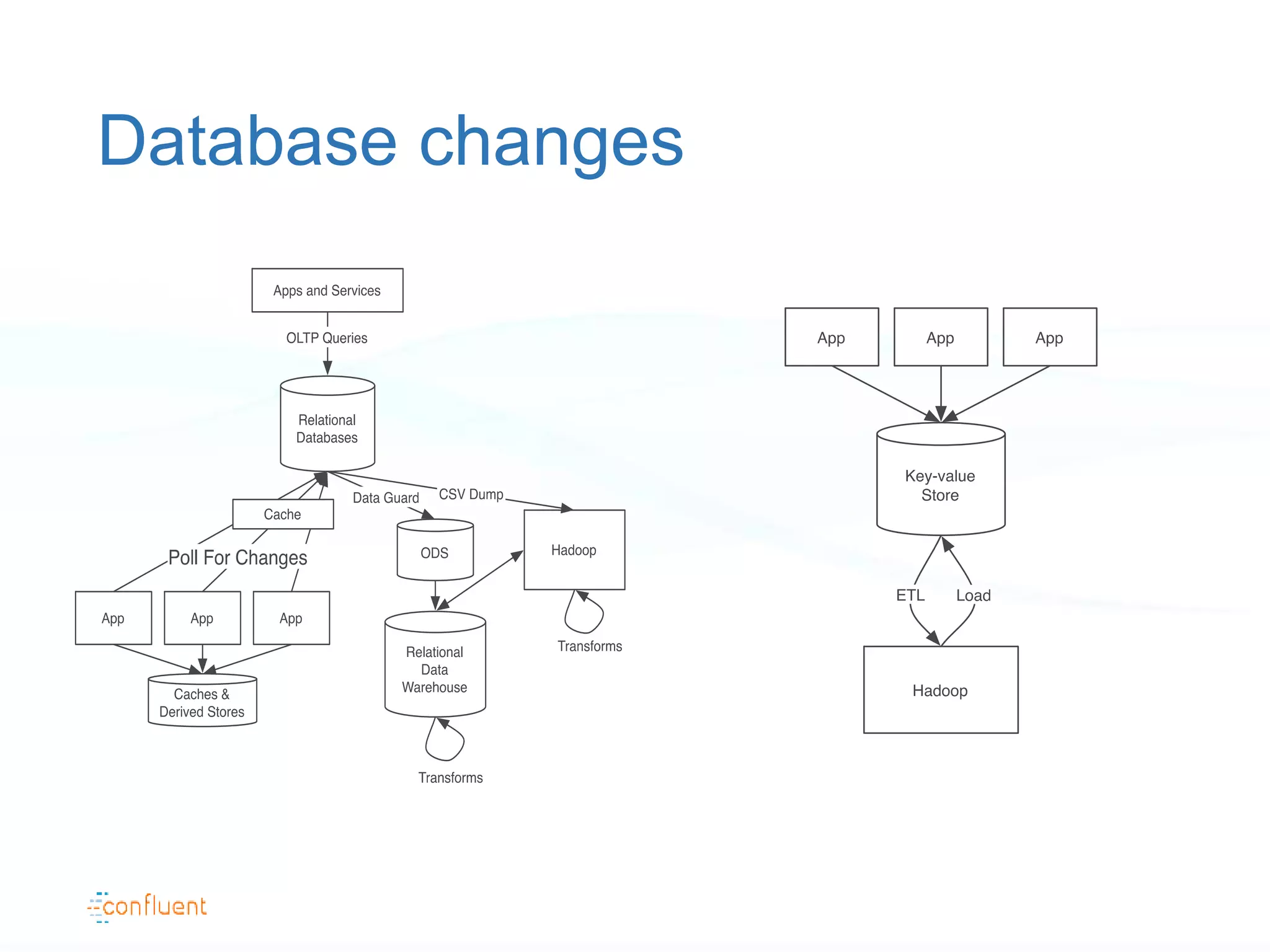
