Embed presentation
Download as PDF, PPTX























This document discusses mining data streams and various methodologies related to stream data processing, including continuous query systems and their challenges. It covers the characteristics of stream data, the architecture of stream data management systems, and methods for approximating and analyzing data streams. Application examples span telecommunications, finance, and industrial processes, highlighting the importance of real-time data processing and multi-dimensional analysis.






























































Introduction to stream data and its relevance. Reference texts are given, along with key topics in mining data streams.
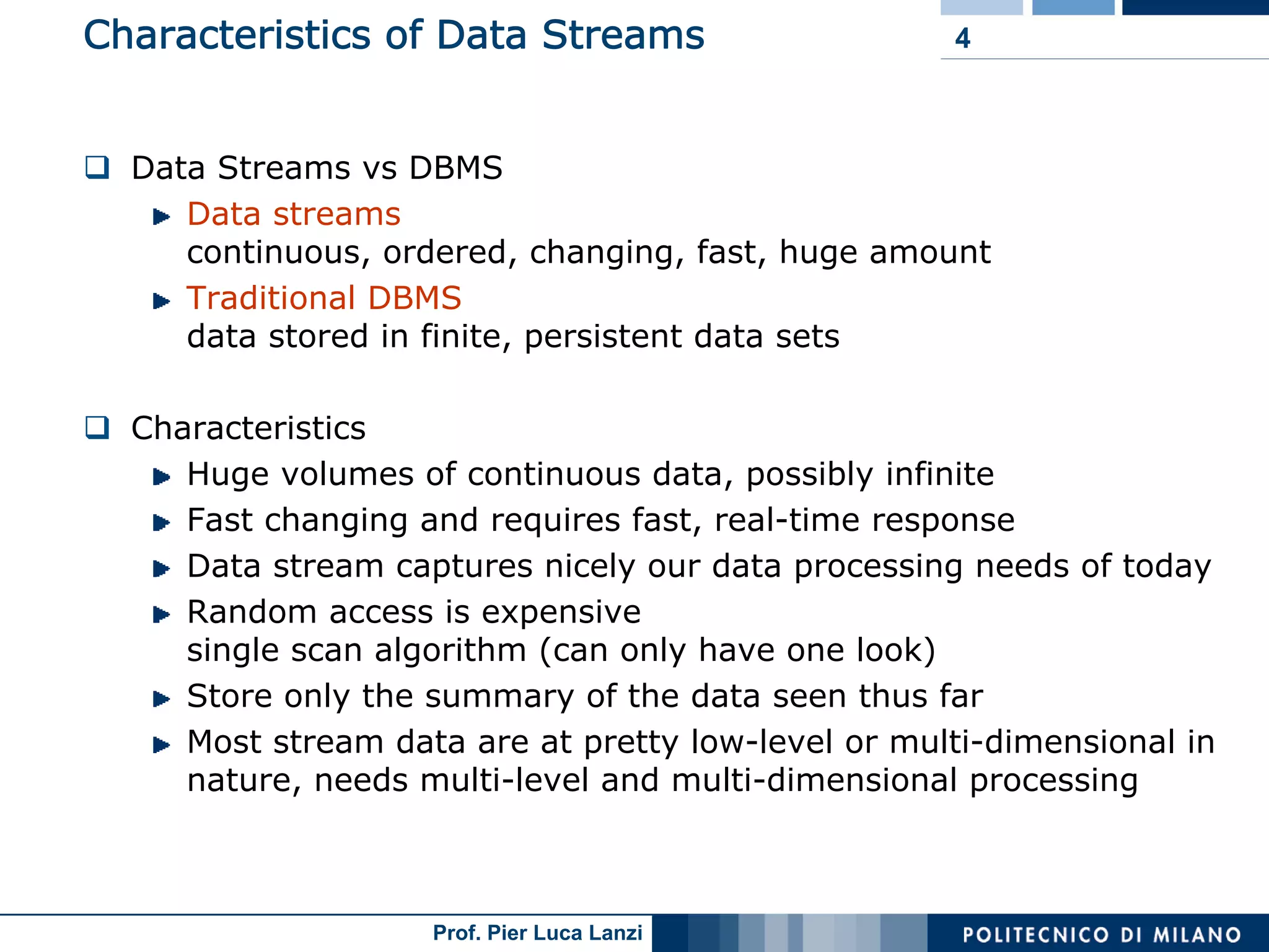
Contrasts stream data with traditional DBMS, noting the continuous, large-scale nature and challenges of access patterns.
Diverse applications such as telecom, finance, engineering, sensor monitoring, and web analytics, highlighting the need for real-time processing.
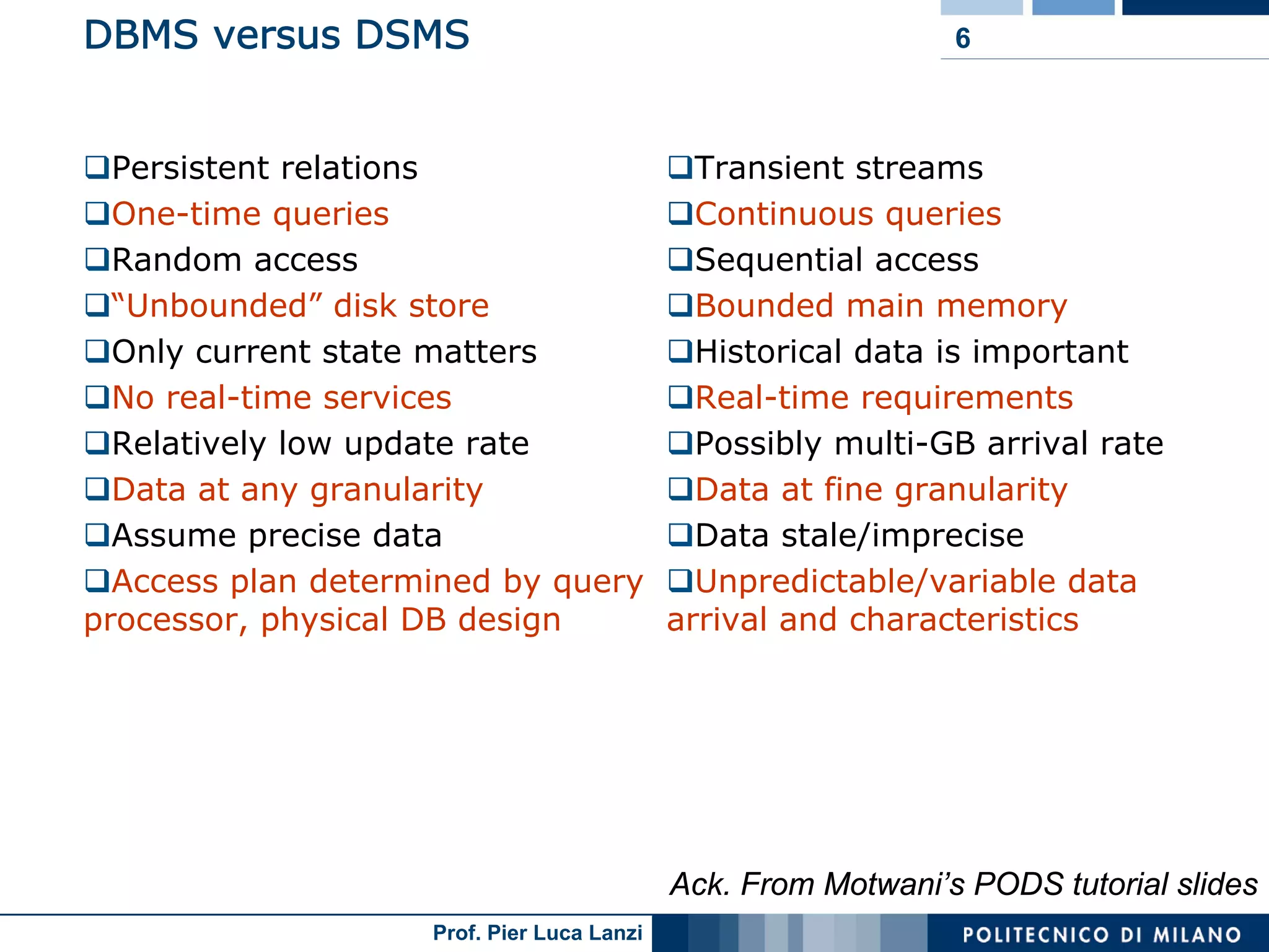
Comparison of data structures in DBMS and DSMS, emphasizing transient stream management and continuous queries.
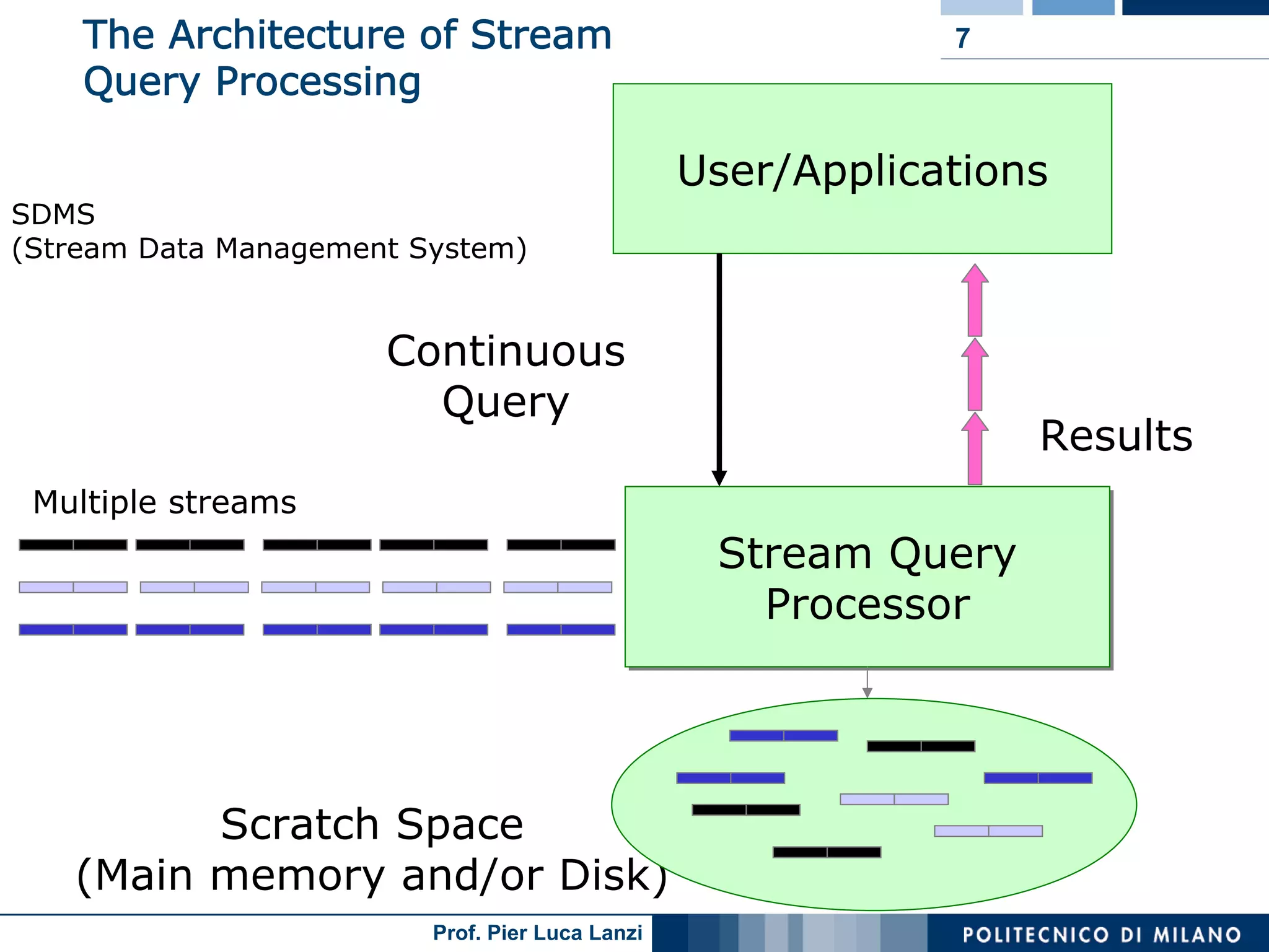
Basic architecture of Stream Data Management Systems (SDMS) and challenges in processing continuous queries efficiently.
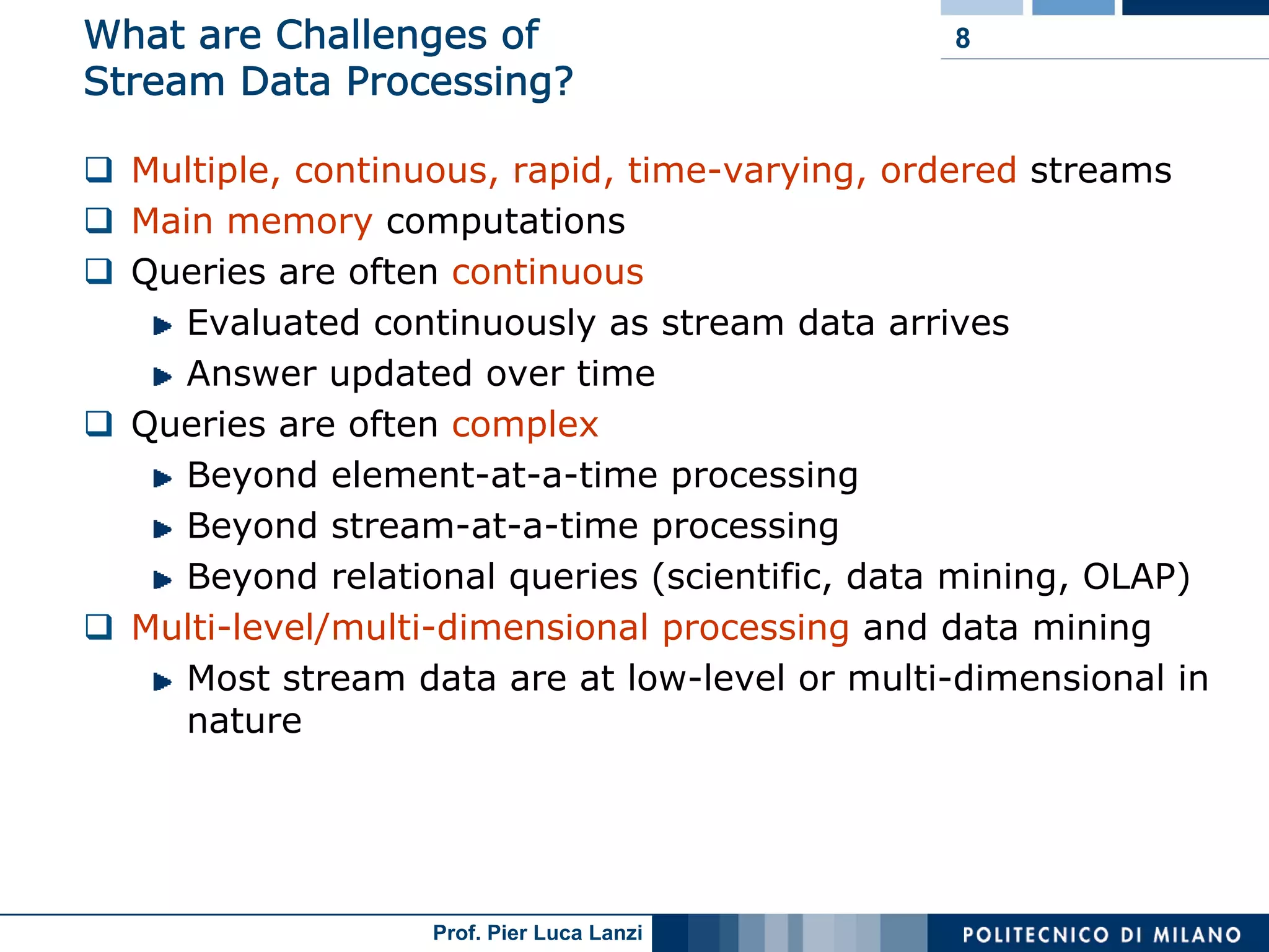
Differentiates between one-time and continuous queries, addressing memory needs, approximation strategies, and data handling methodologies.
