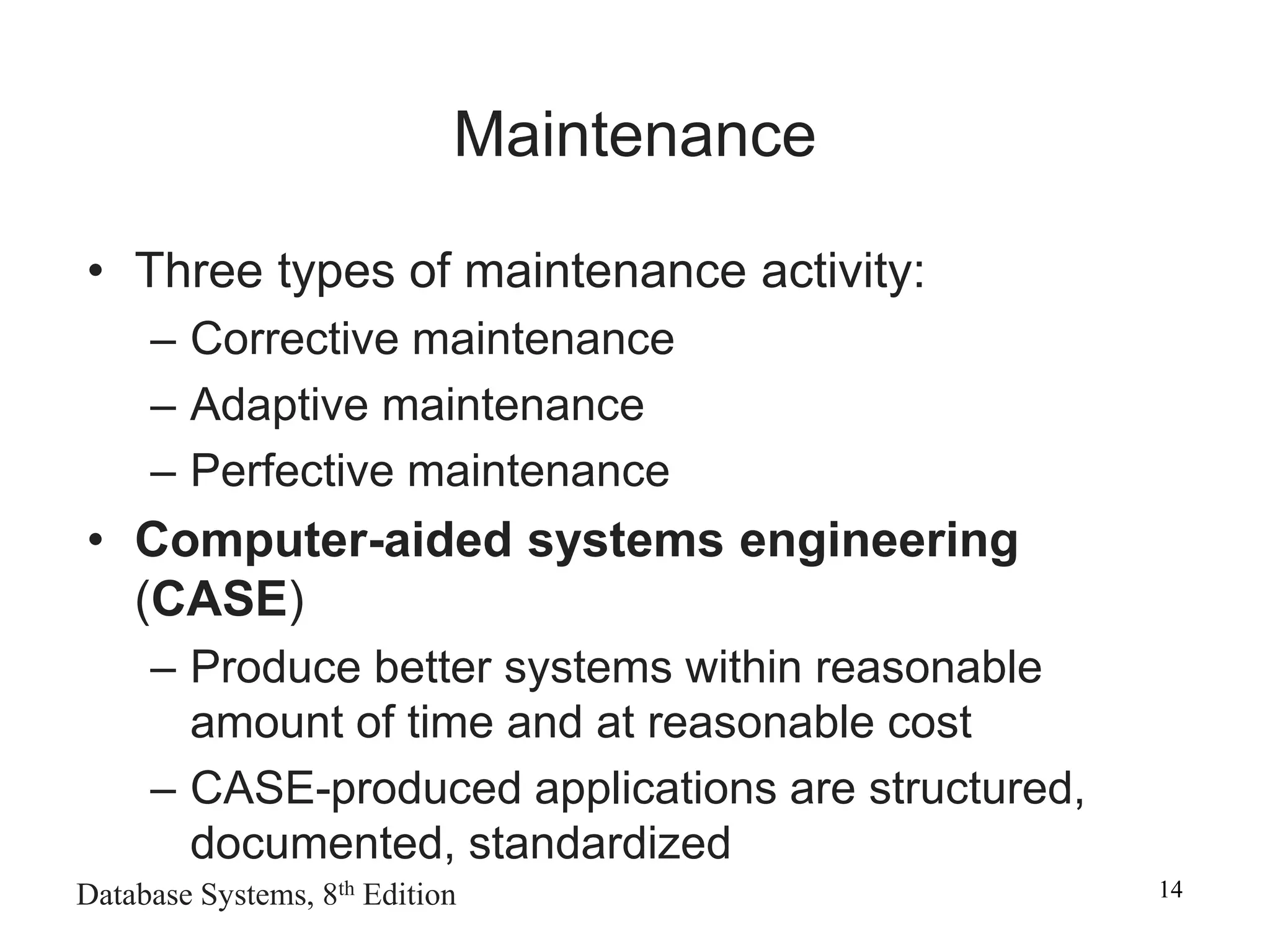
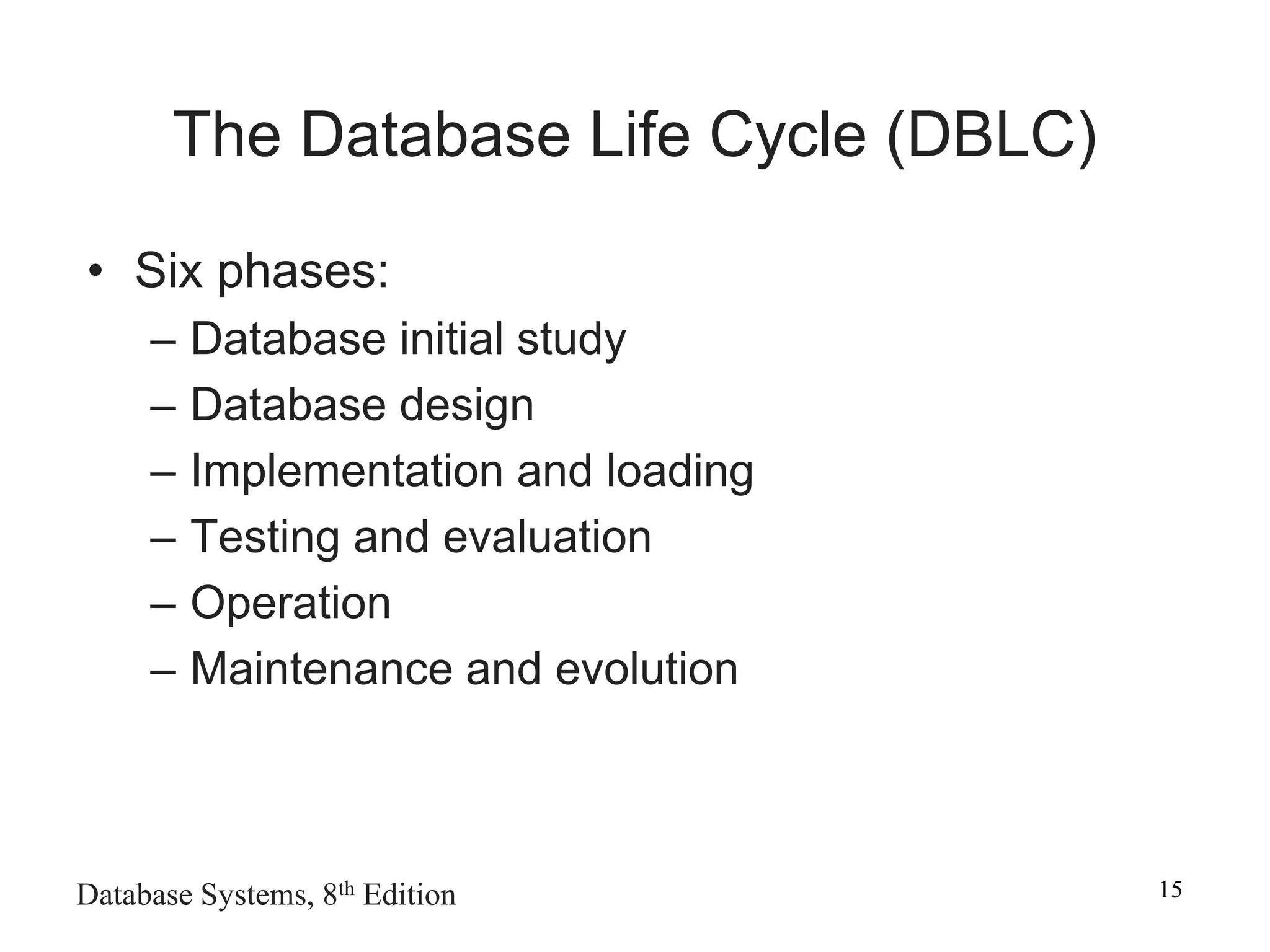
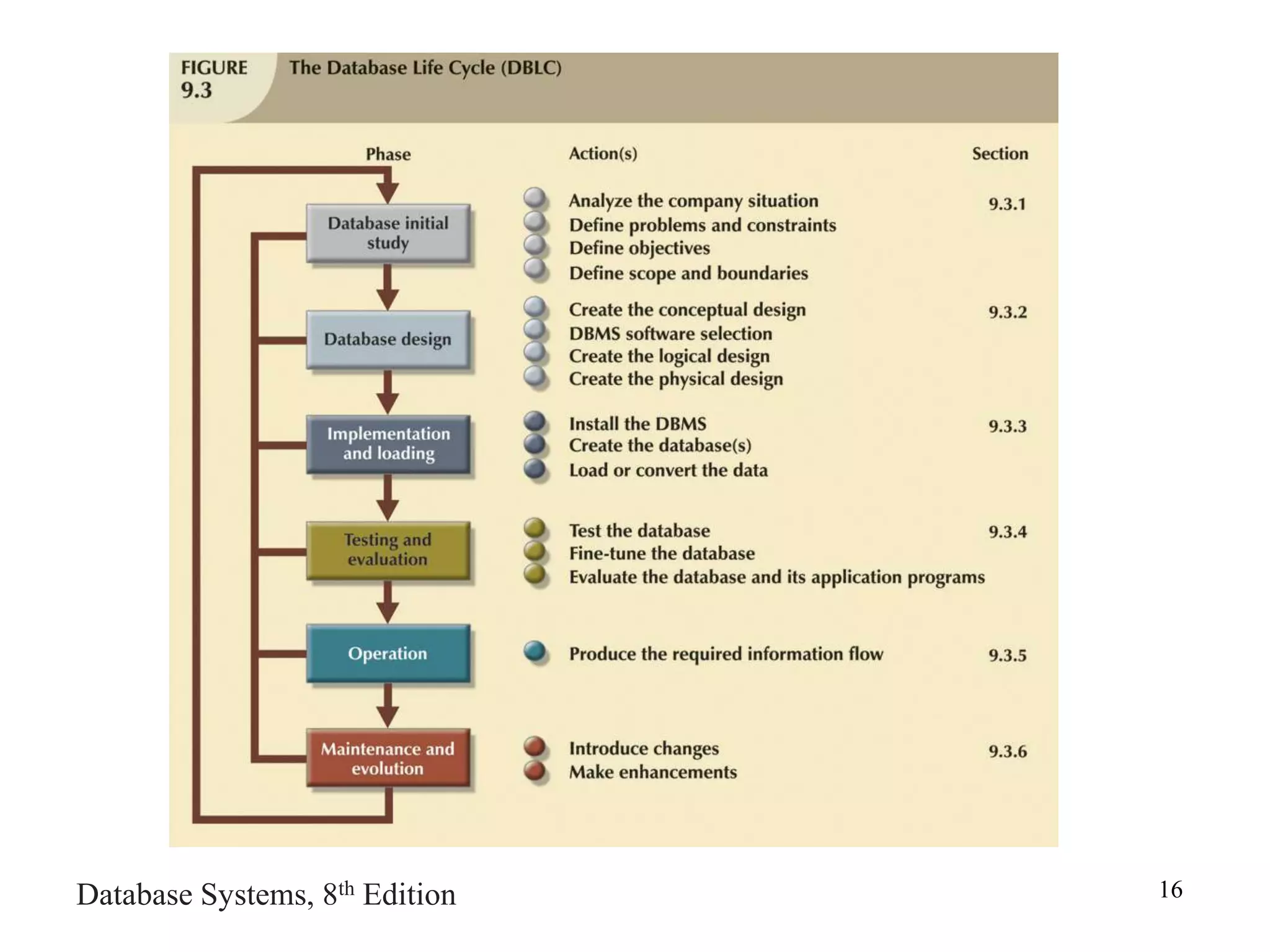
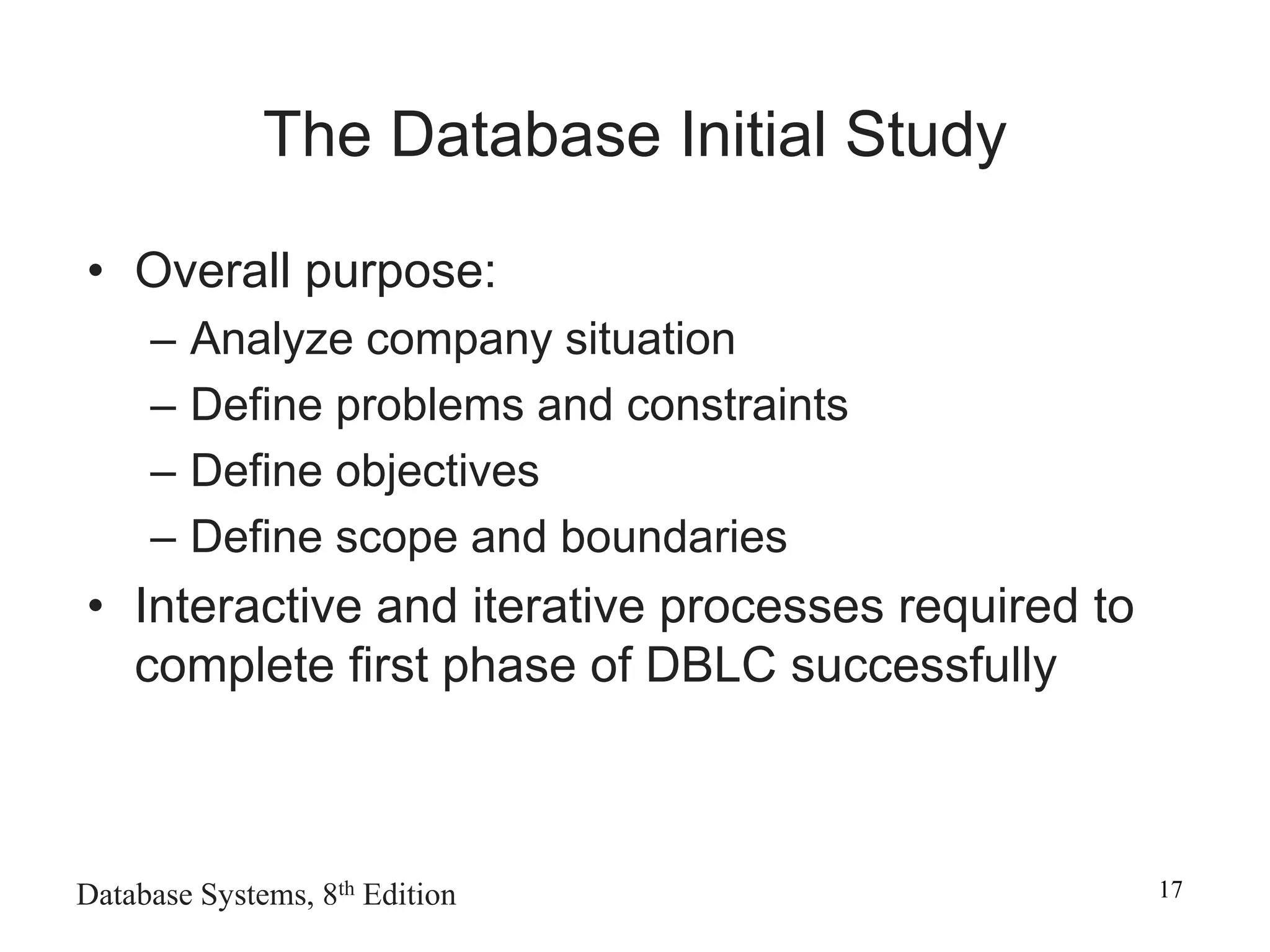