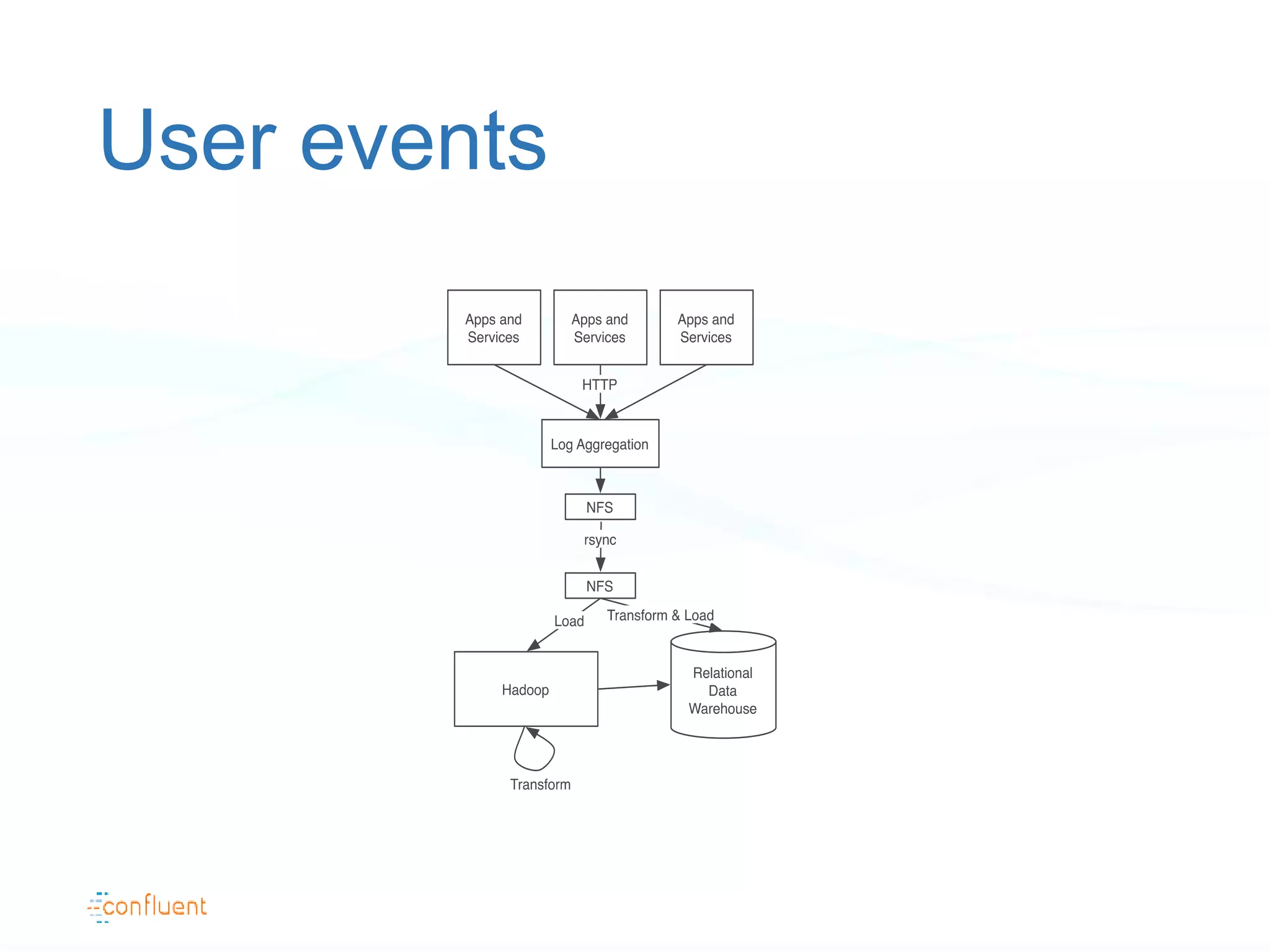