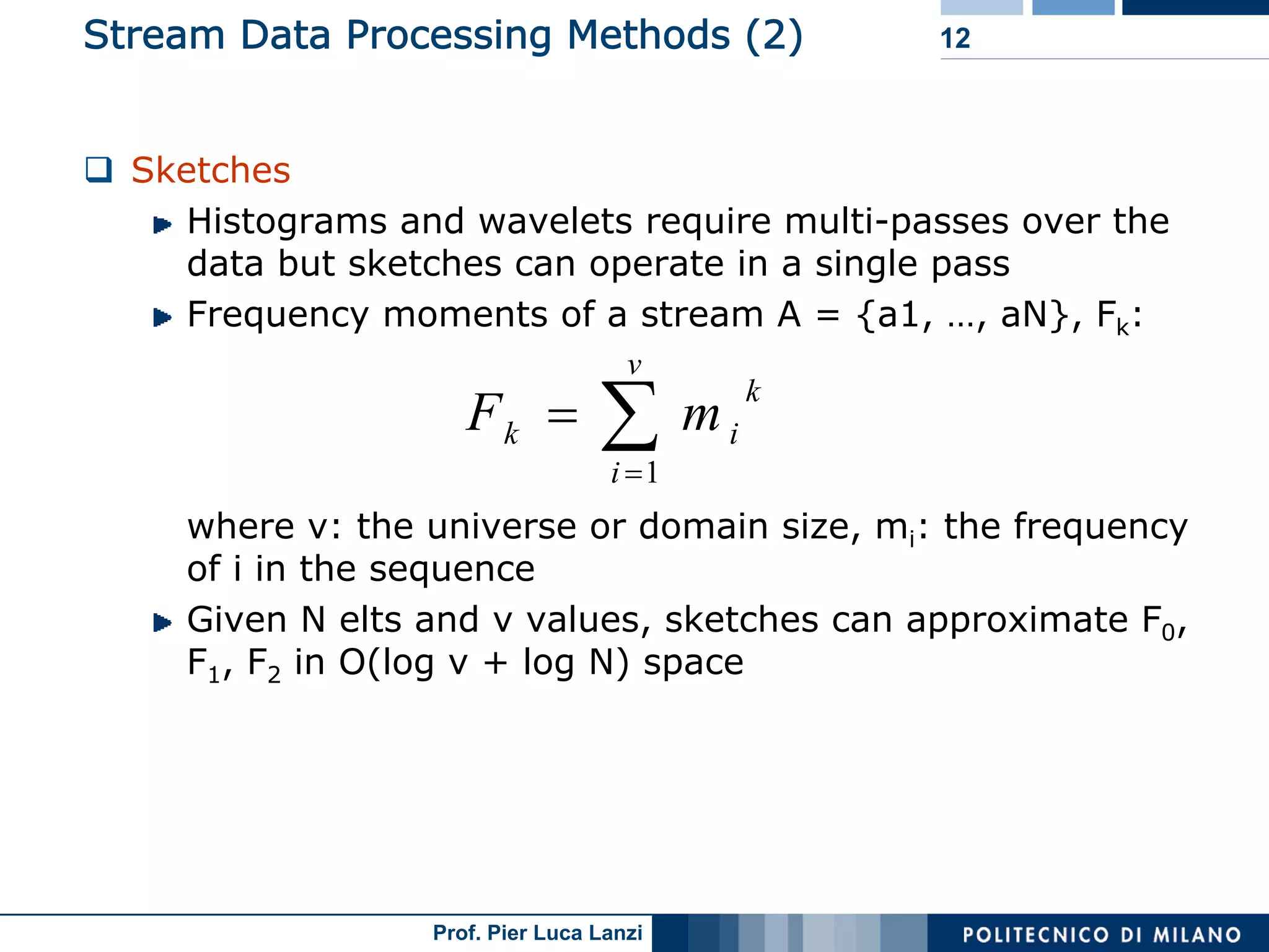
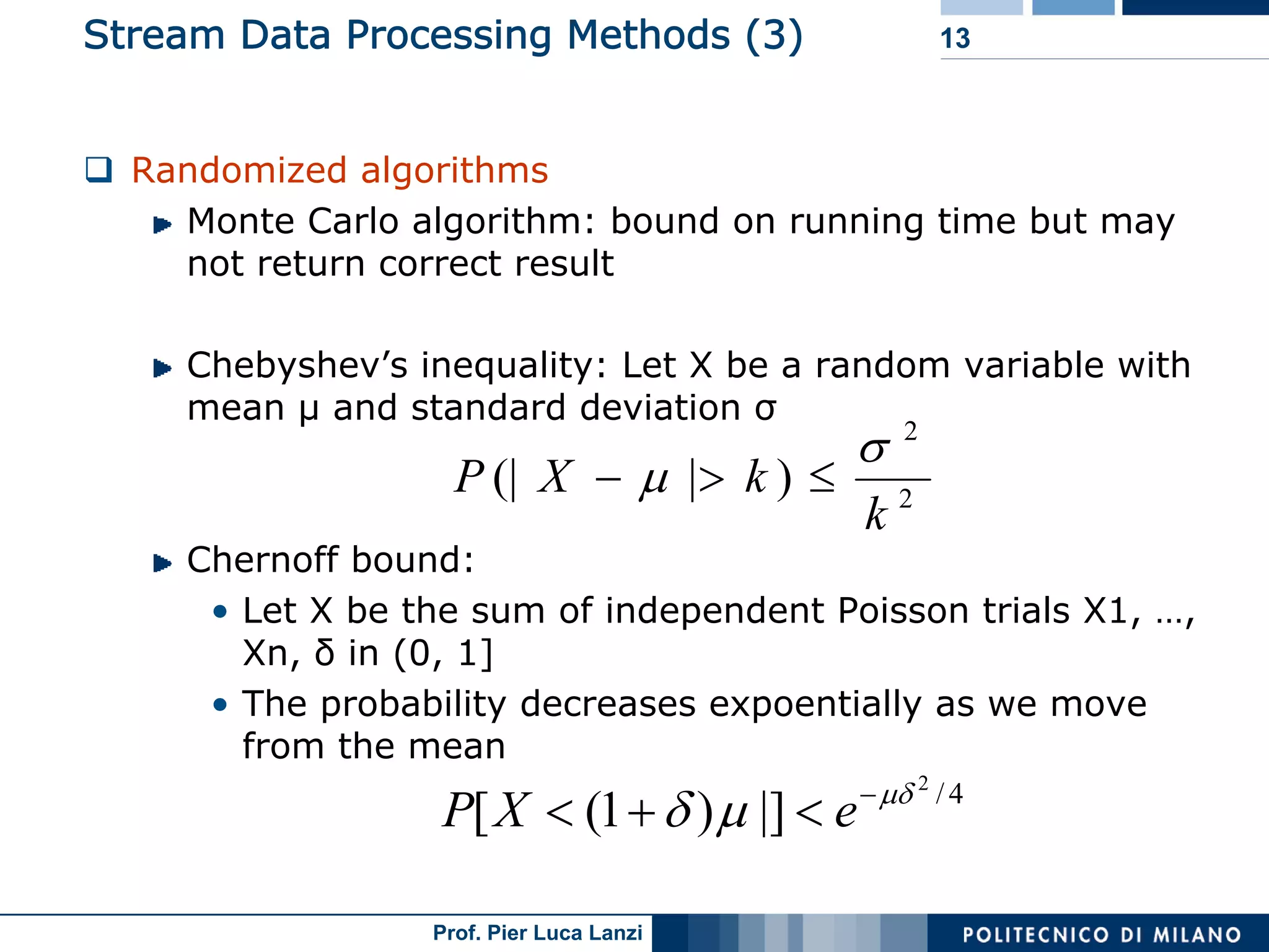
Various methodologies like random sampling, sliding windows, histograms, and sketches for efficient stream data processing.
Methods for approximate responses in streams, including batching, sampling techniques, and synopsis data structures.
Research projects and prototypes involving stream data management systems from various institutions.
Differentiates between stream mining and querying, discussing challenges and tasks like outlier detection and clustering.