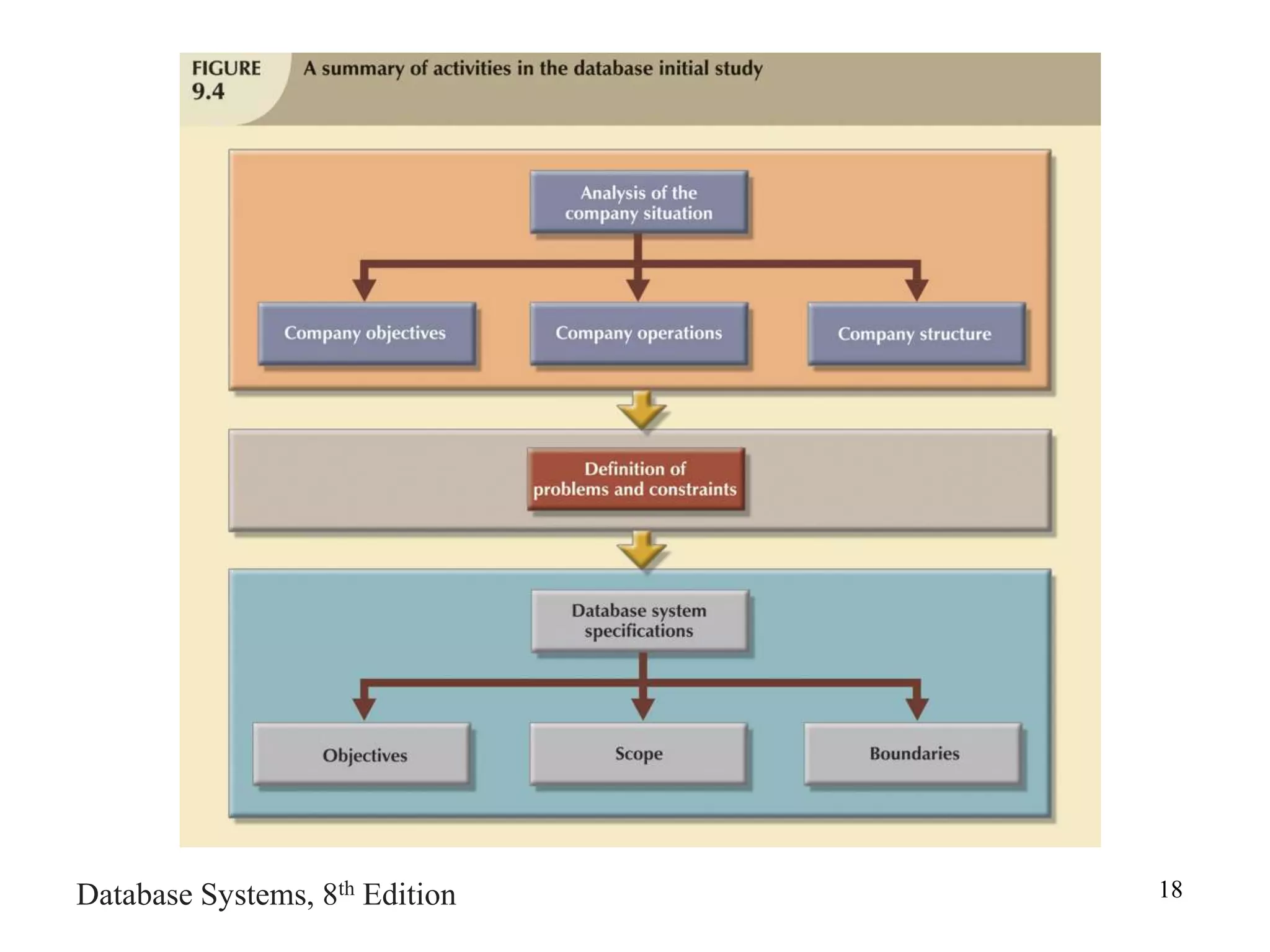
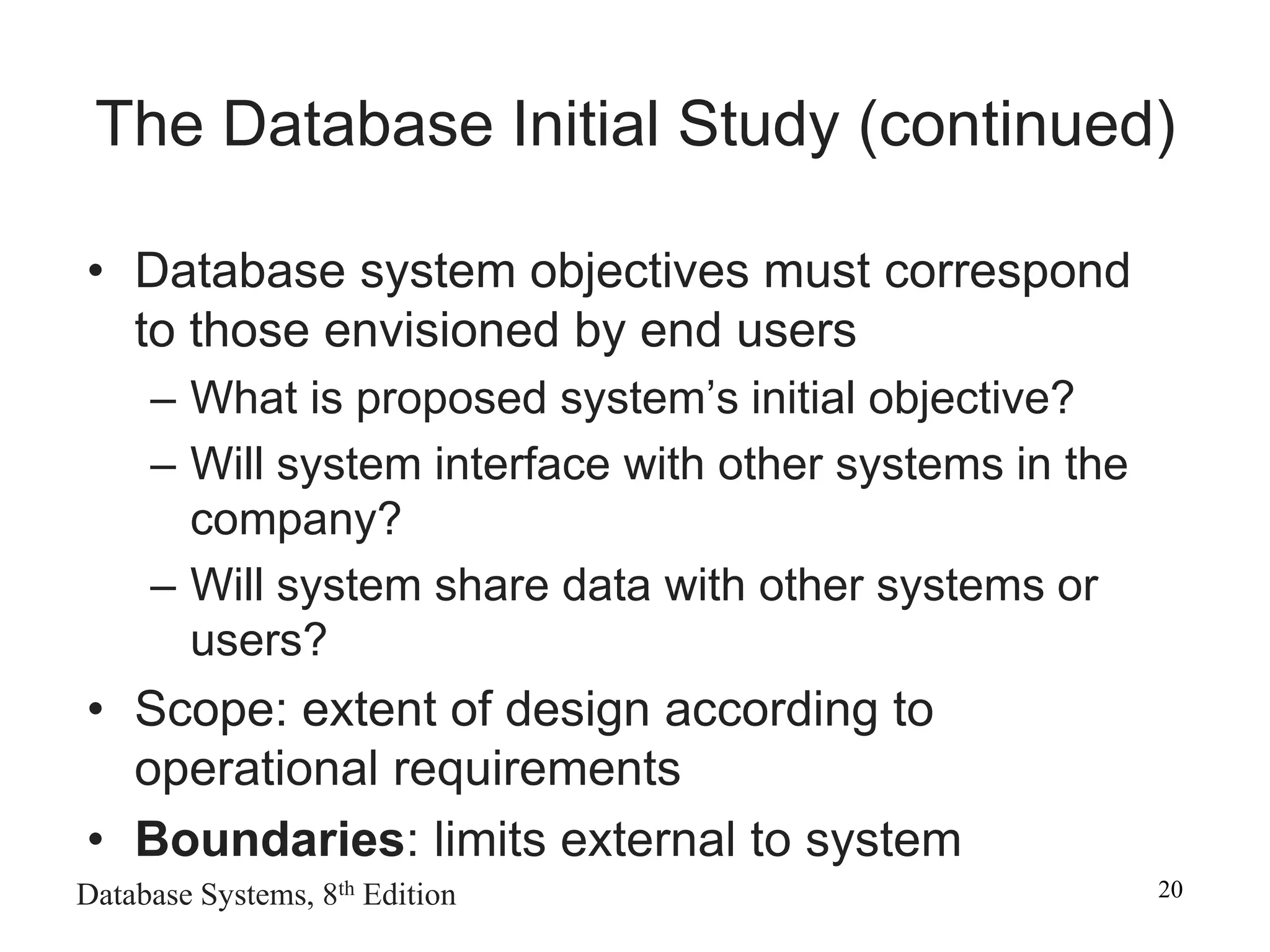
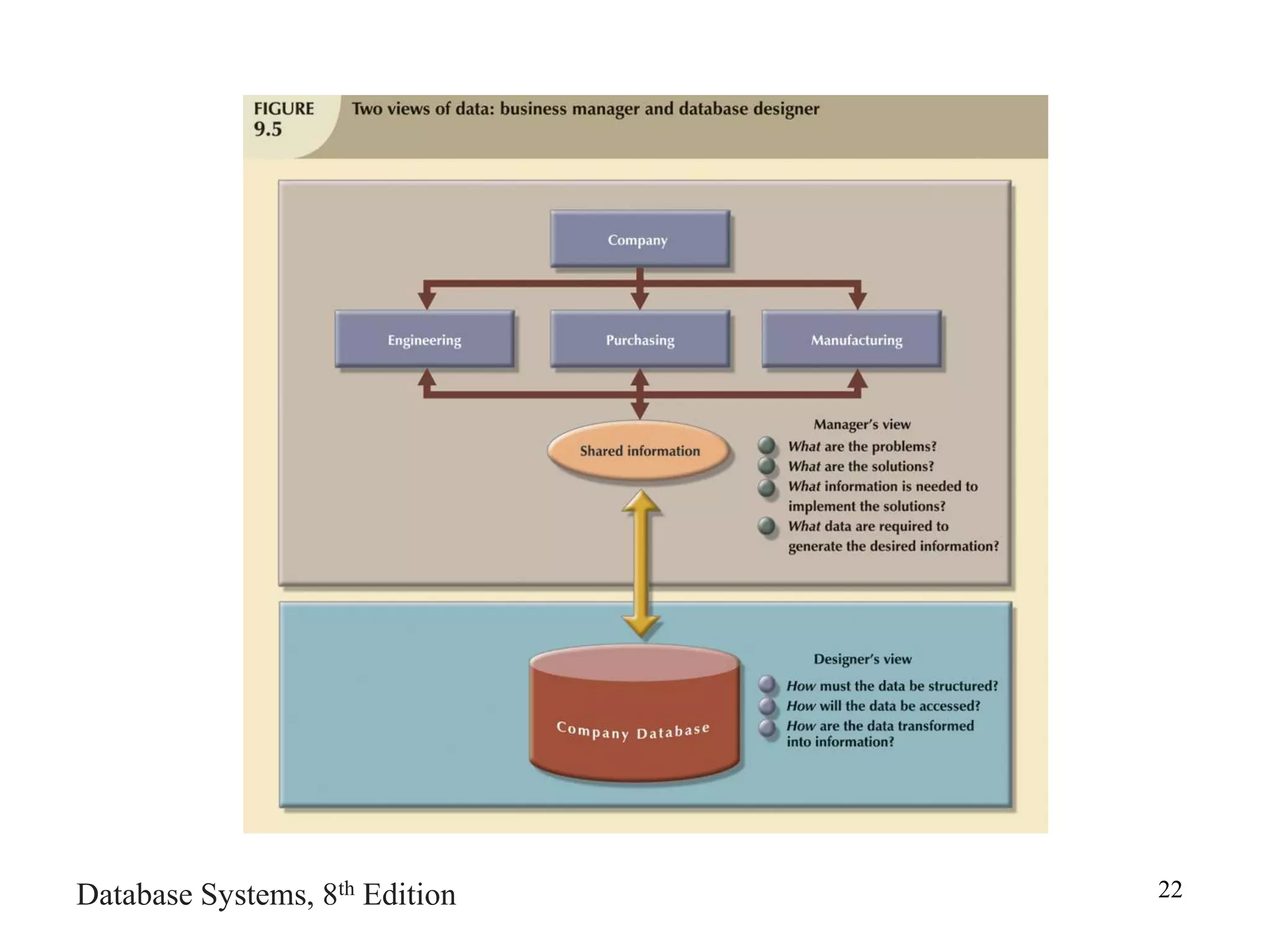
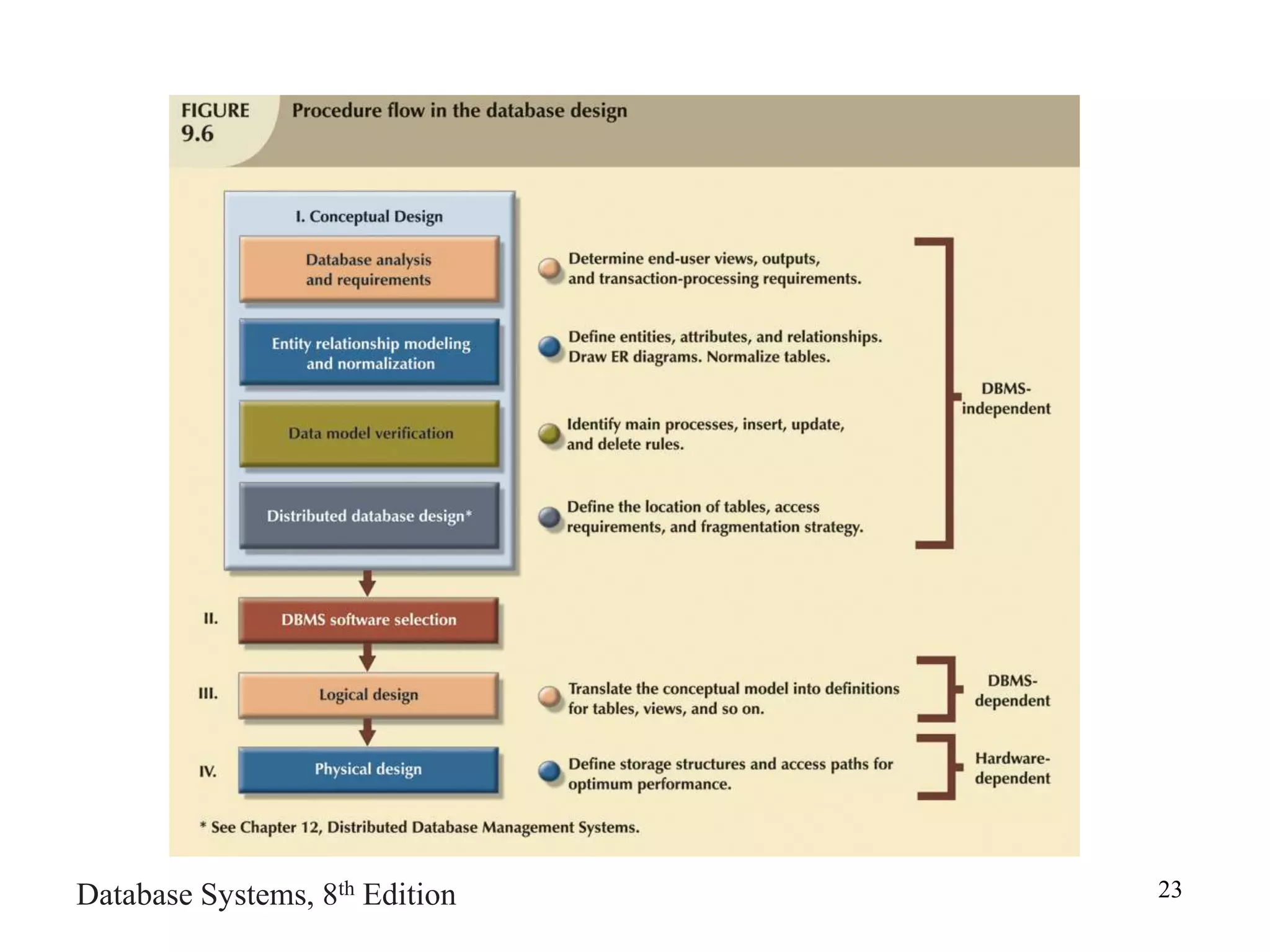