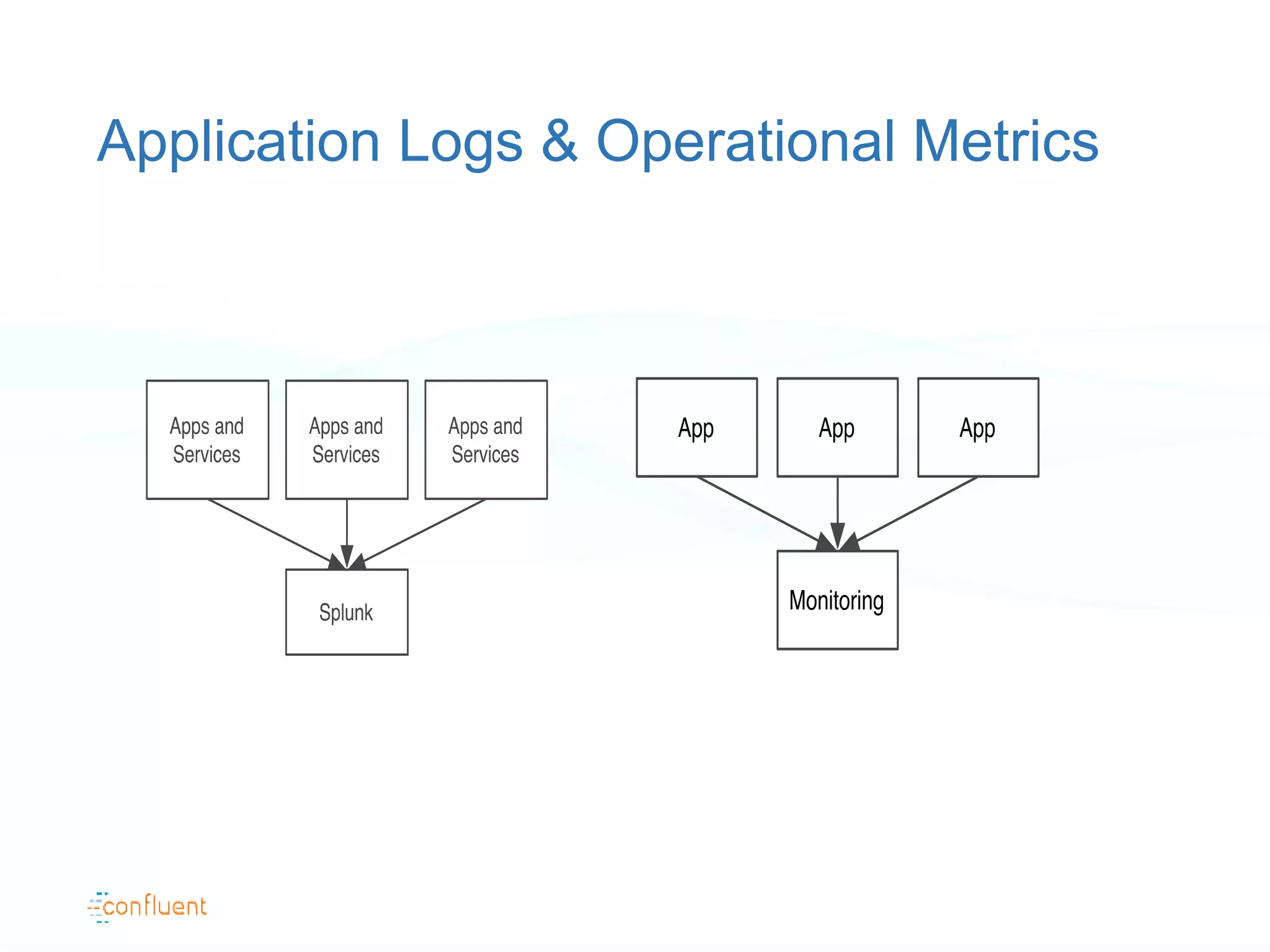