Challenges in analyzing low-level and multi-dimensional stream data requiring fast real-time detection capabilities.
Examples illustrating trends in web click streams and power consumption, emphasizing average usage metrics.
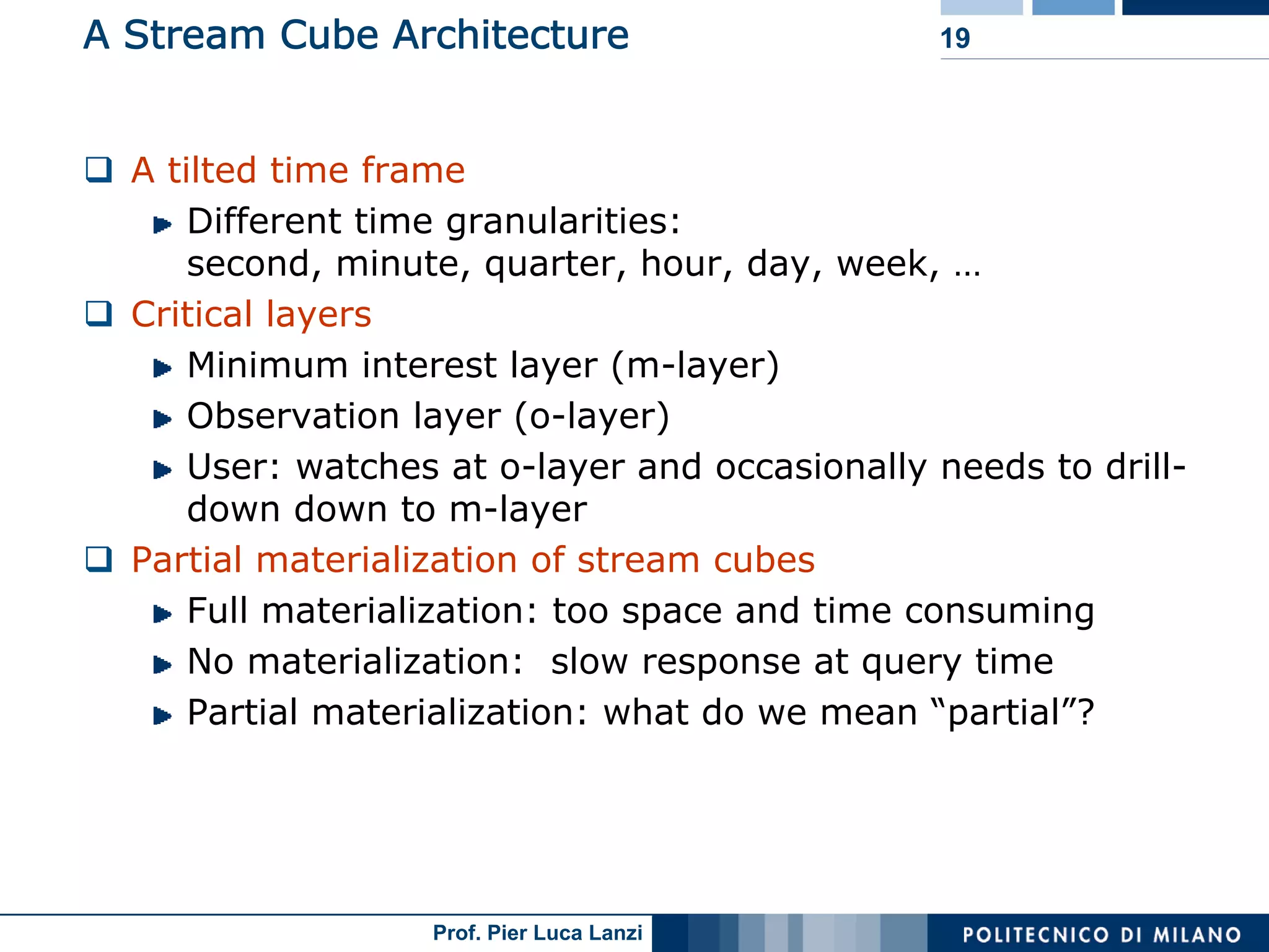
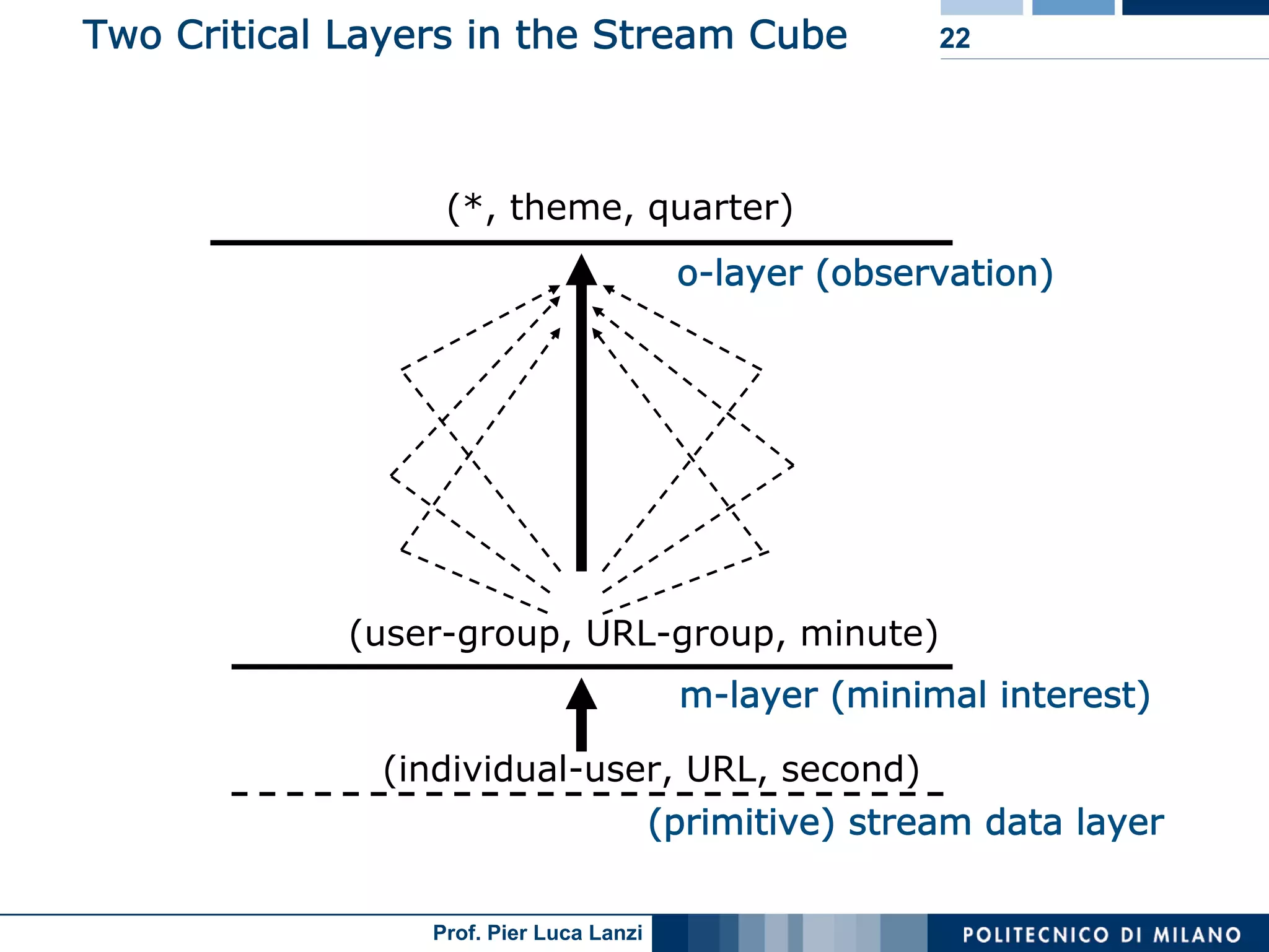
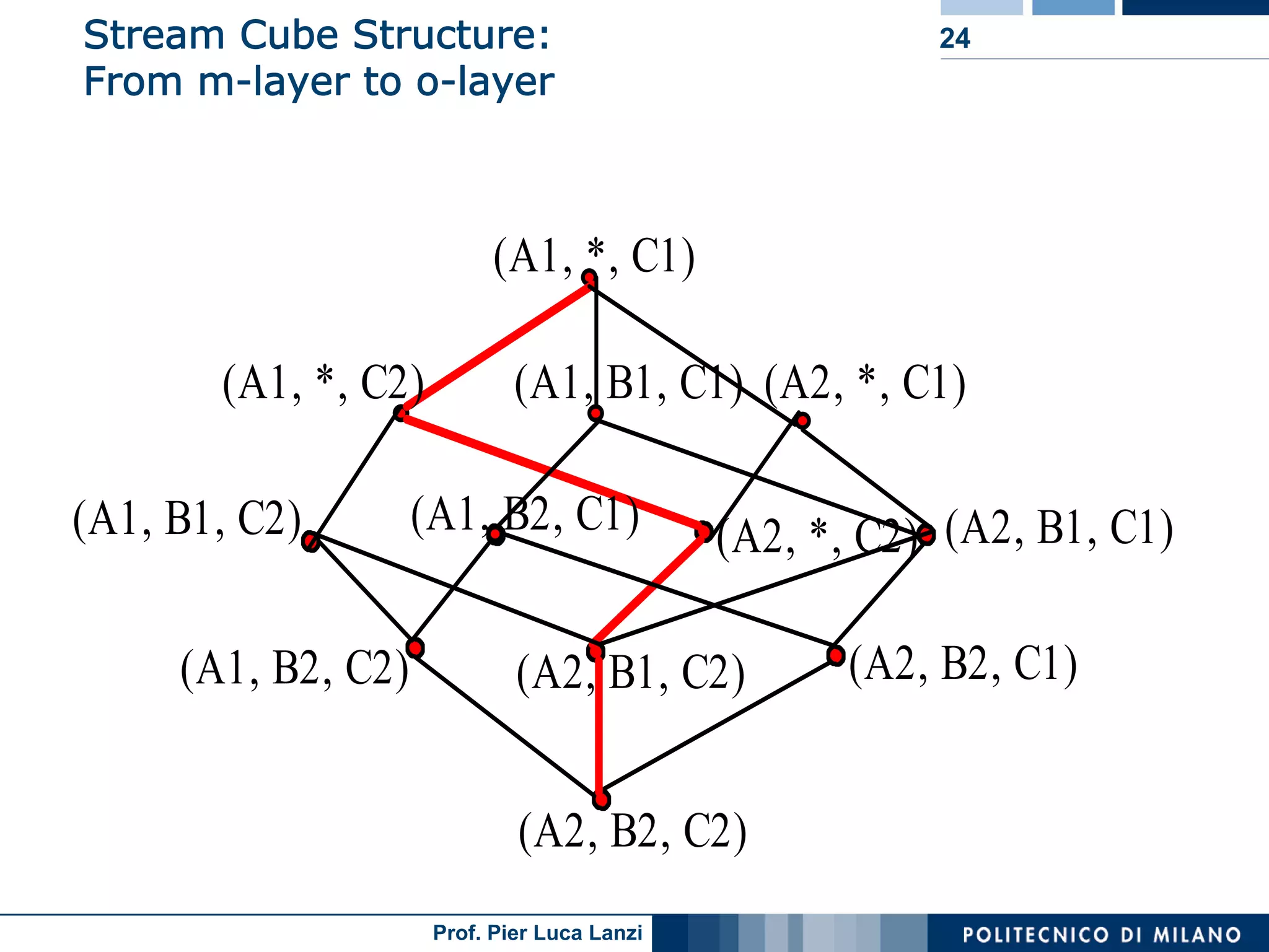
Describes the structure of a stream cube, integrating different time granularities for efficient analysis of stream data.
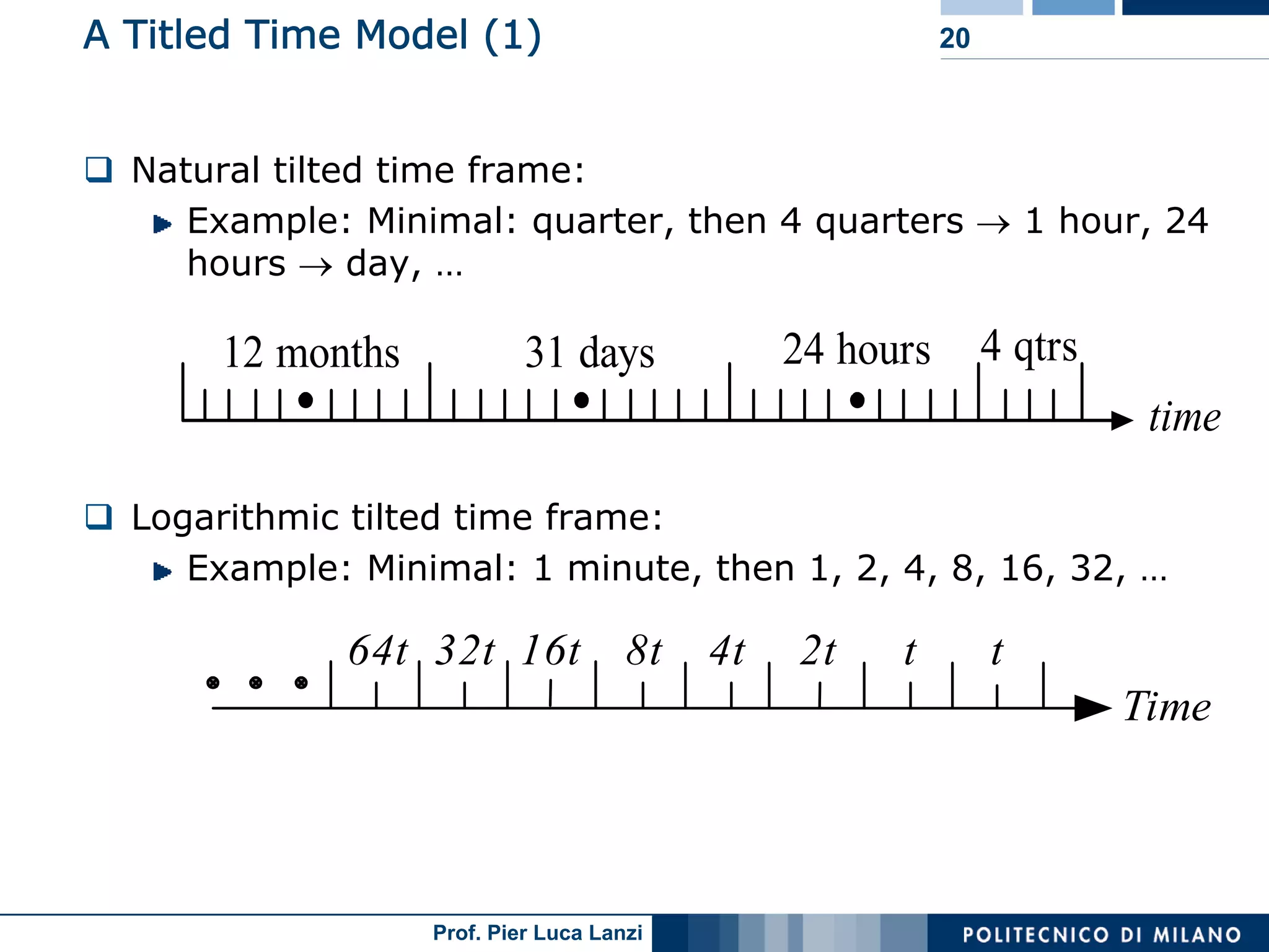
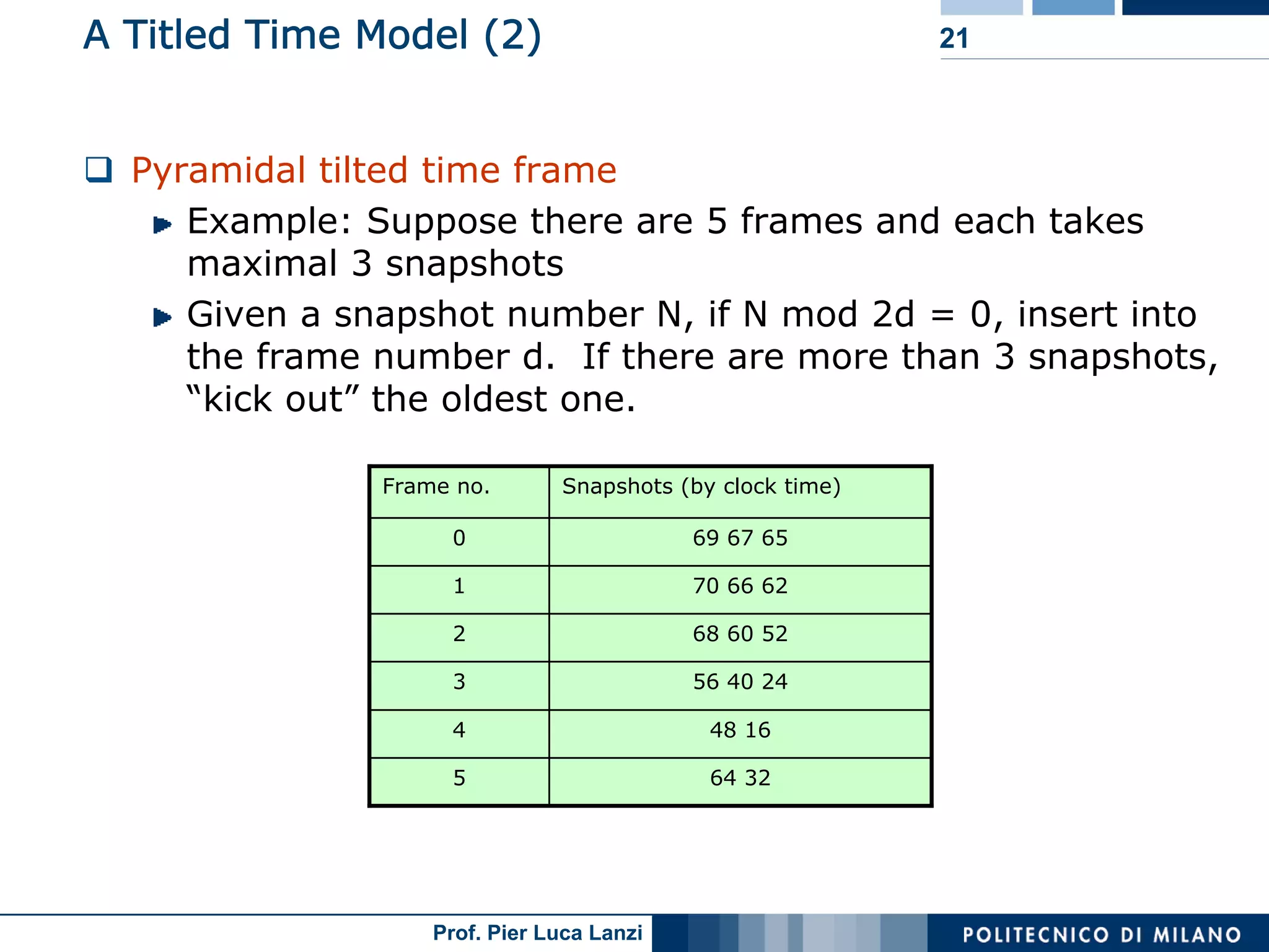
Describes models for organizing time data in streams for efficient analysis, categorized by time intervals.