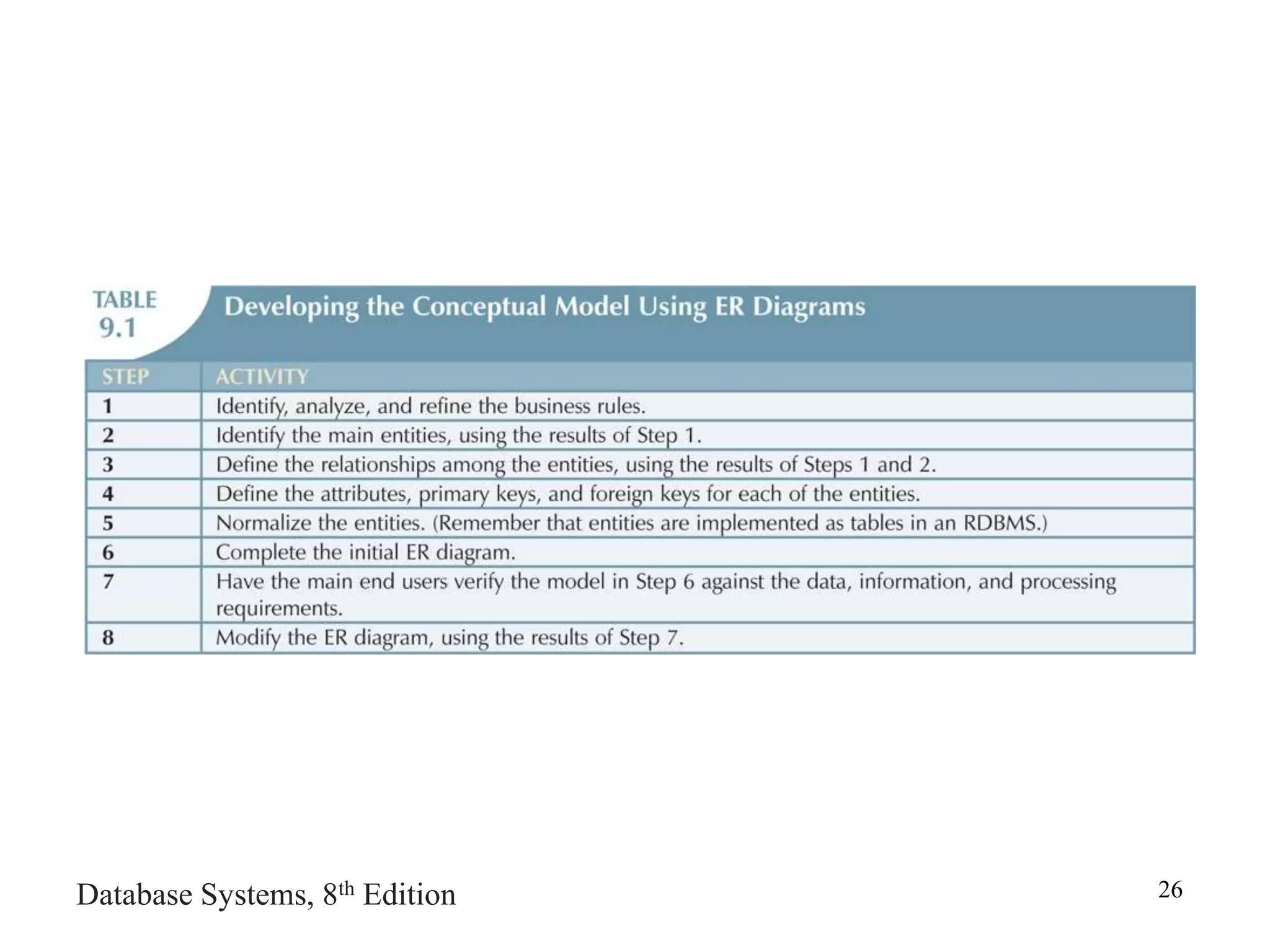
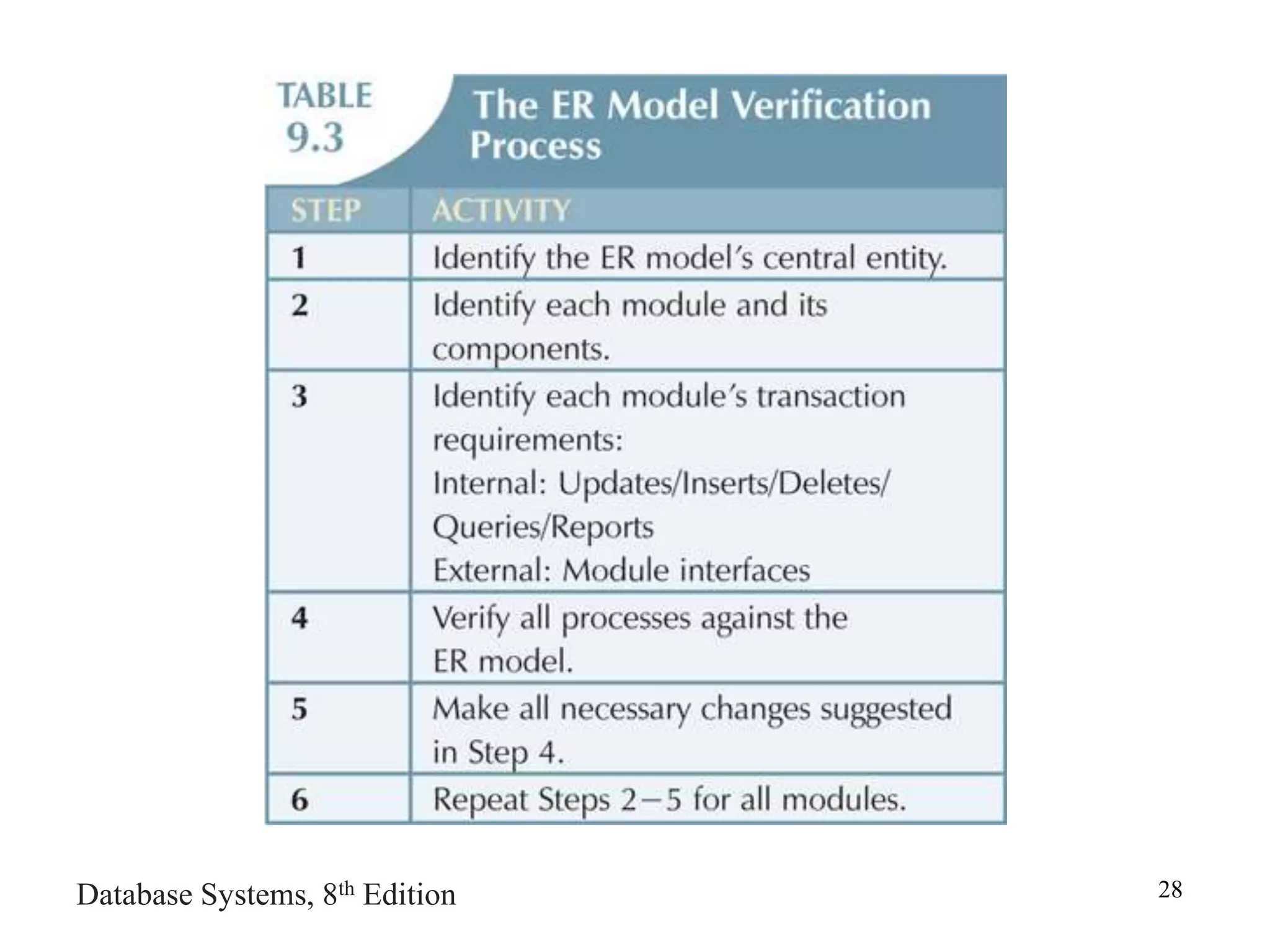
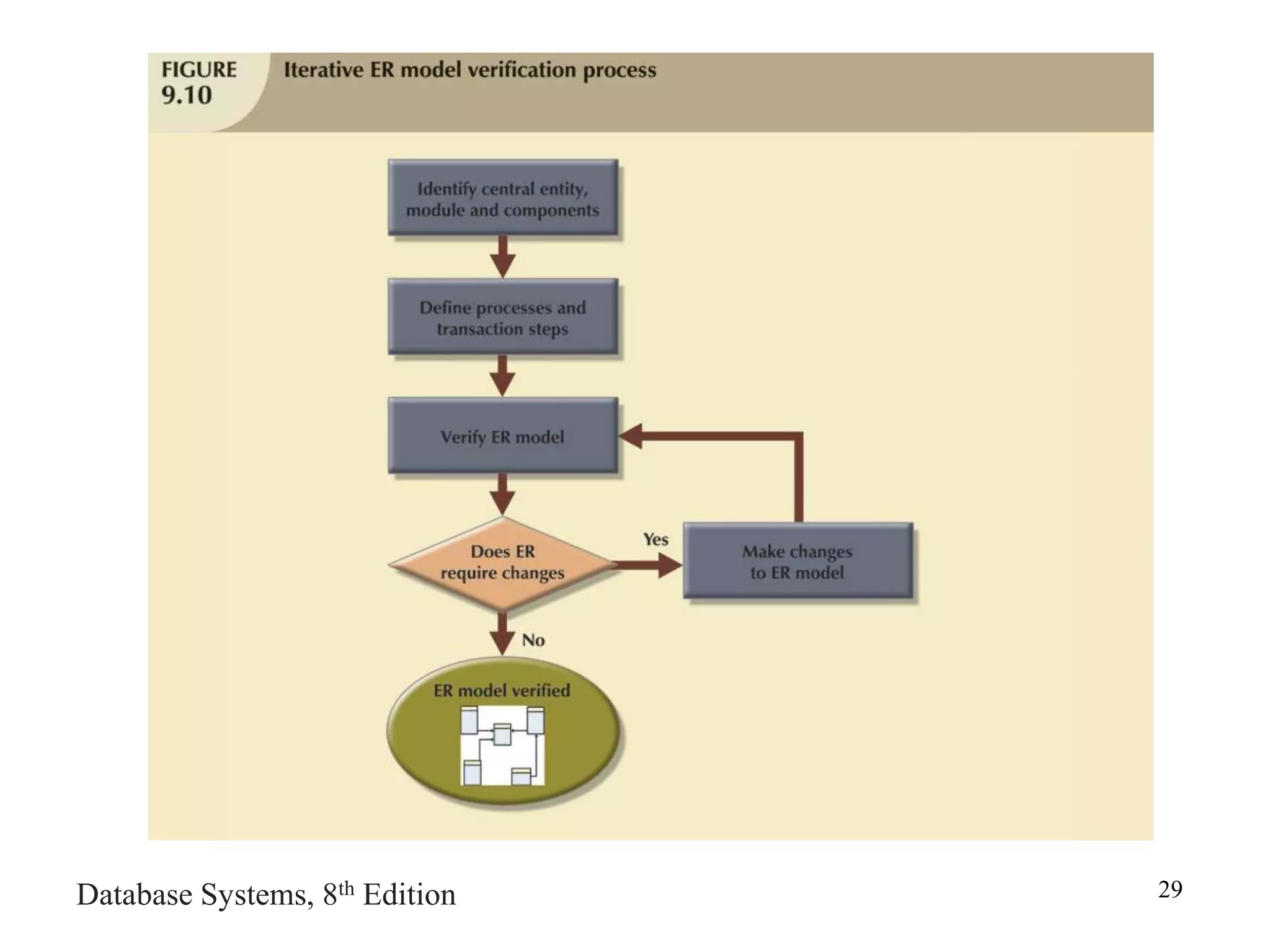
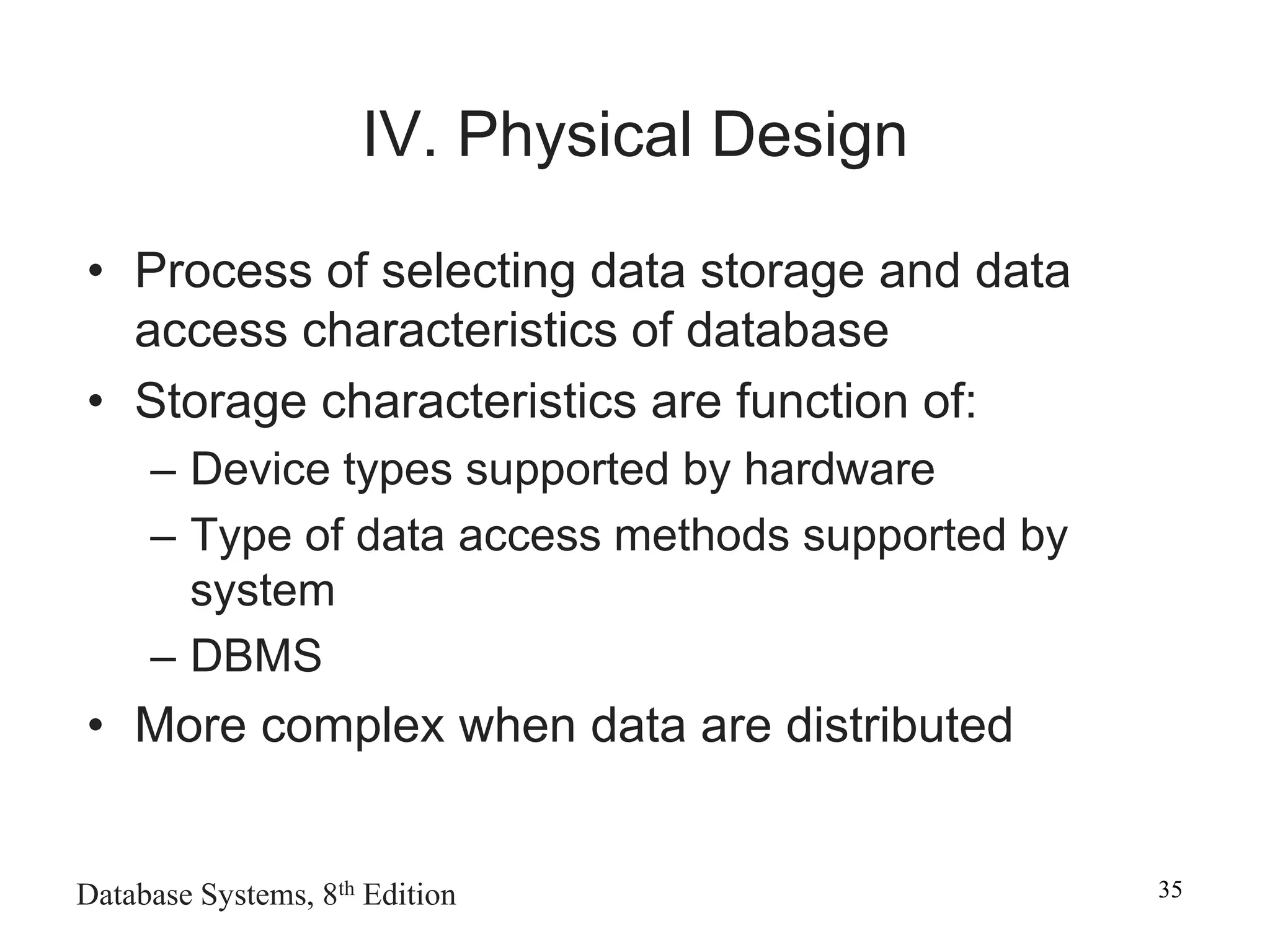