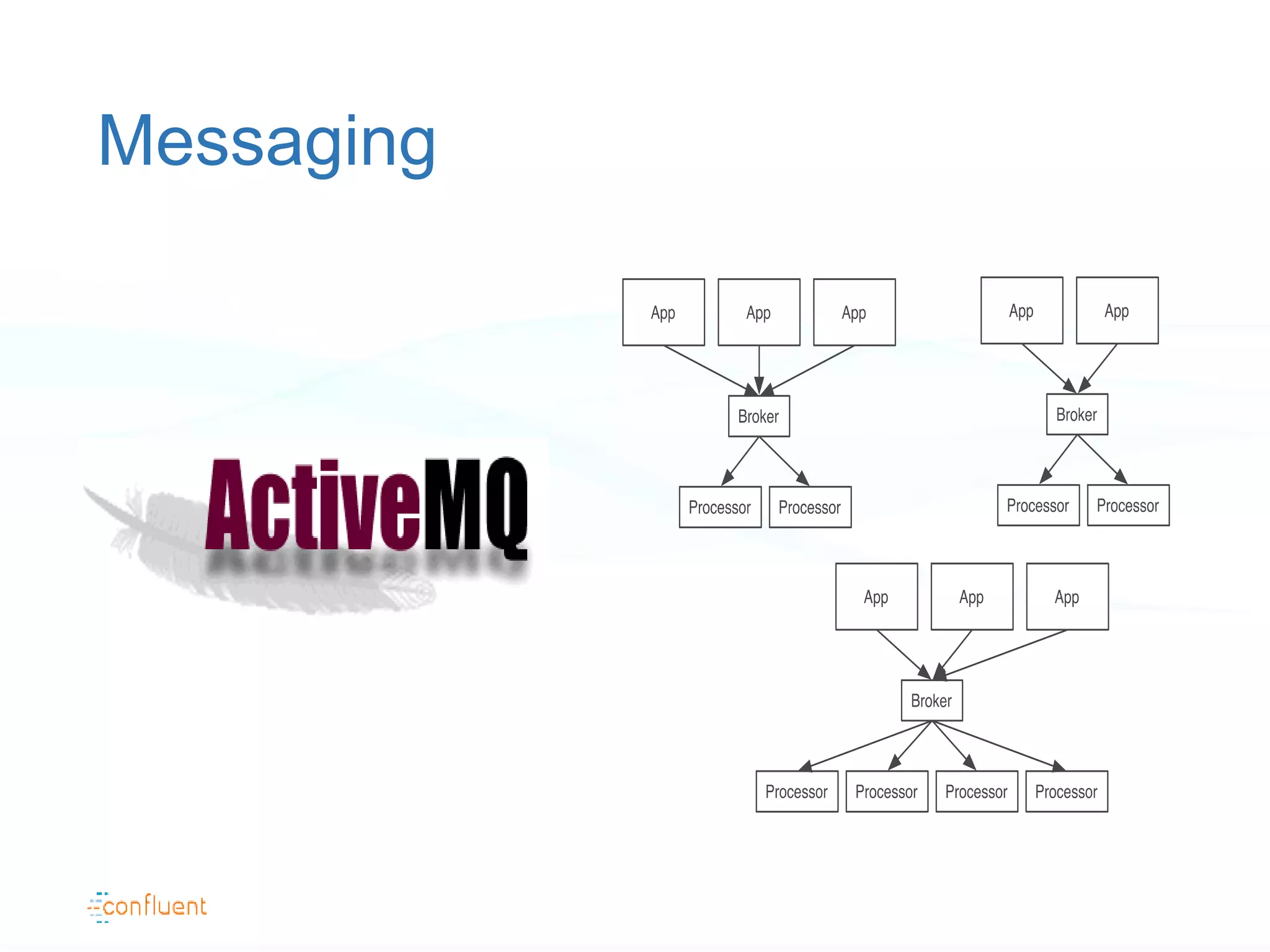