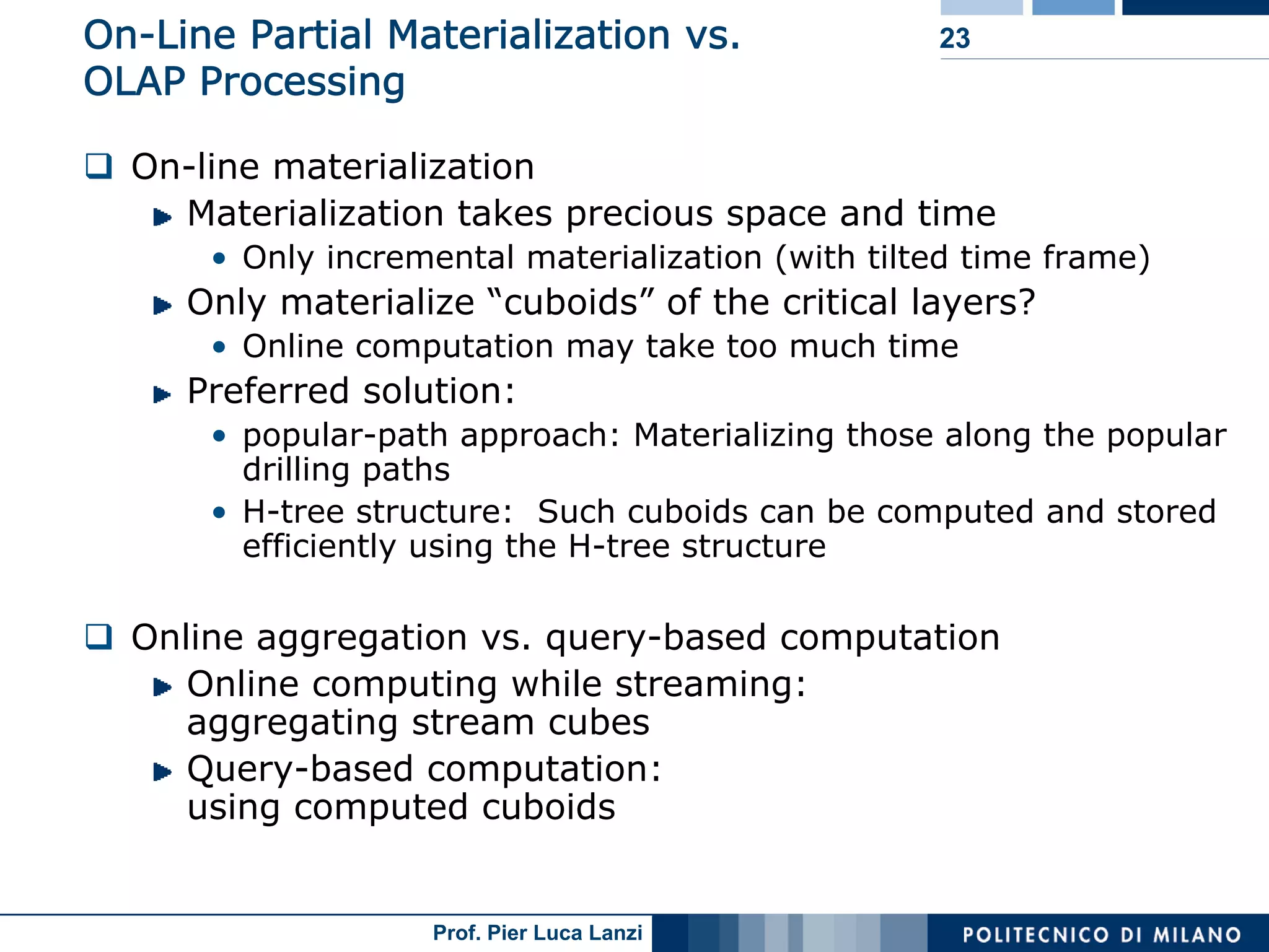
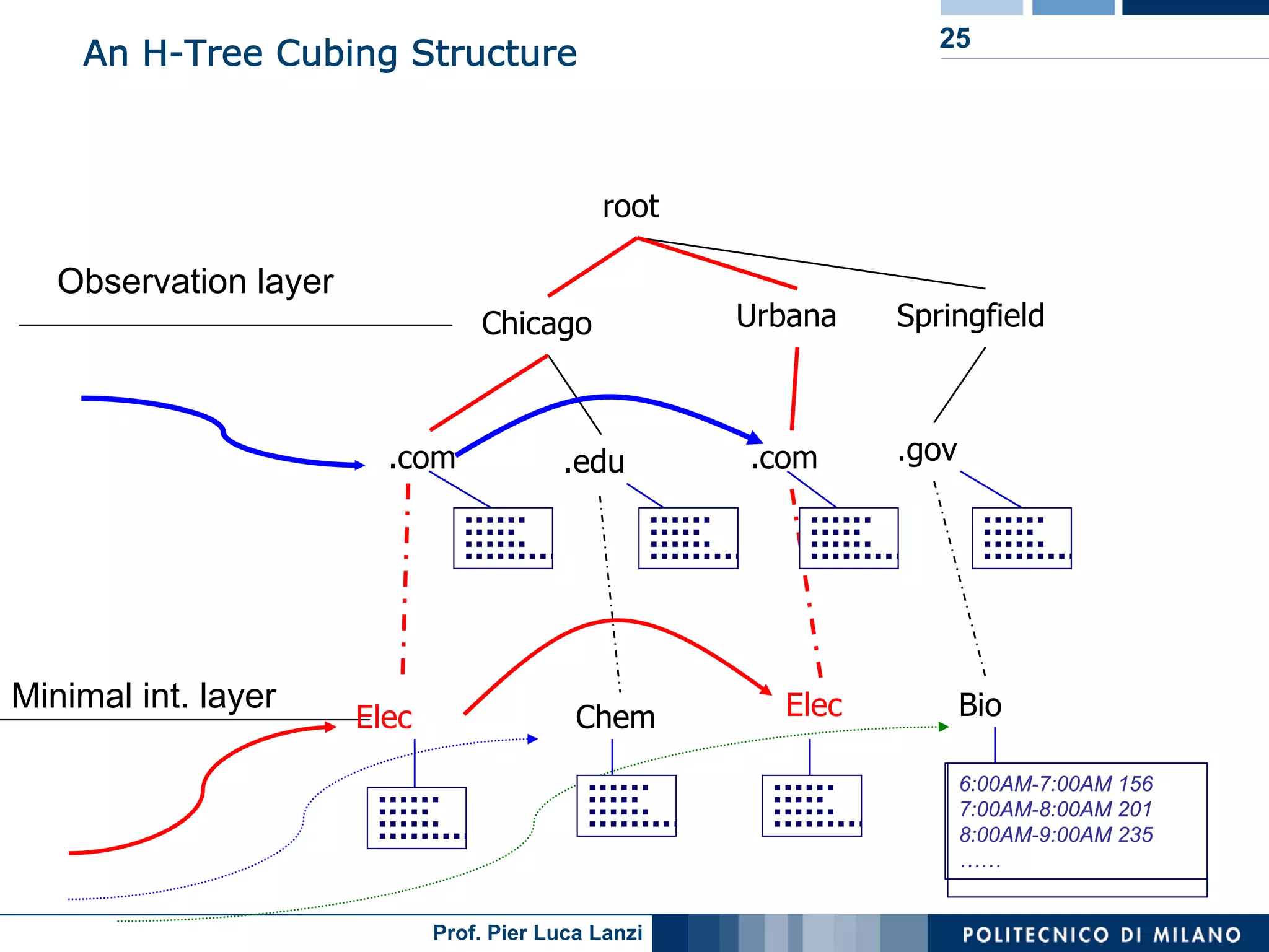
Details on the H-Tree structure and its role in efficient storage and analysis of stream cubes.
Advantages of using H-tree structures for stream cubing, focusing on efficiency and space utilization.