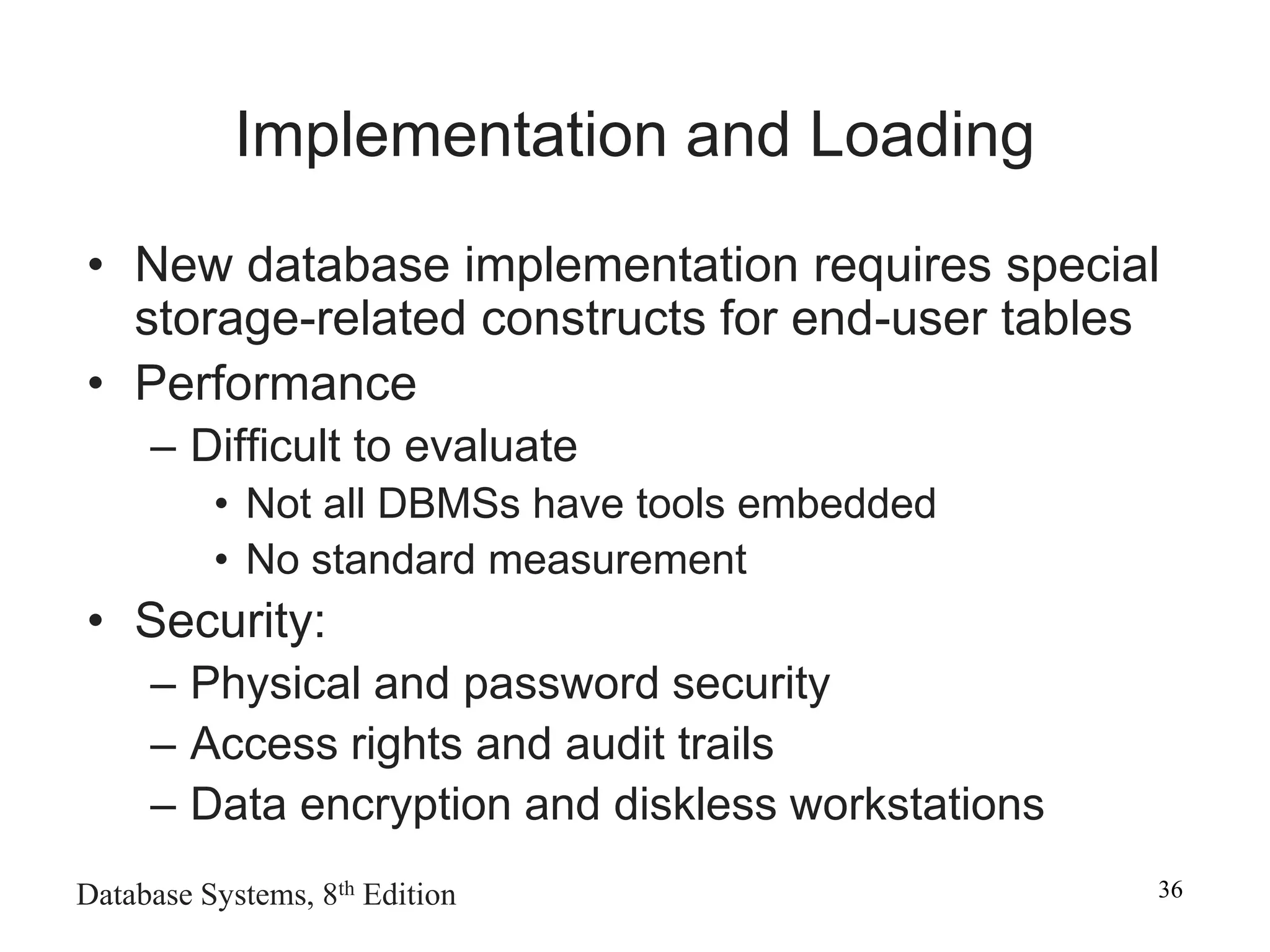
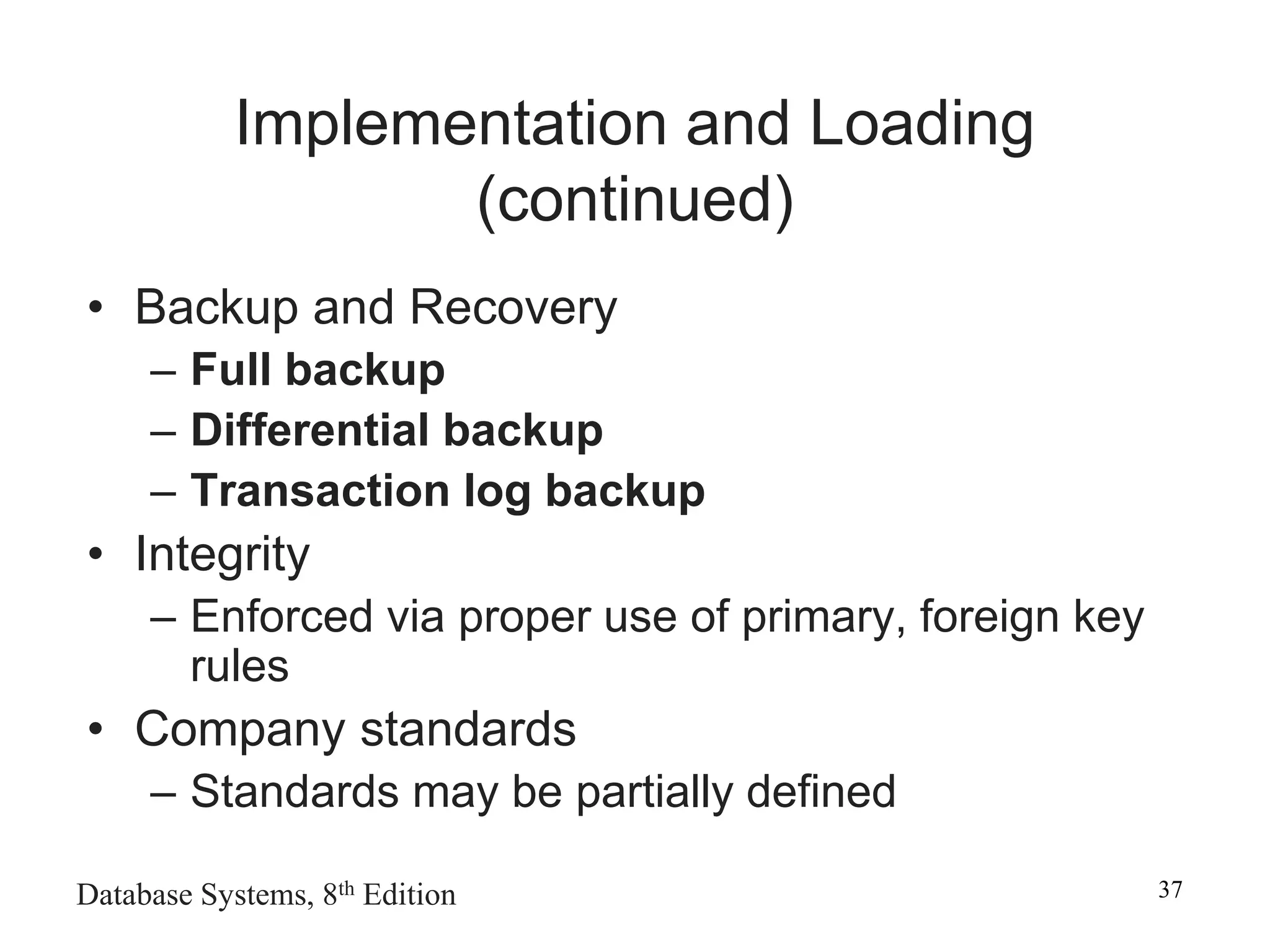
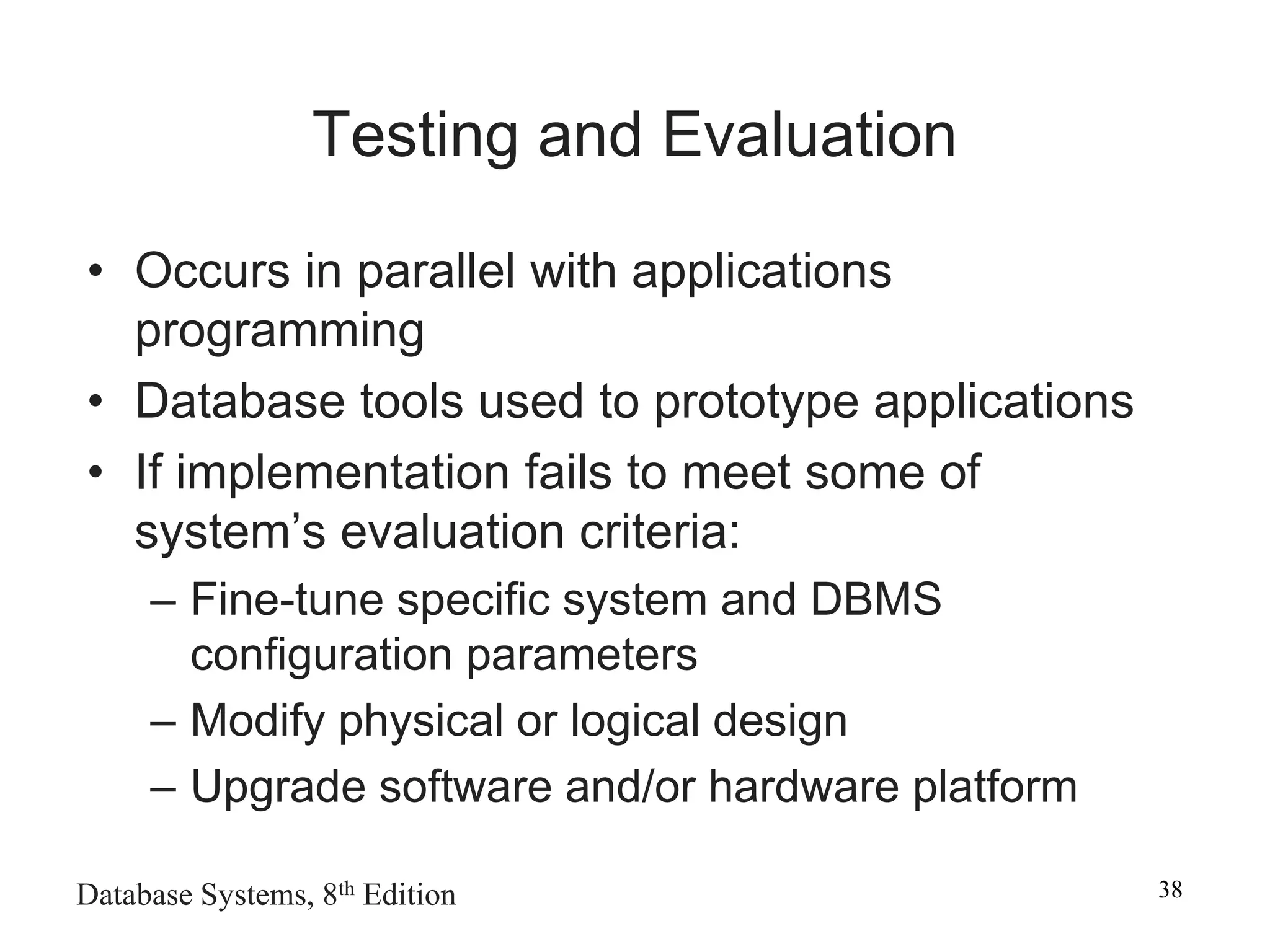
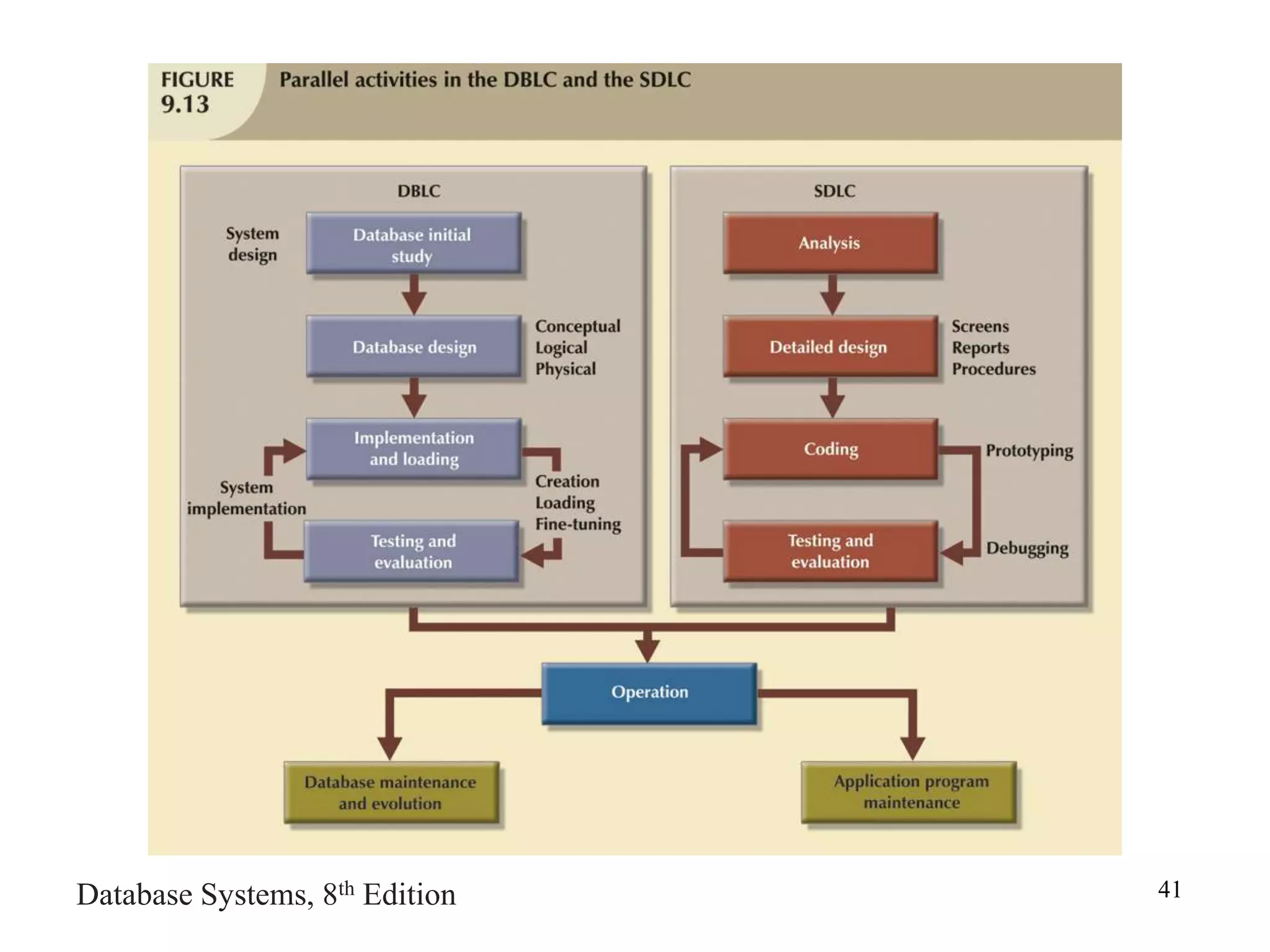