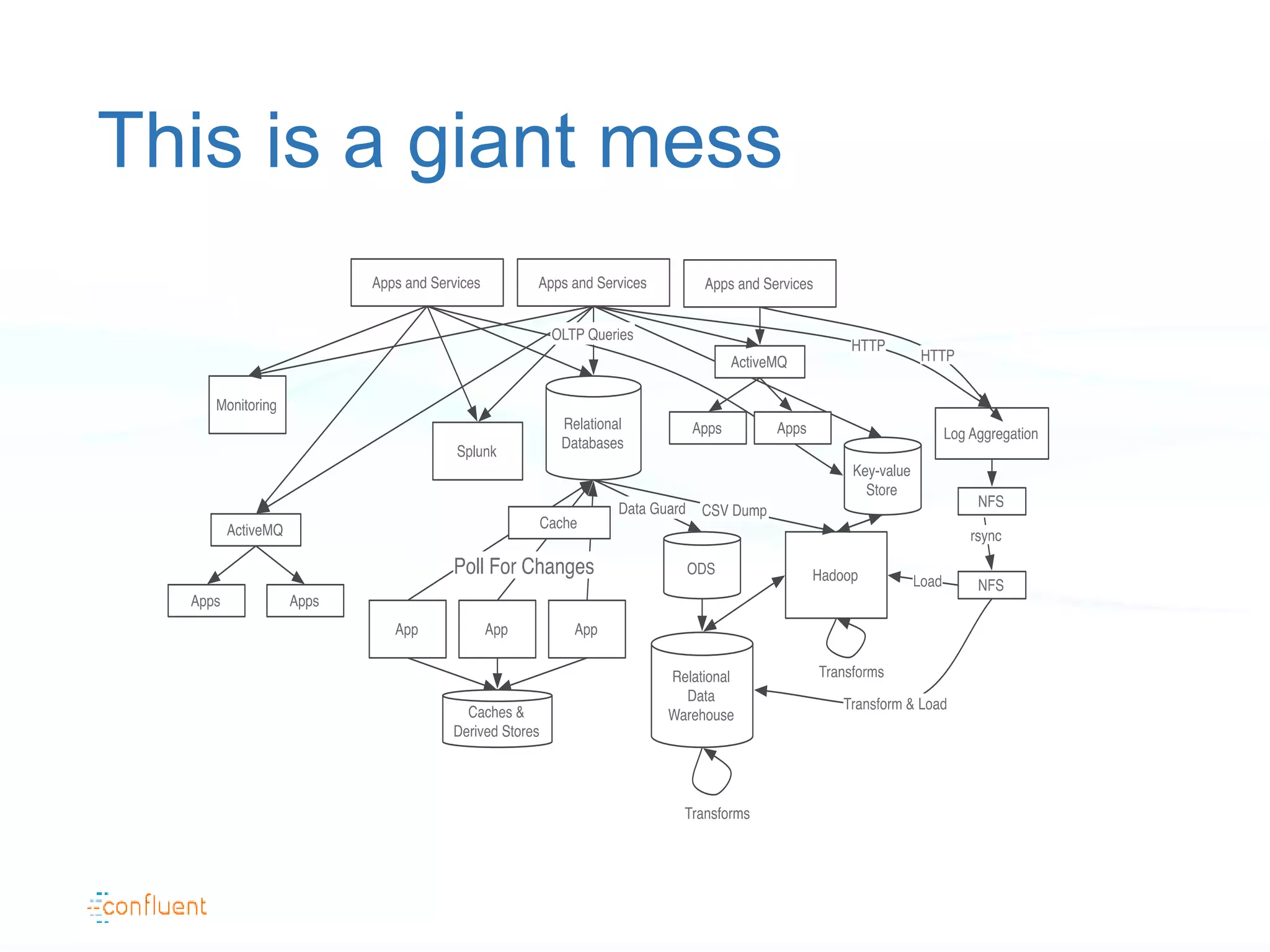