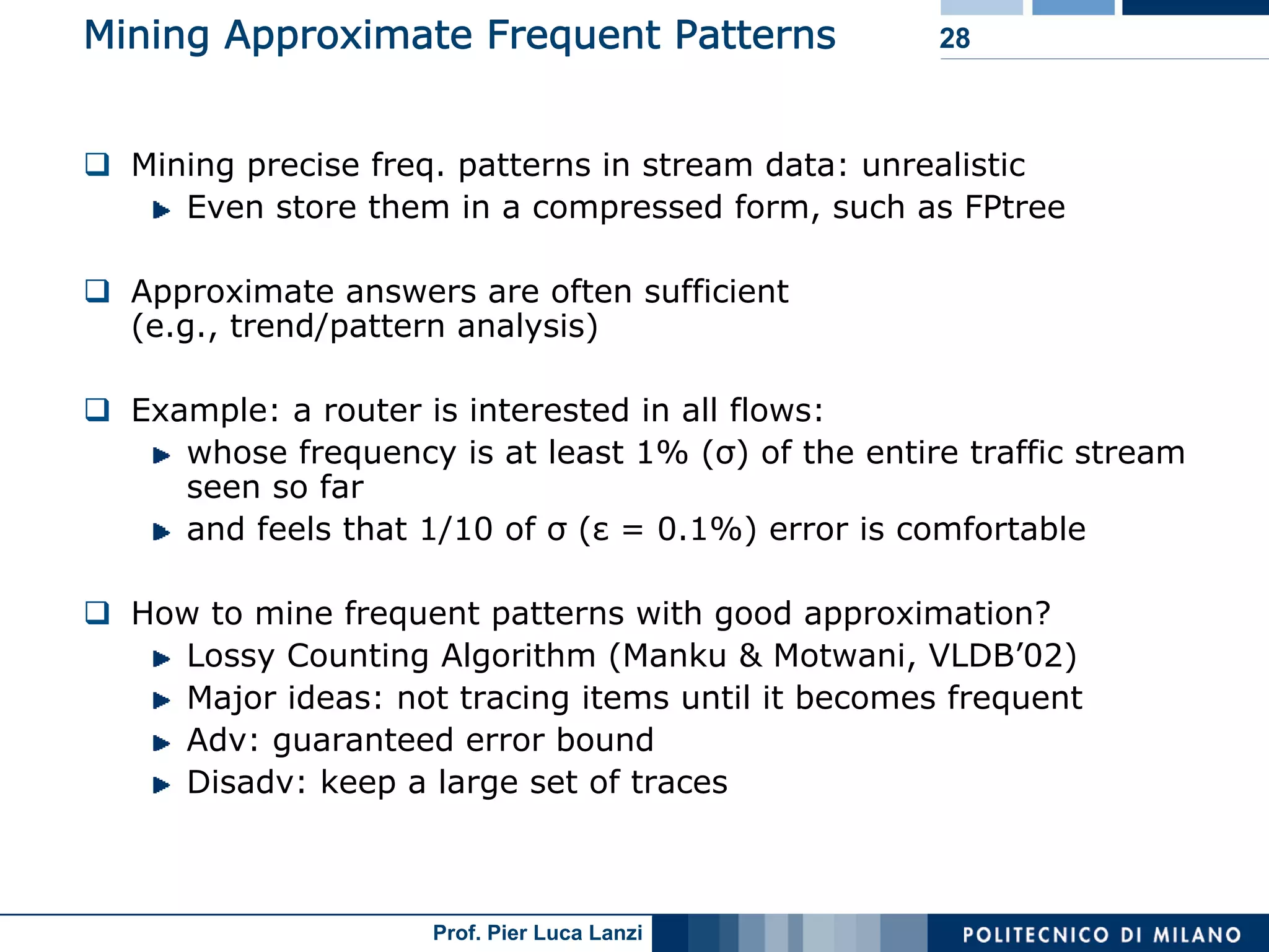
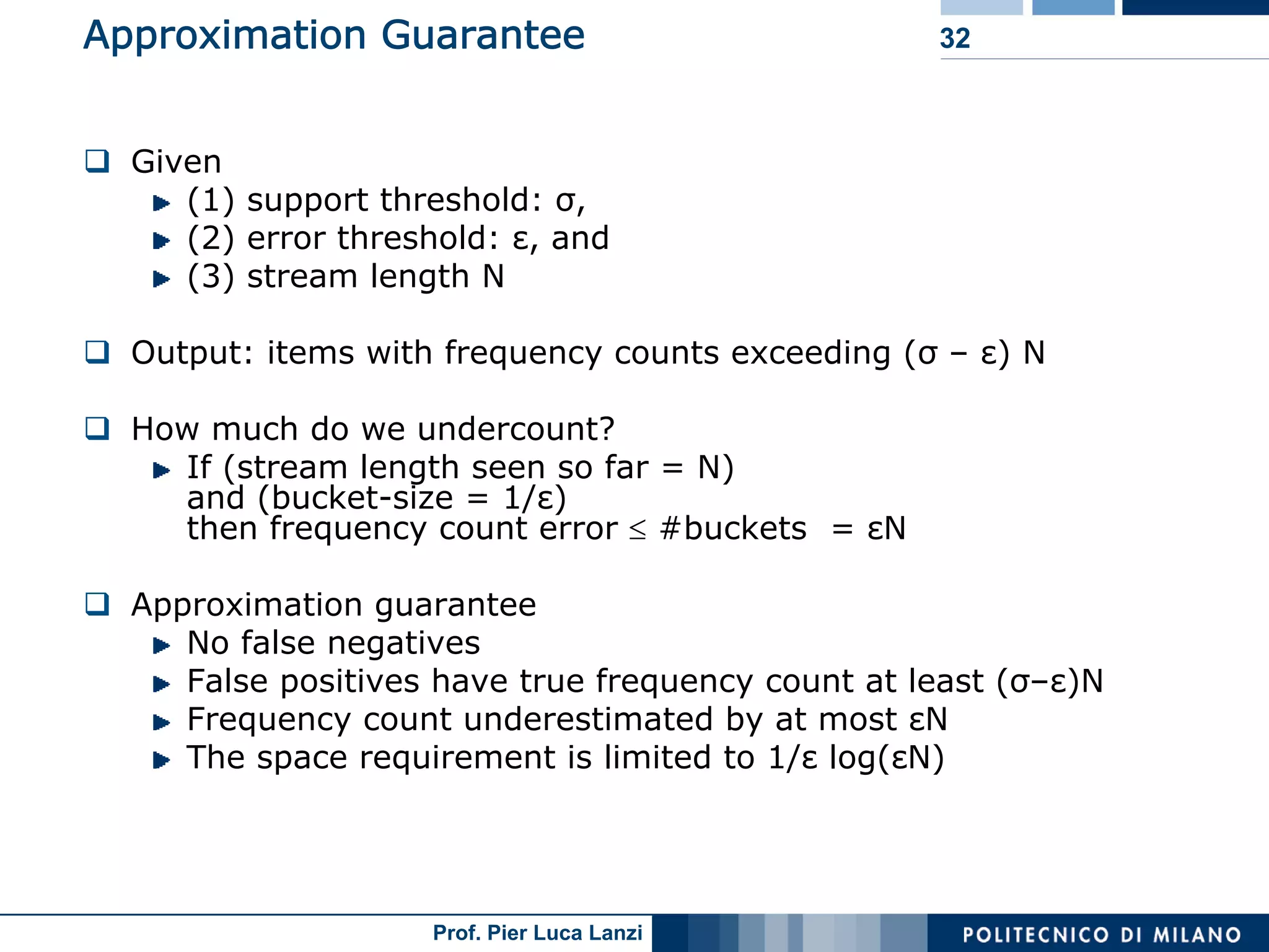
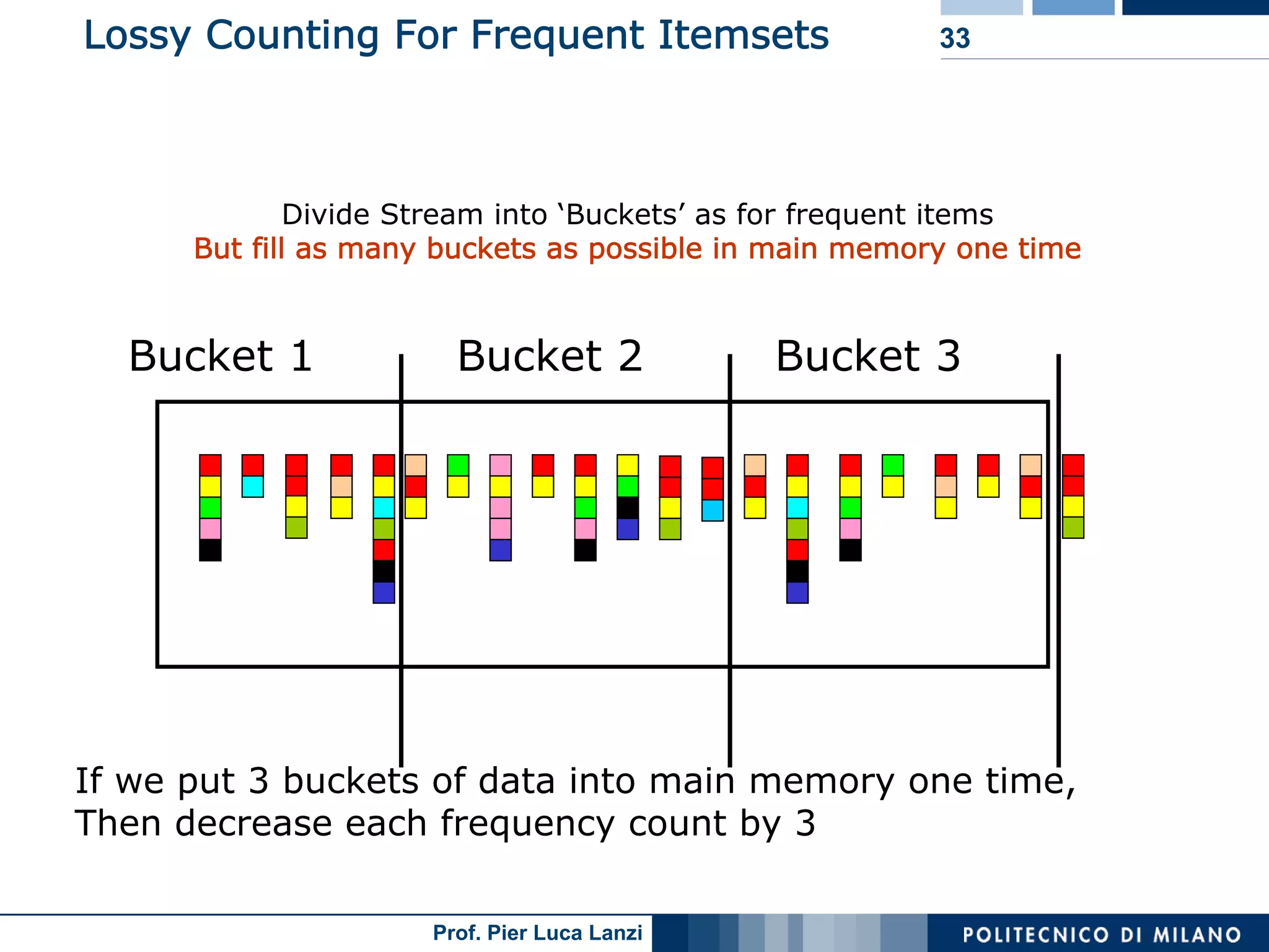
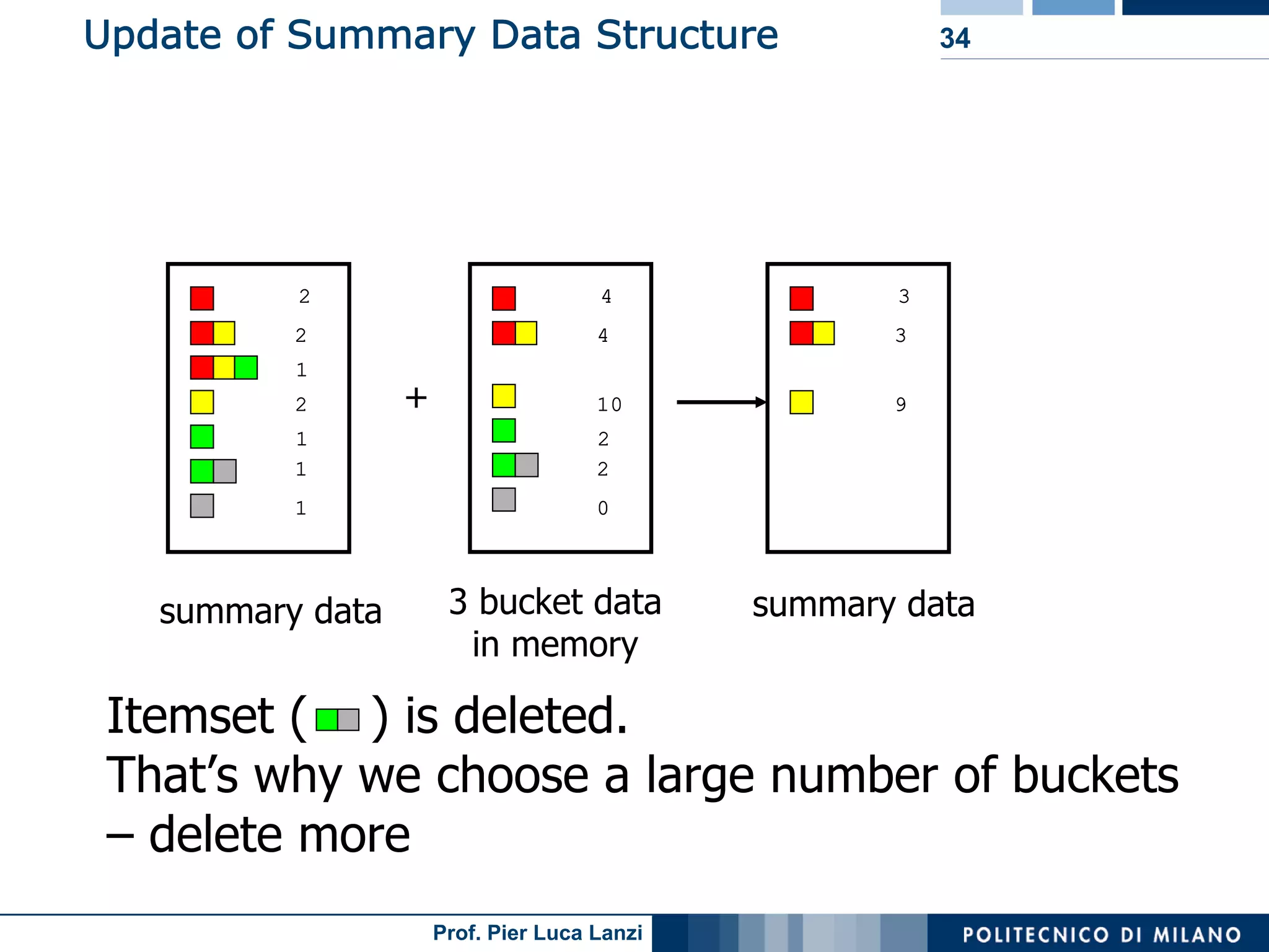
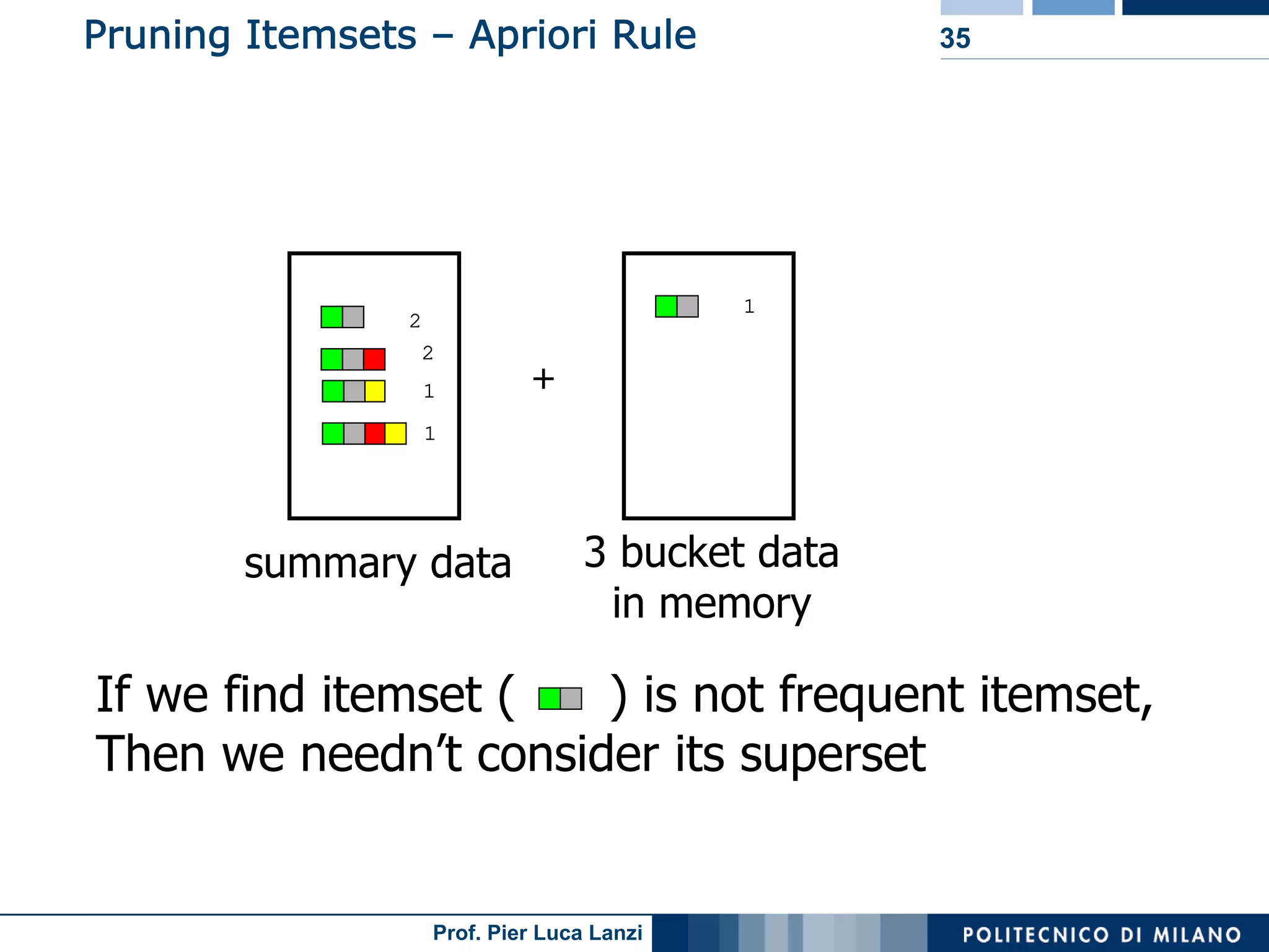
Challenges and methodologies for mining frequent patterns in streams, including approximation techniques.
