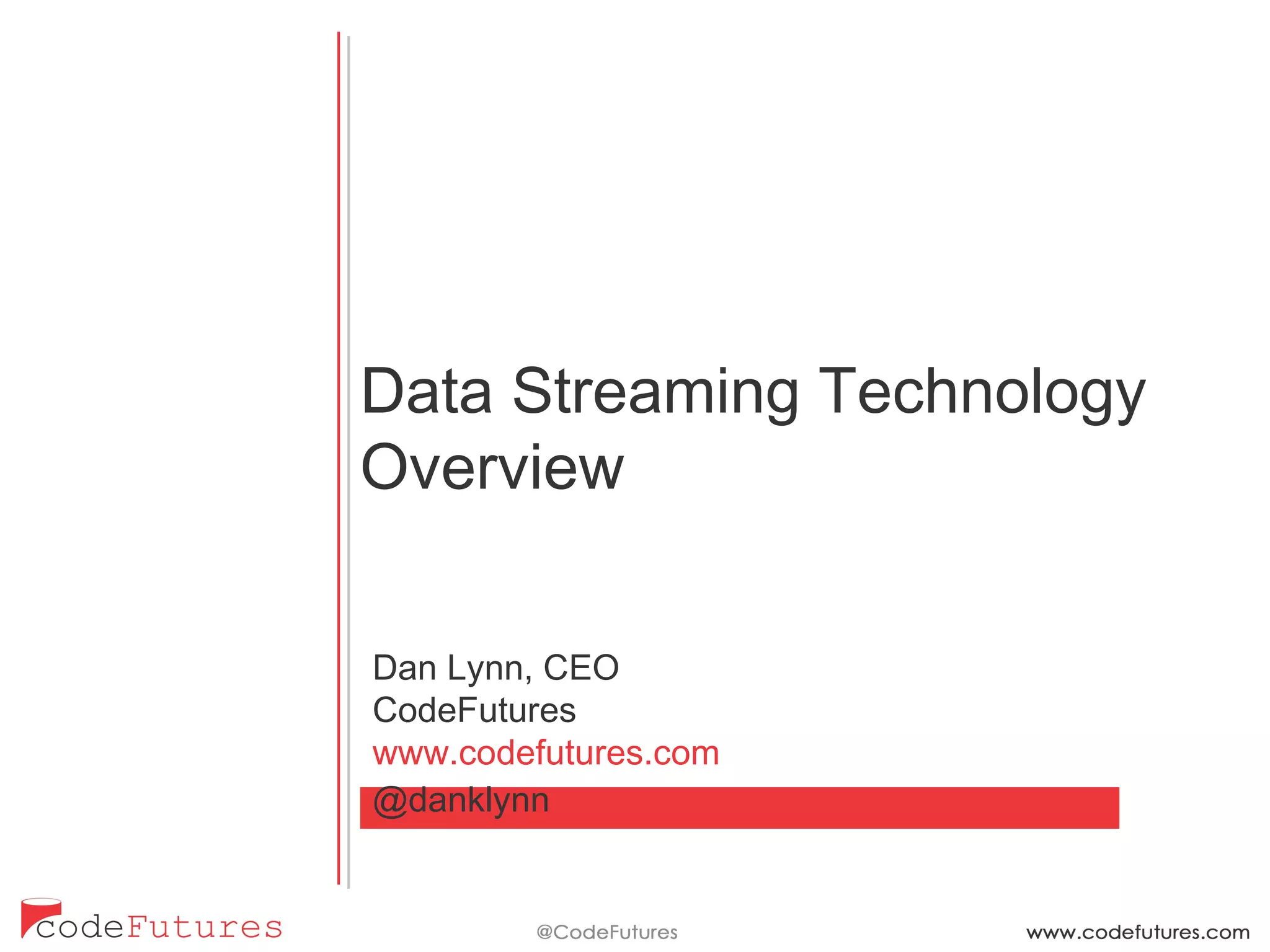
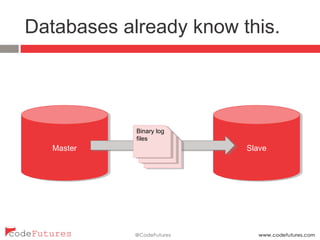
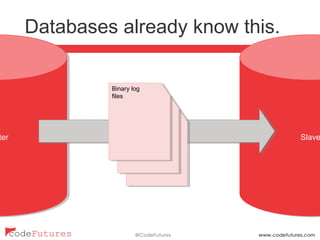
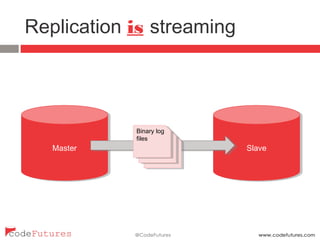
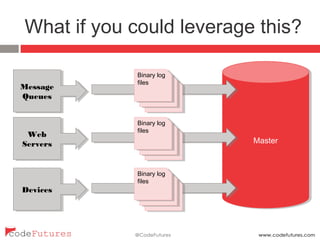
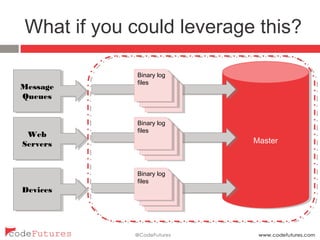
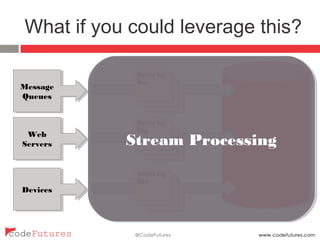
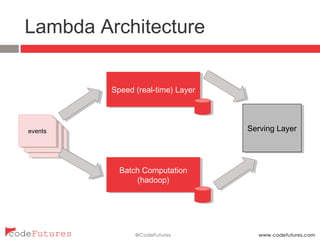
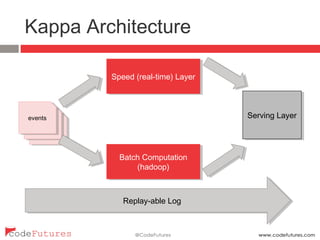
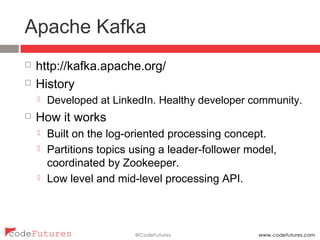
This document provides an overview of stream processing technologies. It defines stream processing as processing events in the order they occur. Common patterns like lambda architecture and kappa architecture are described. Specific stream processing technologies are then outlined, including Apache Storm, Apache Kafka, Apache Samza, Apache Spark Streaming, LinkedIn Databus, AgilData and Hailstorm. The document promotes stream processing by noting how databases already process transactions in order through replication logs.