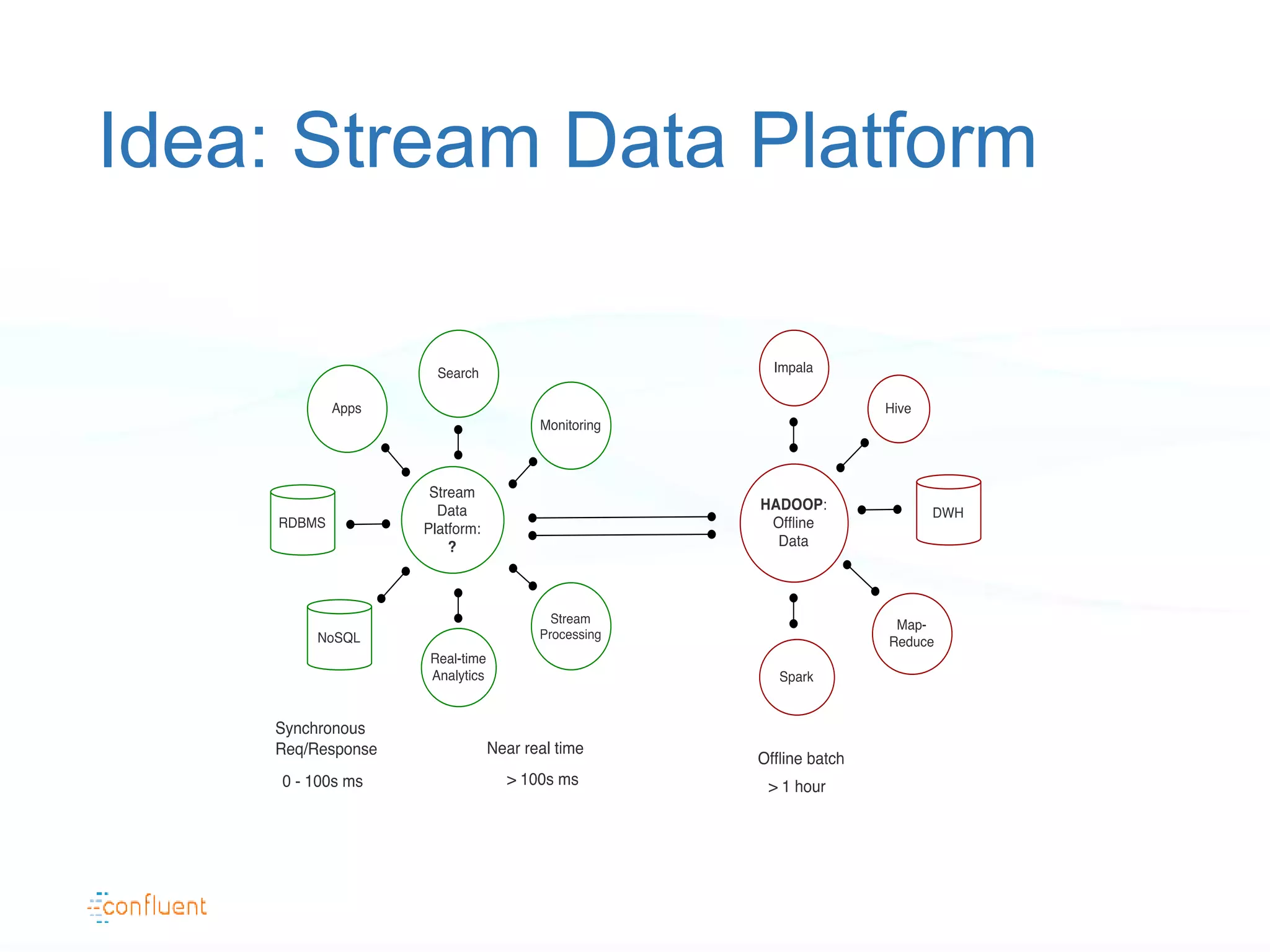