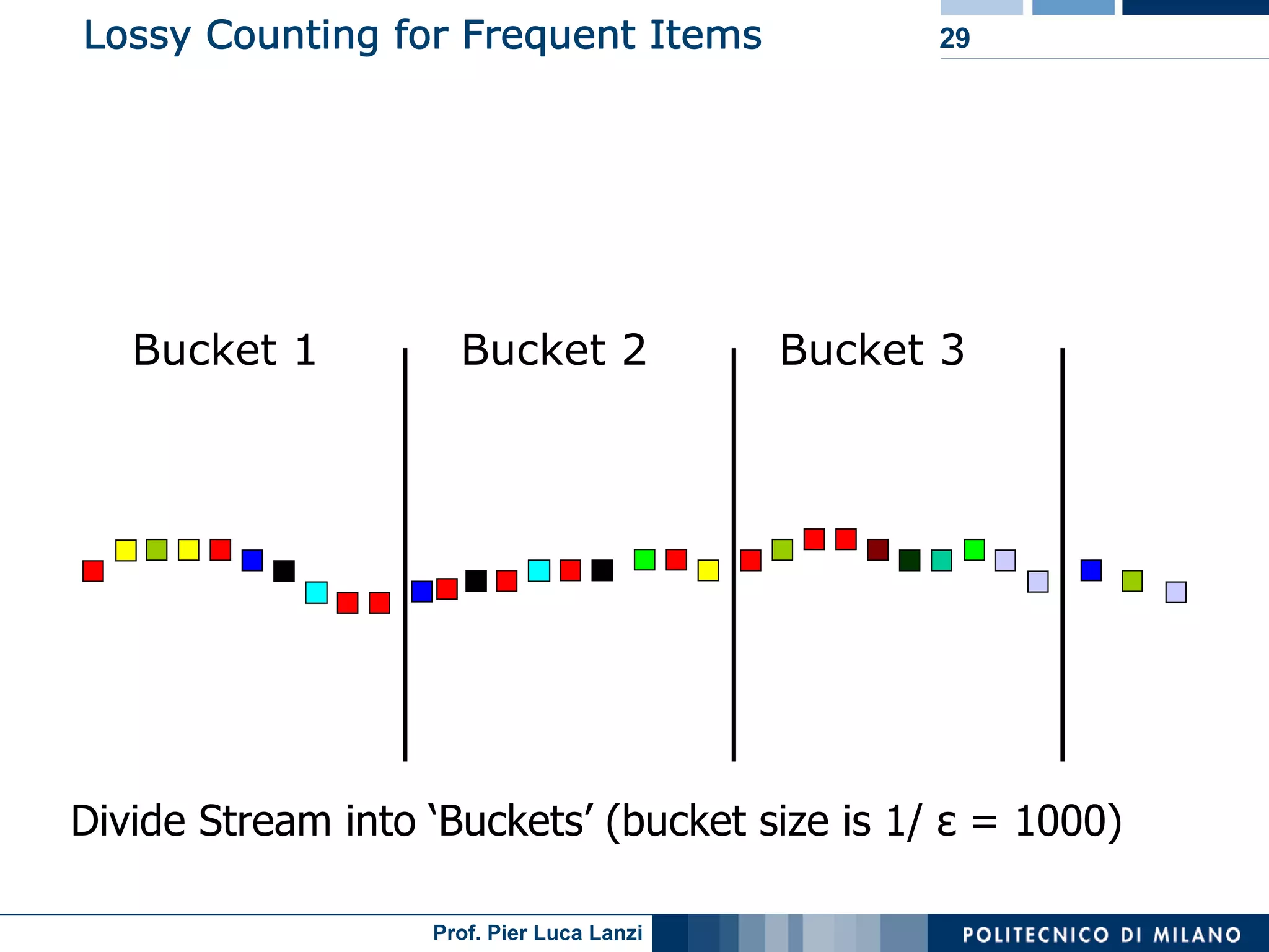
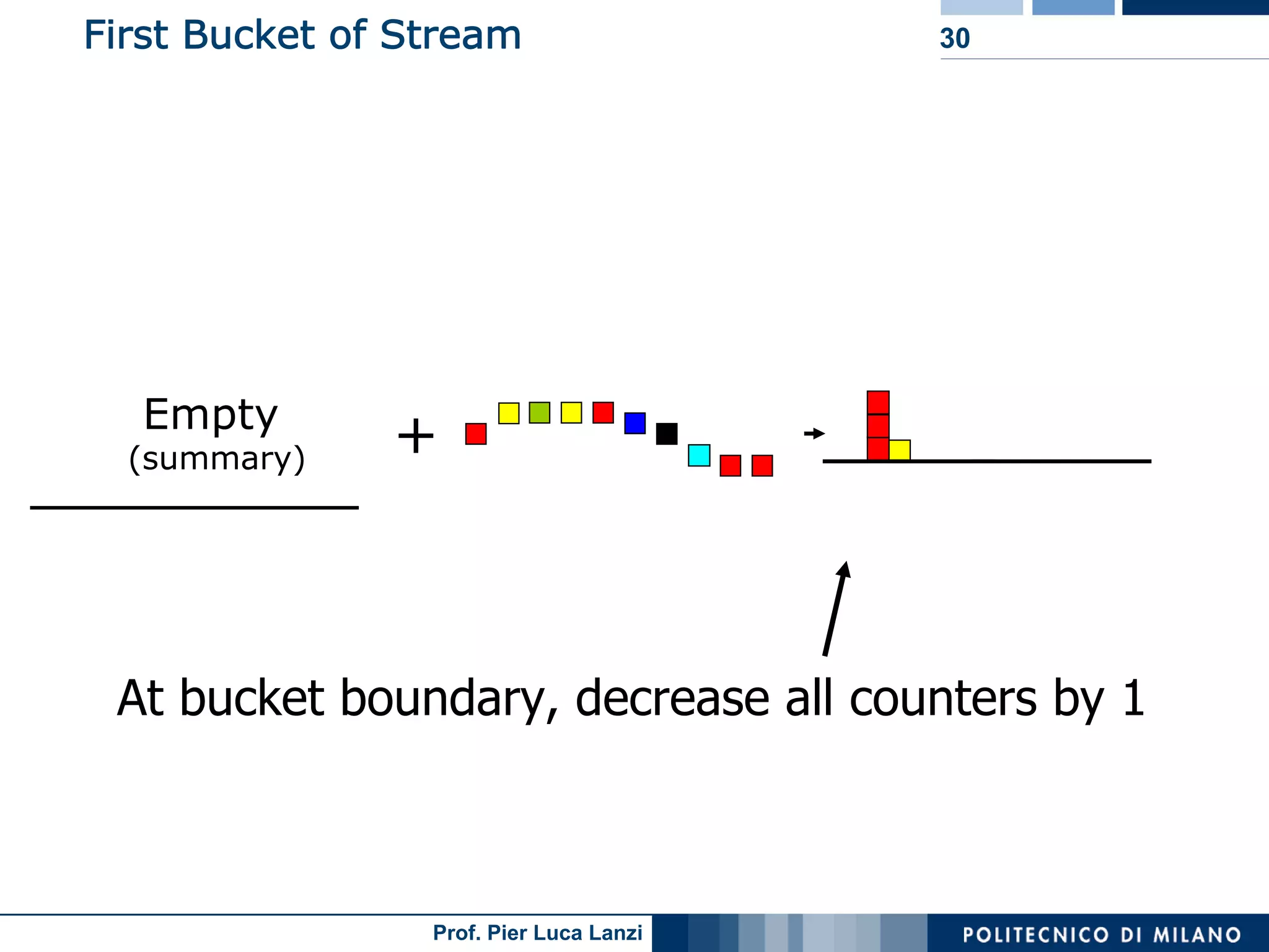
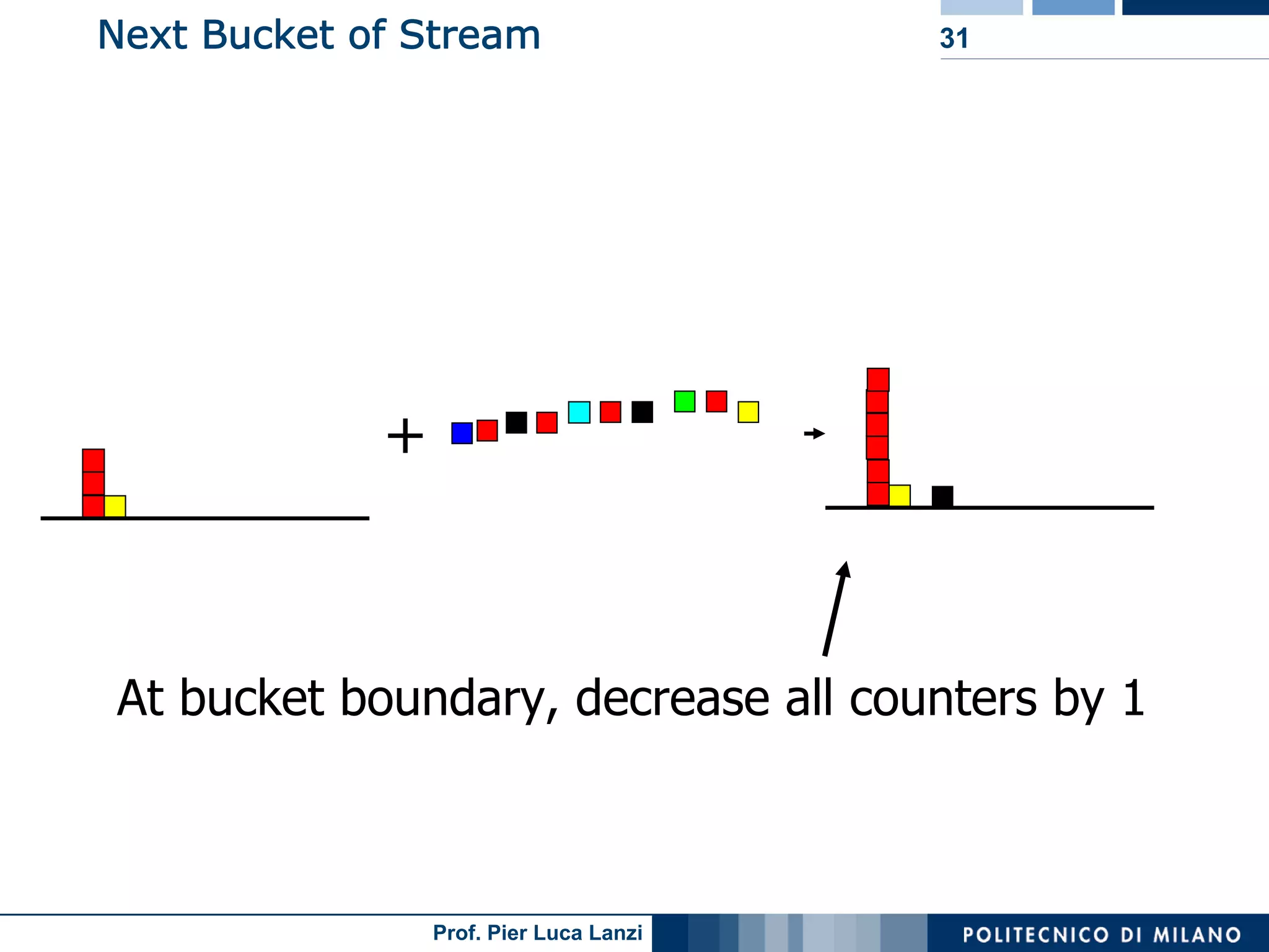
Focuses on algorithms like loss counting for efficient mining of frequent patterns in streaming data.
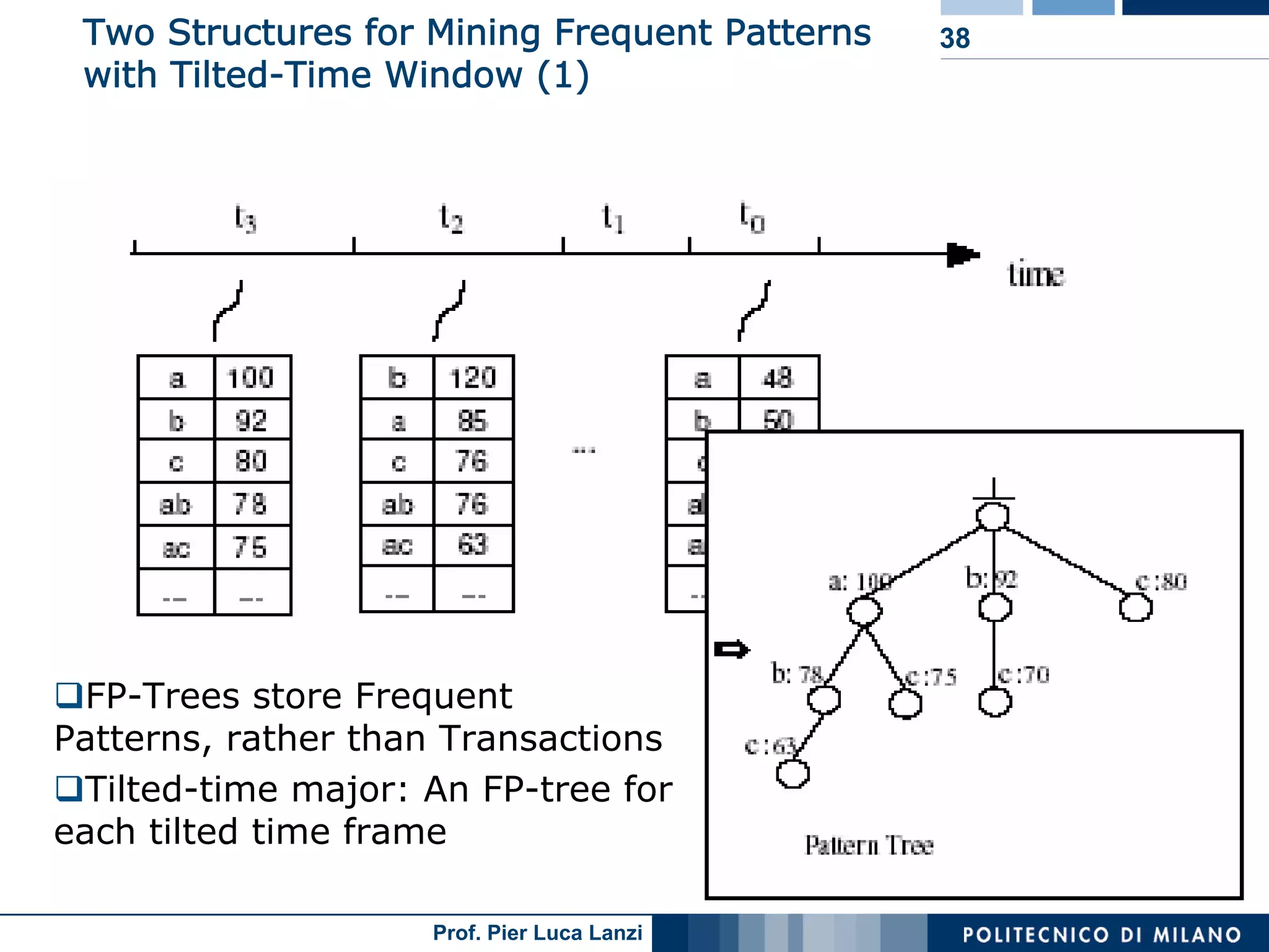
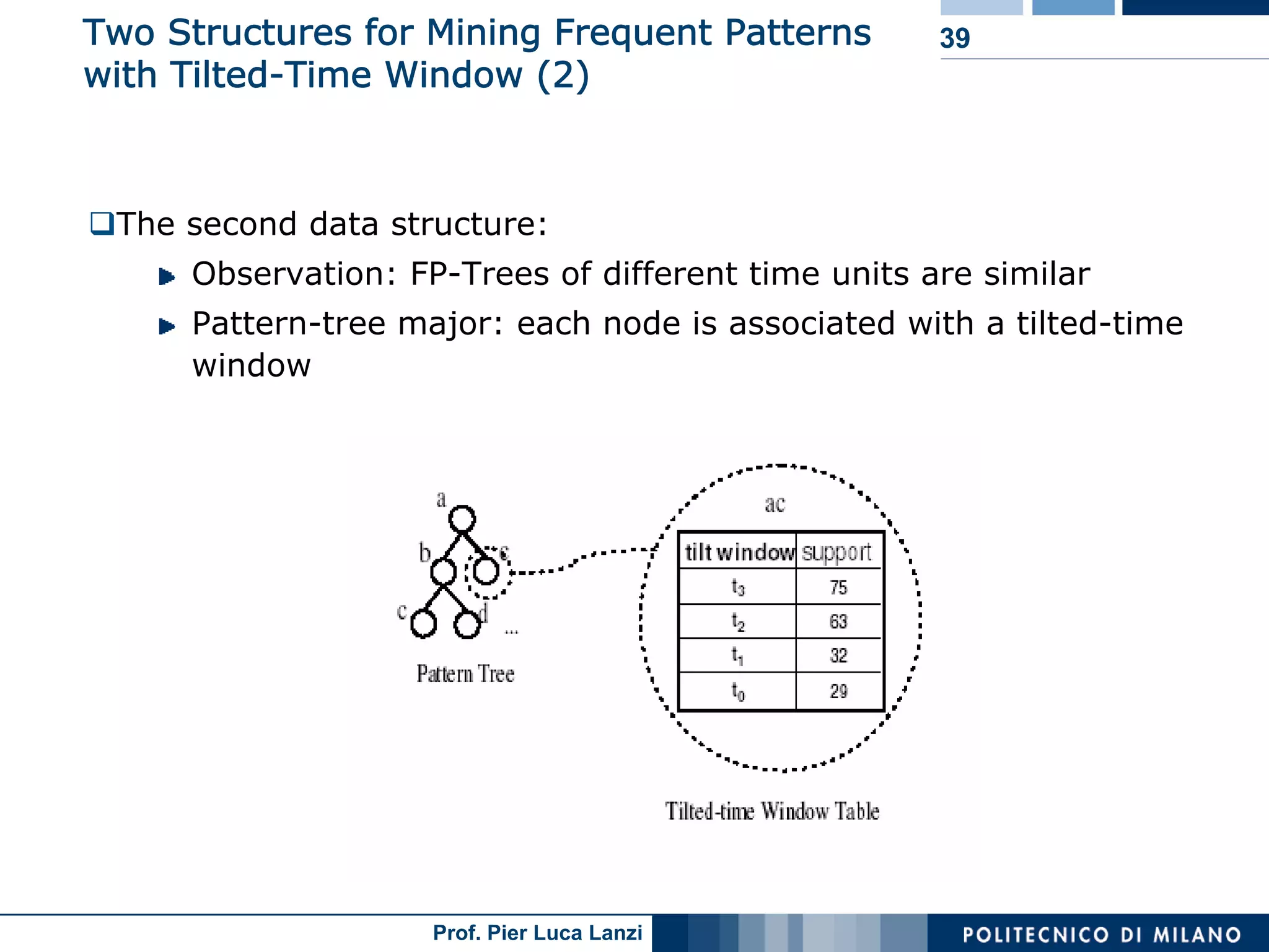
Techniques to track changes in frequent patterns using tilted-time window frames.