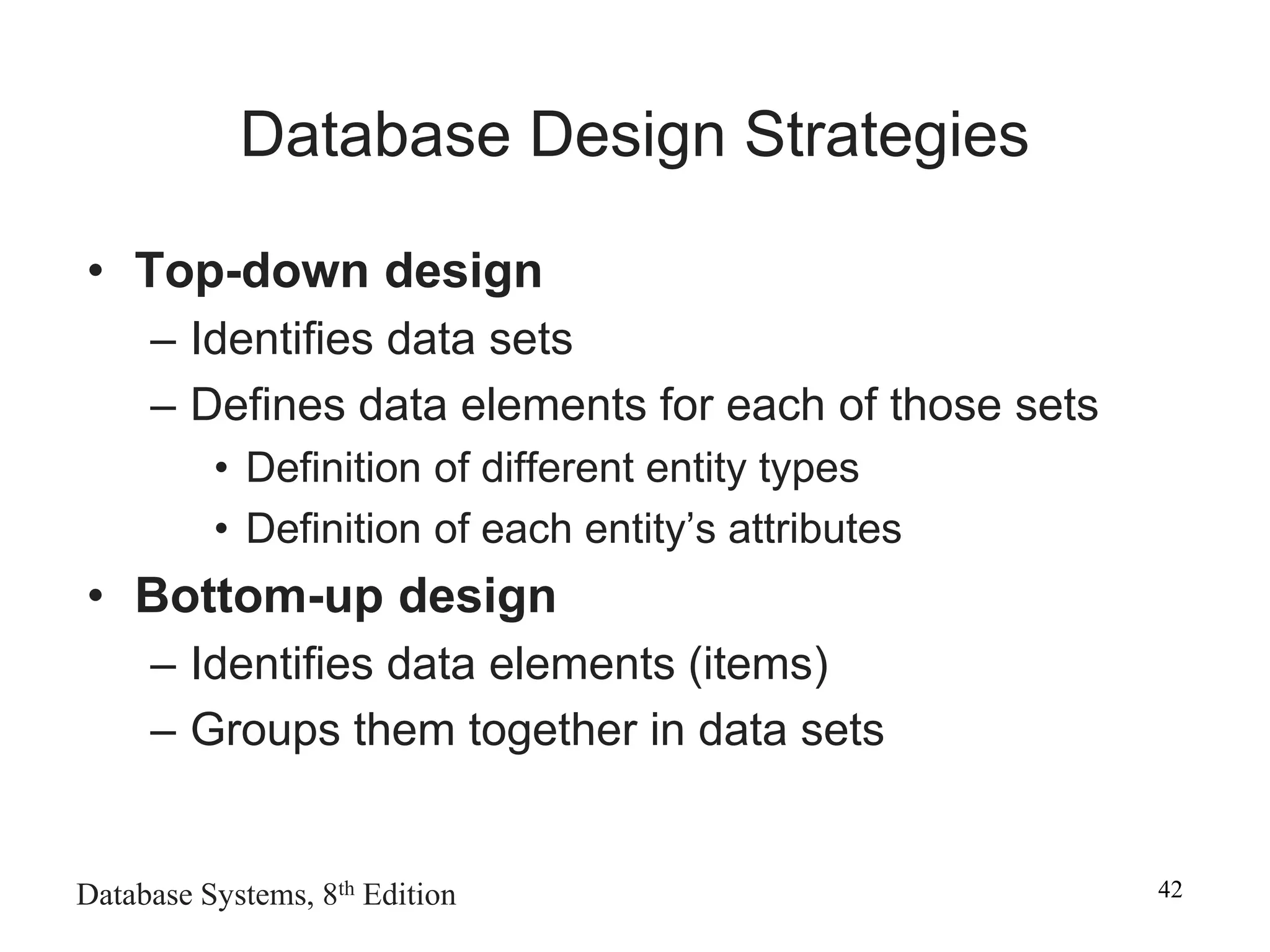
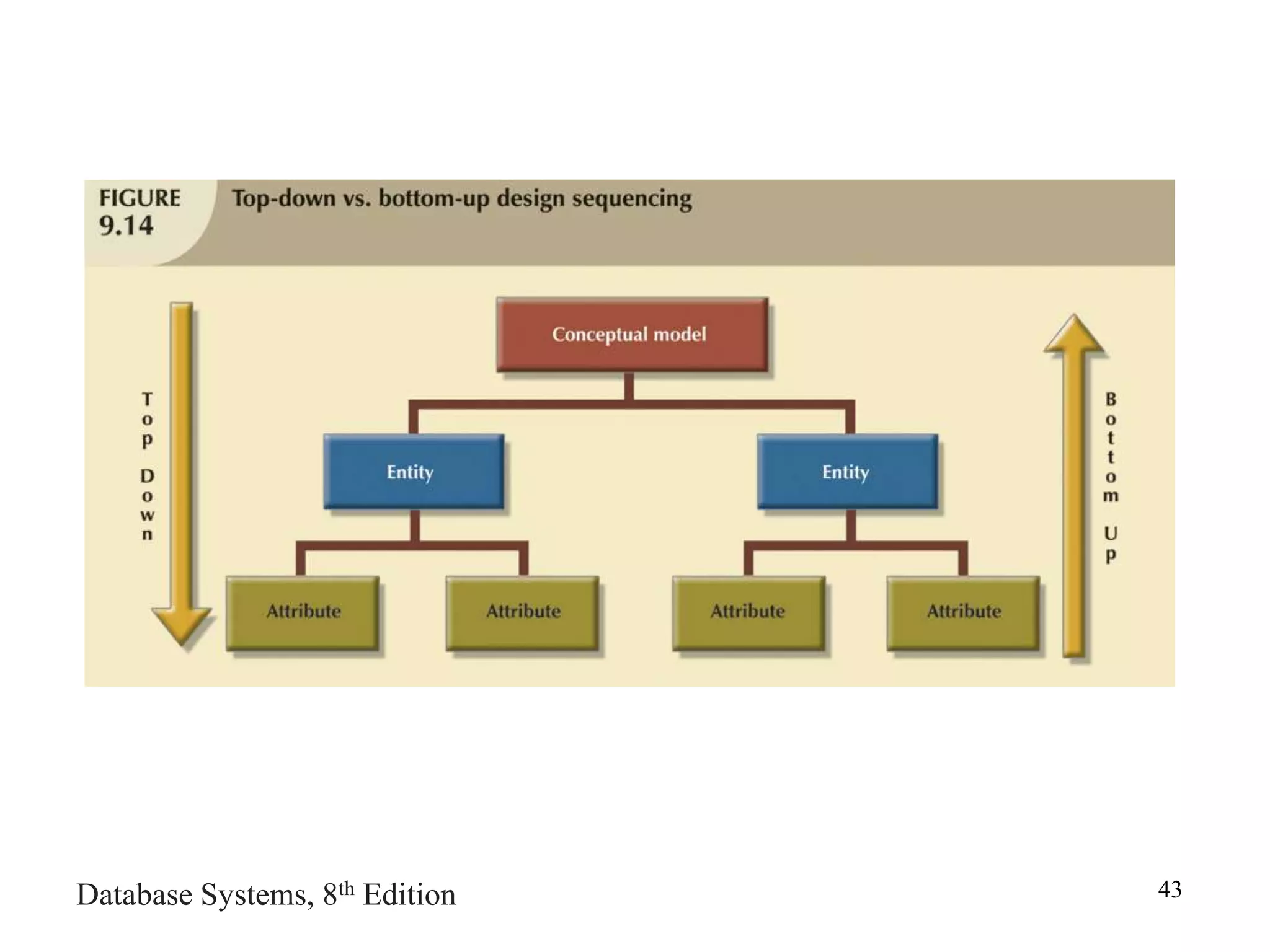
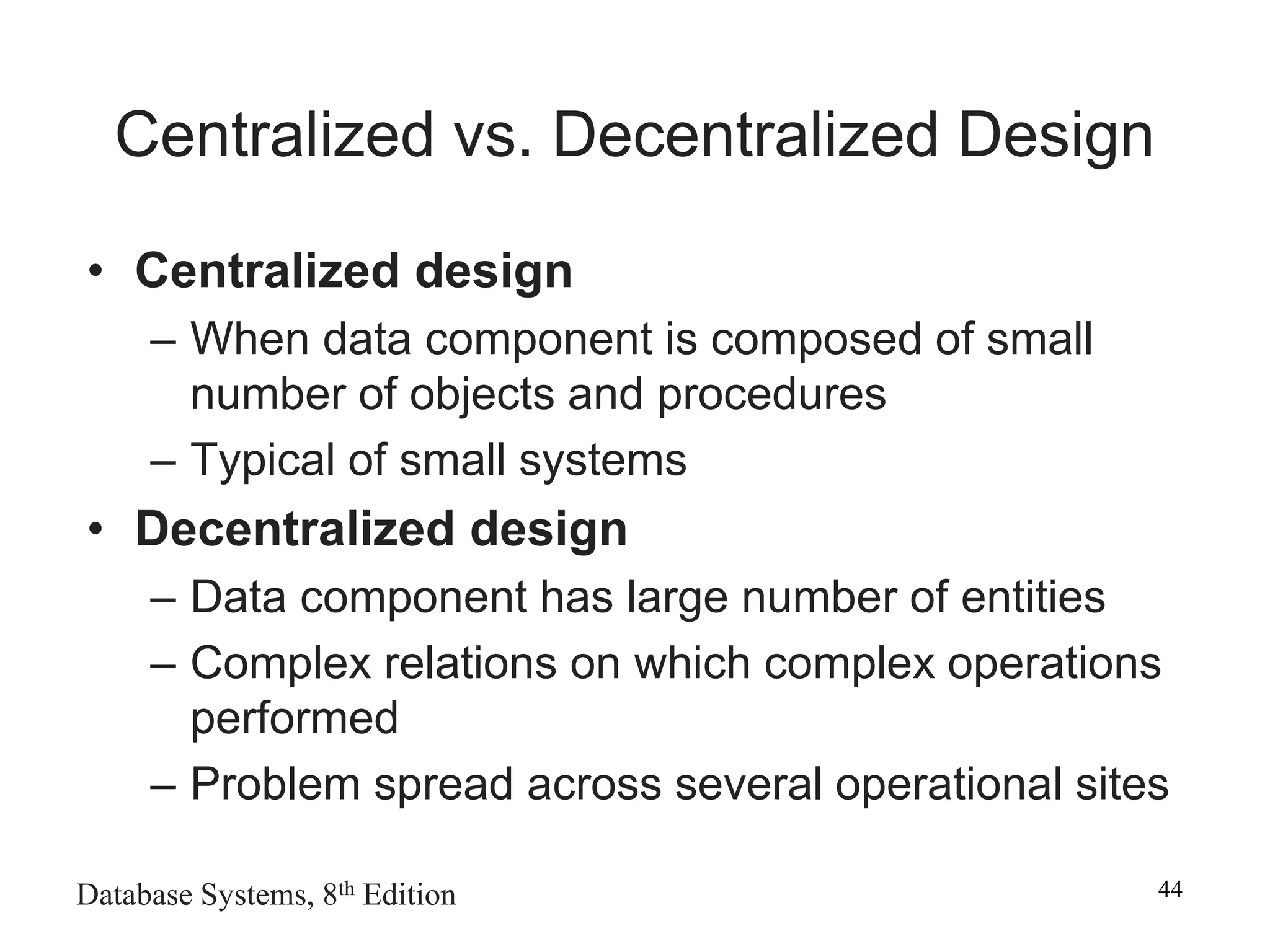
This chapter discusses database design and the systems development life cycle (SDLC). It explains that the SDLC traces the development of an information system through planning, analysis, design, implementation, and maintenance phases. Within the information system, the database life cycle (DBLC) describes the development of the database through initial study, design, implementation, testing, operation, and maintenance phases. The chapter also covers topics of conceptual database design, logical design, and physical design.