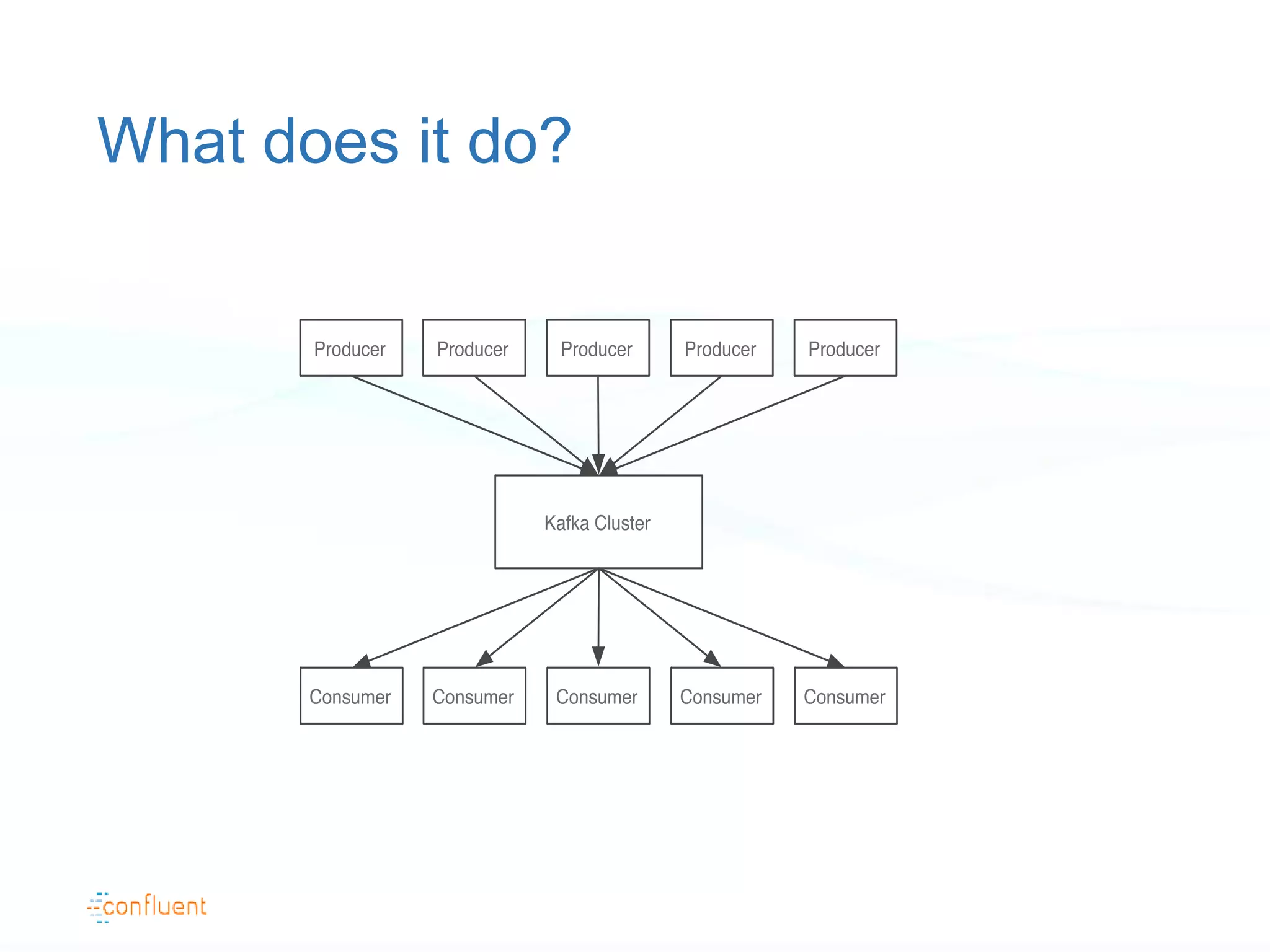