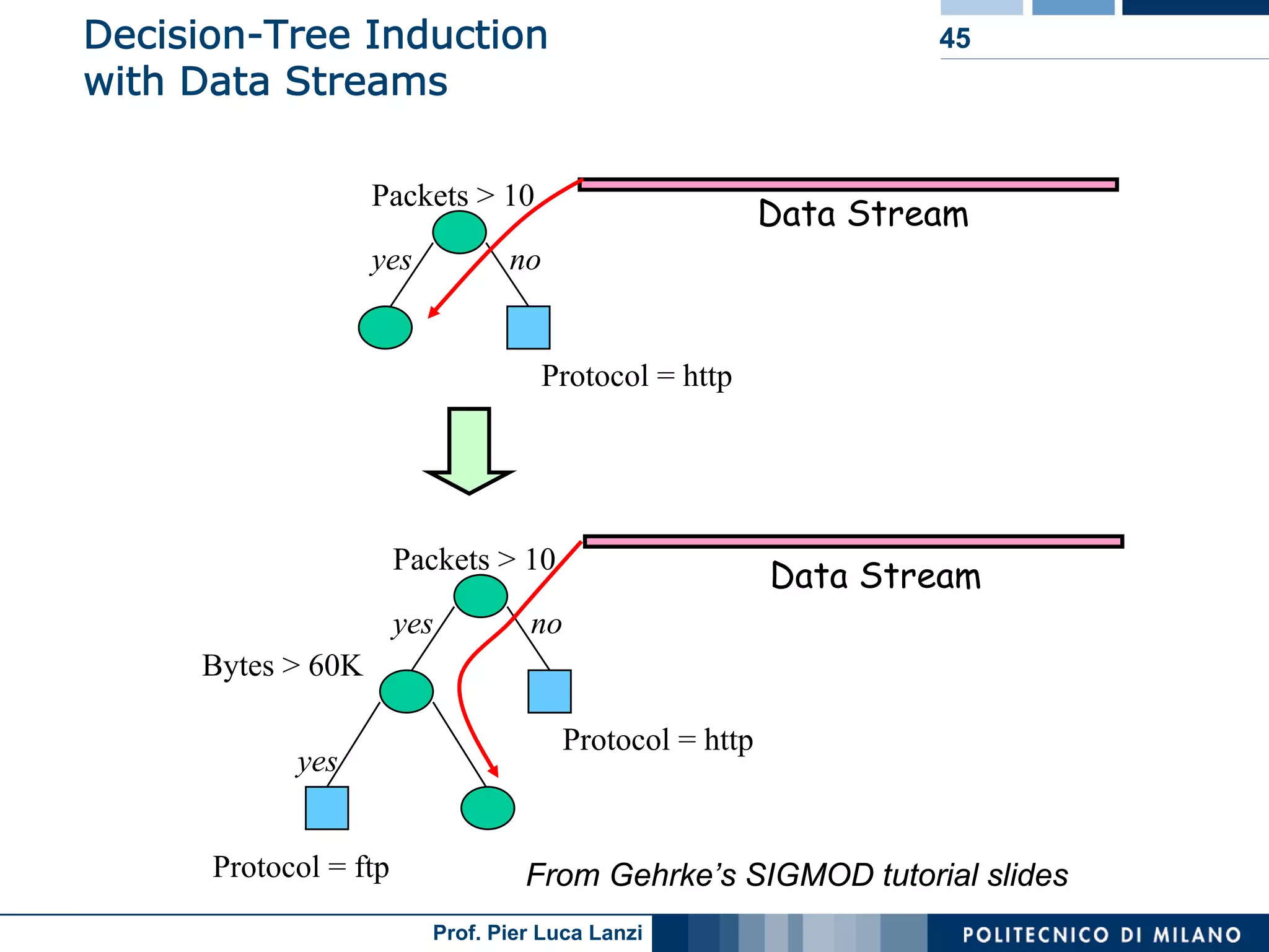
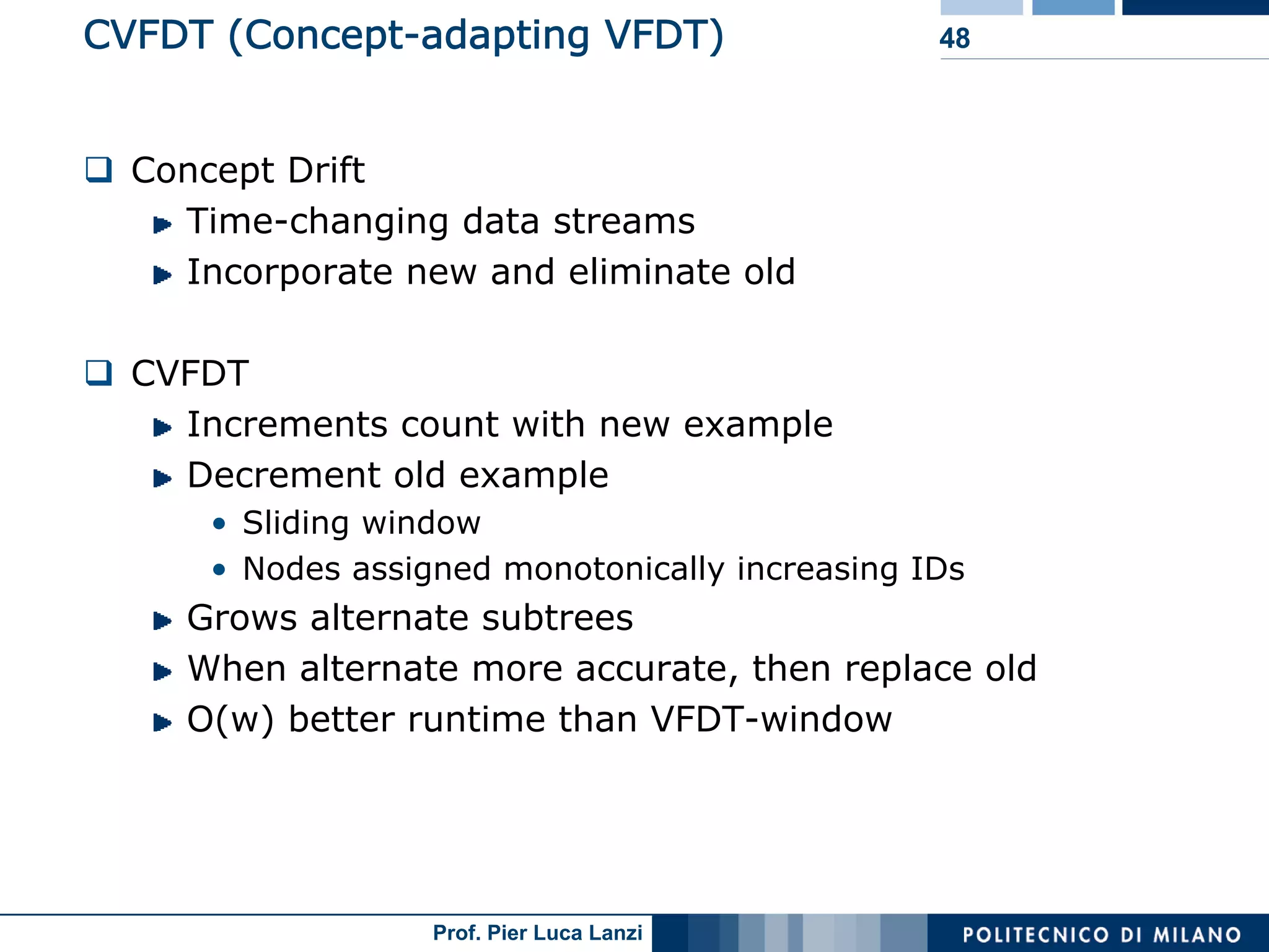
Discusses challenges in classifying dynamic data streams and known methods like decision trees.
Introduces Hoeffding trees for stream classification and its effectiveness based on limited sample analysis.
VFDT method enhancements improve speed and memory usage for fast decision tree classification.
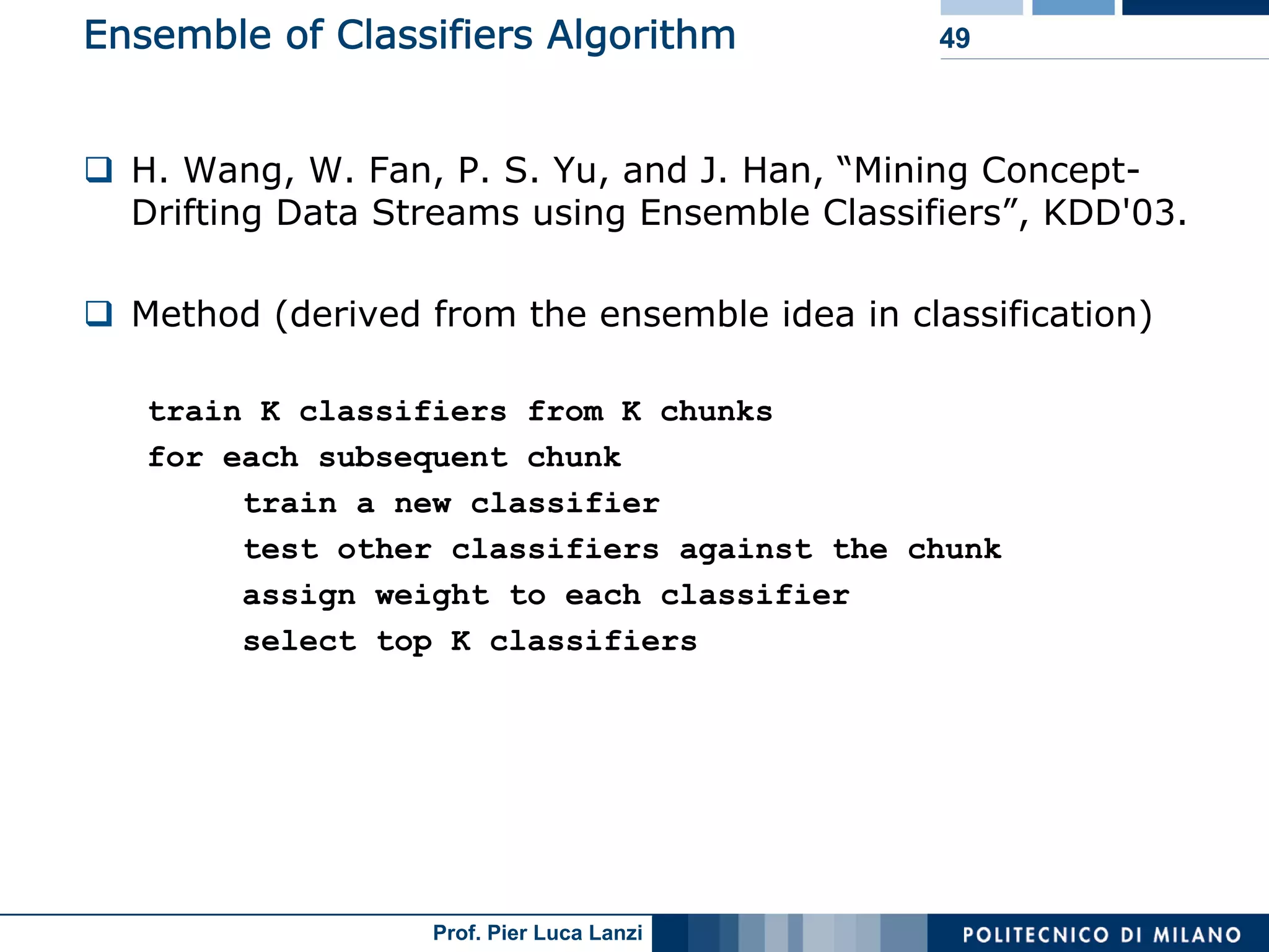
Ensemble classifiers adapt to concept drift, incrementally improving classification accuracy over time.
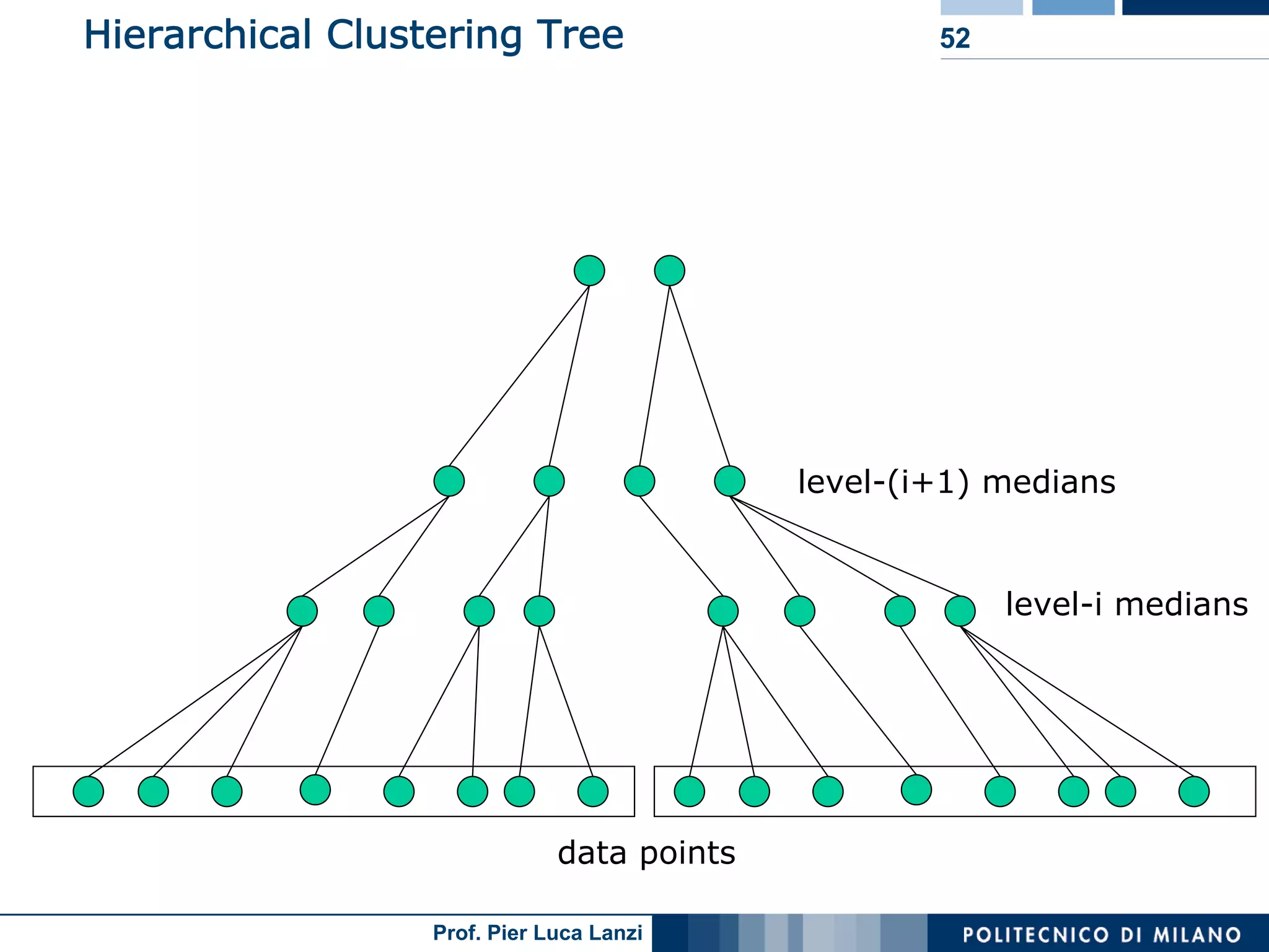
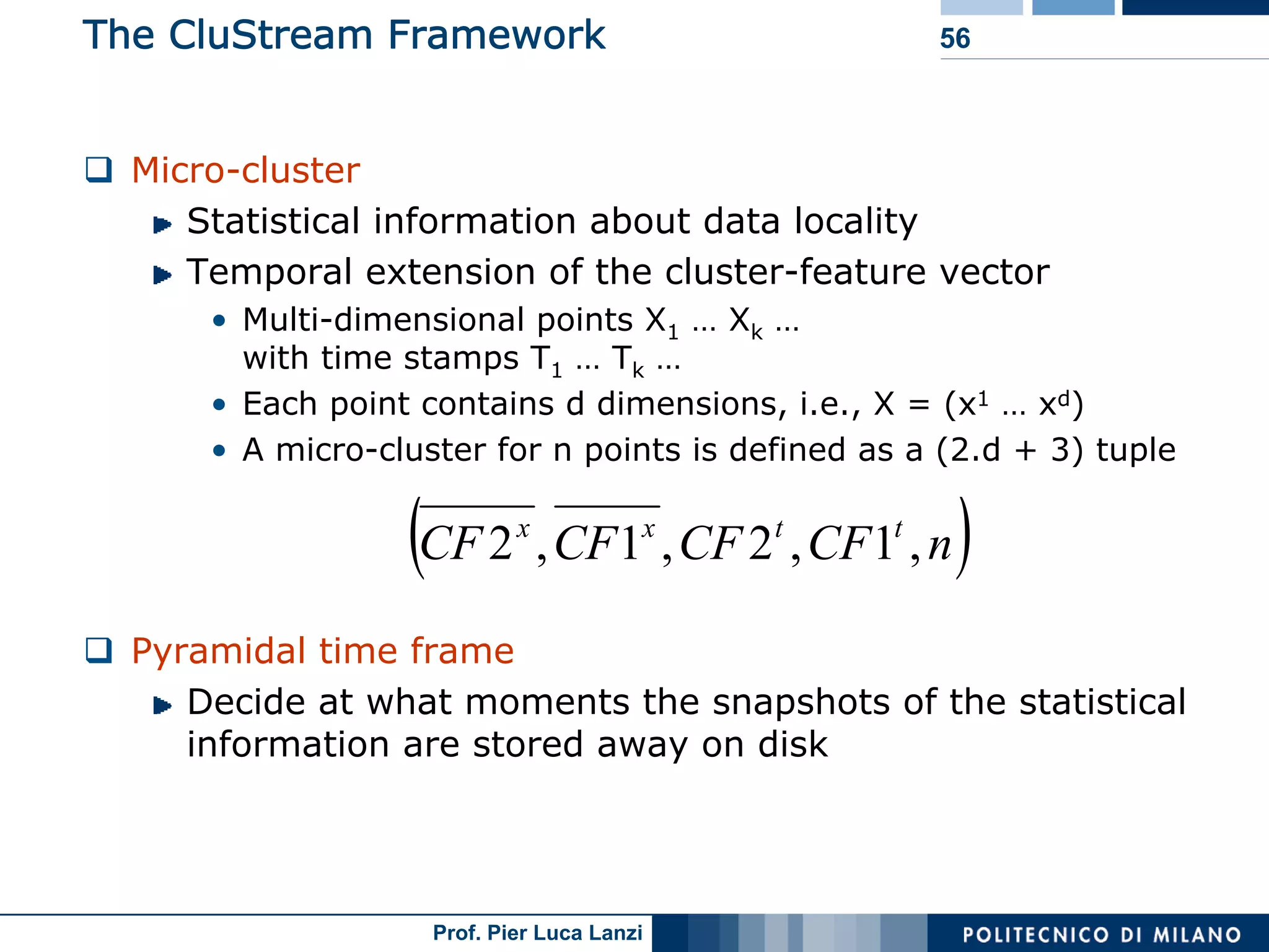
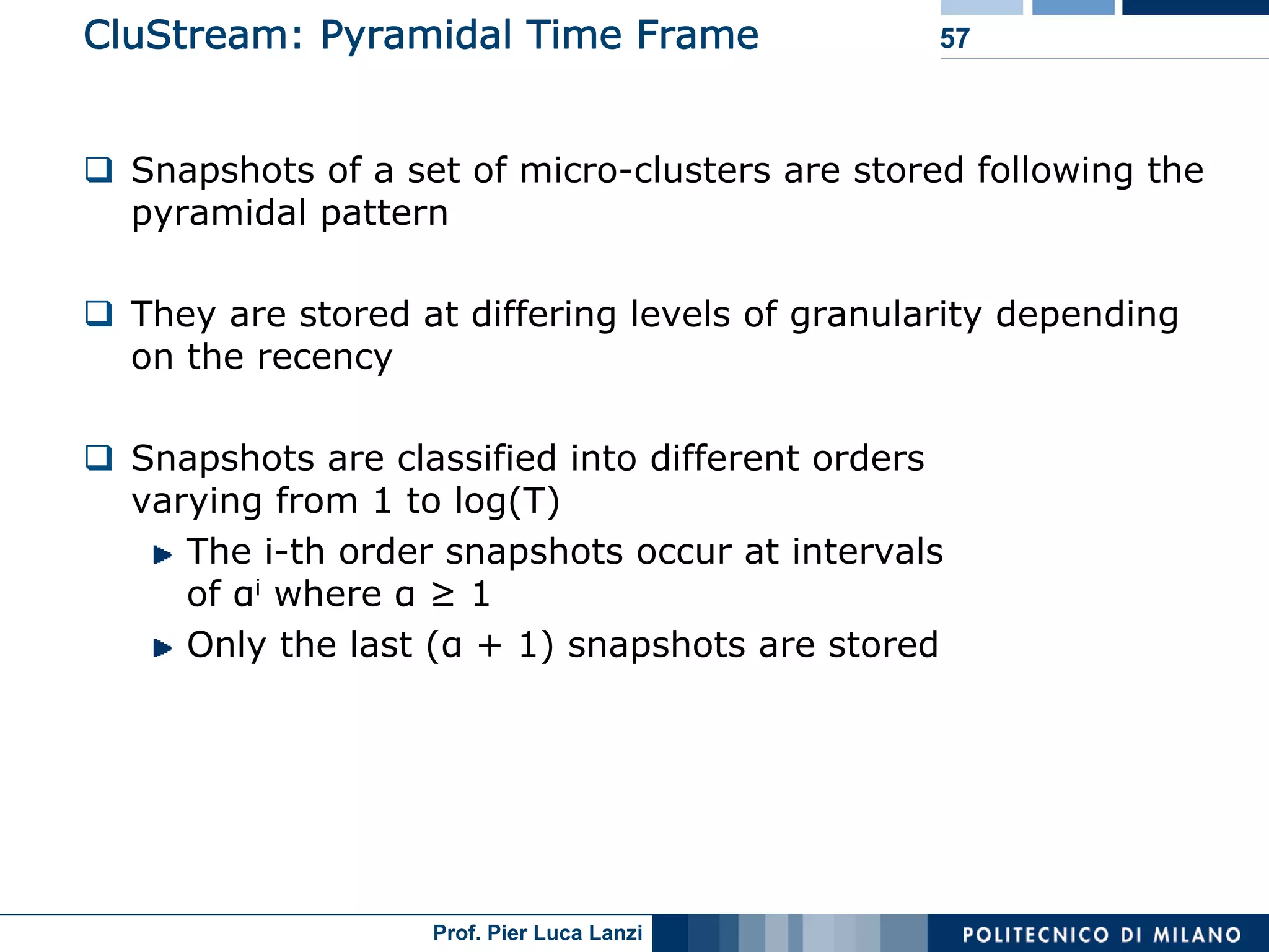
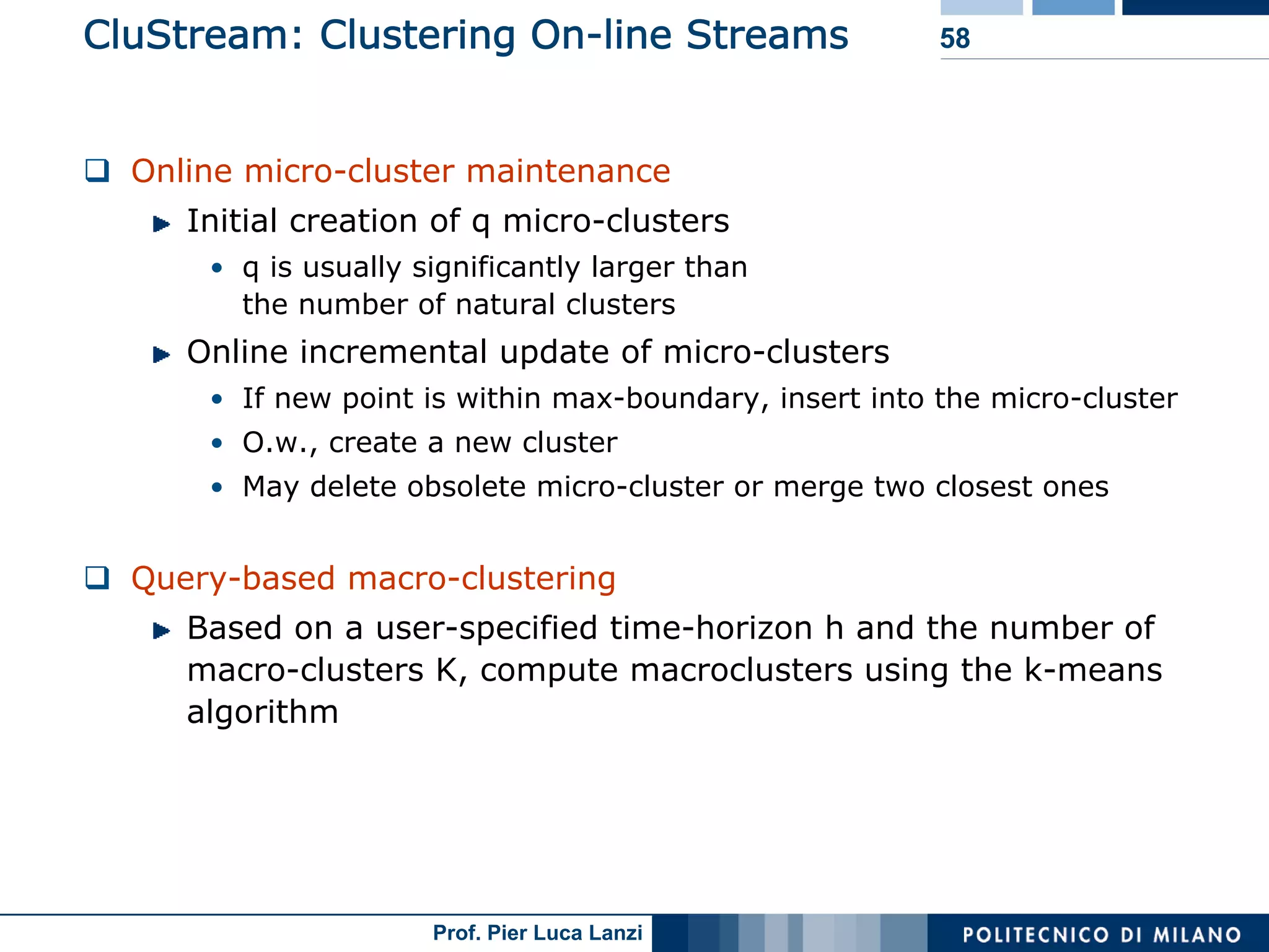
Diverse approaches for clustering evolving data streams, focusing on micro-clustering and macro-clustering strategies.
Outlines CluStream framework for efficient clustering of evolving streams using online/offline processes.
Highlights open research topics in mining stream data, including clustering and anomaly detection.
Concludes on the ongoing research in stream mining, summarizing the focus on system architecture and efficiency.
Lists references for further reading on stream data mining research and methodologies.