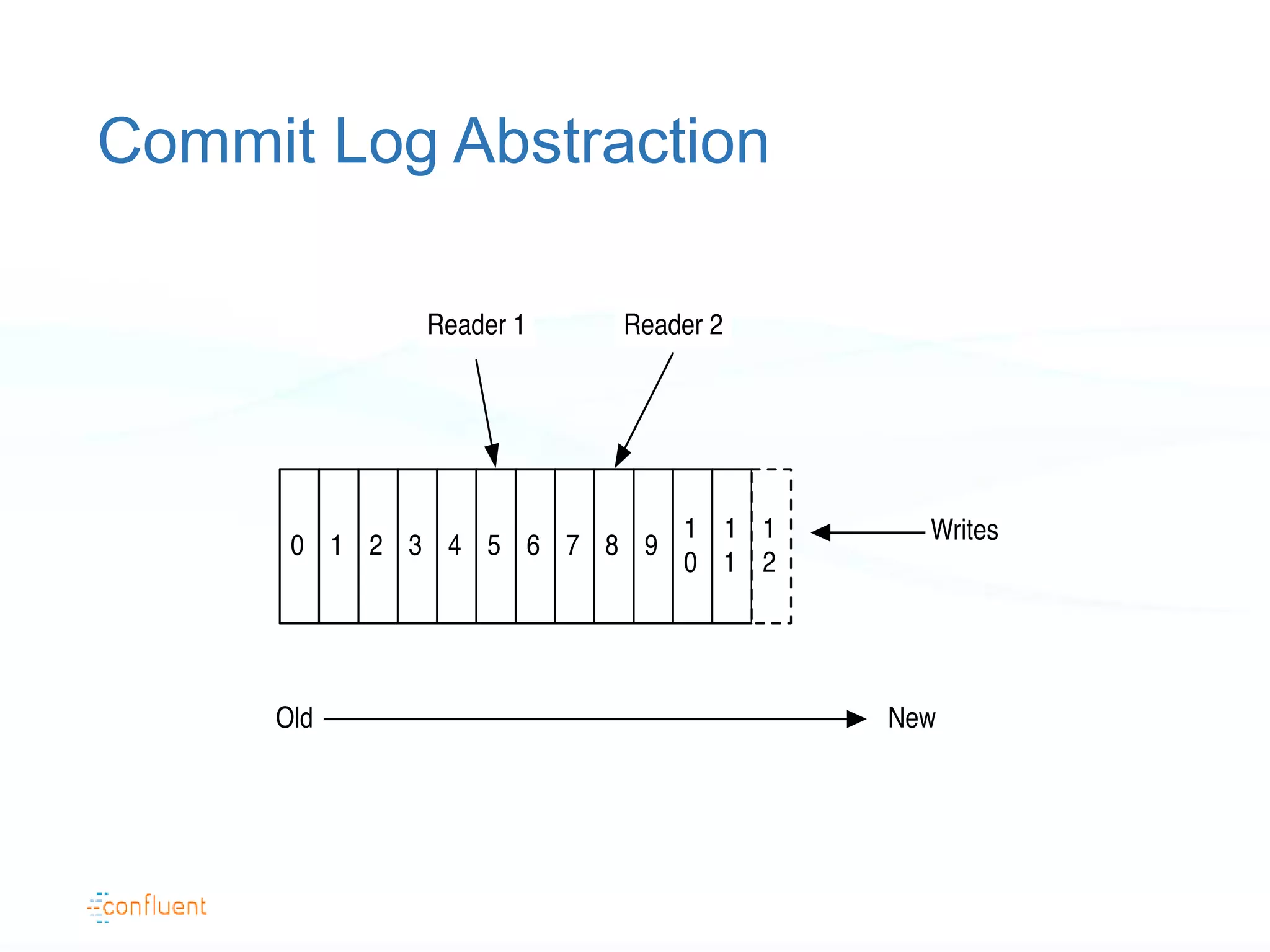
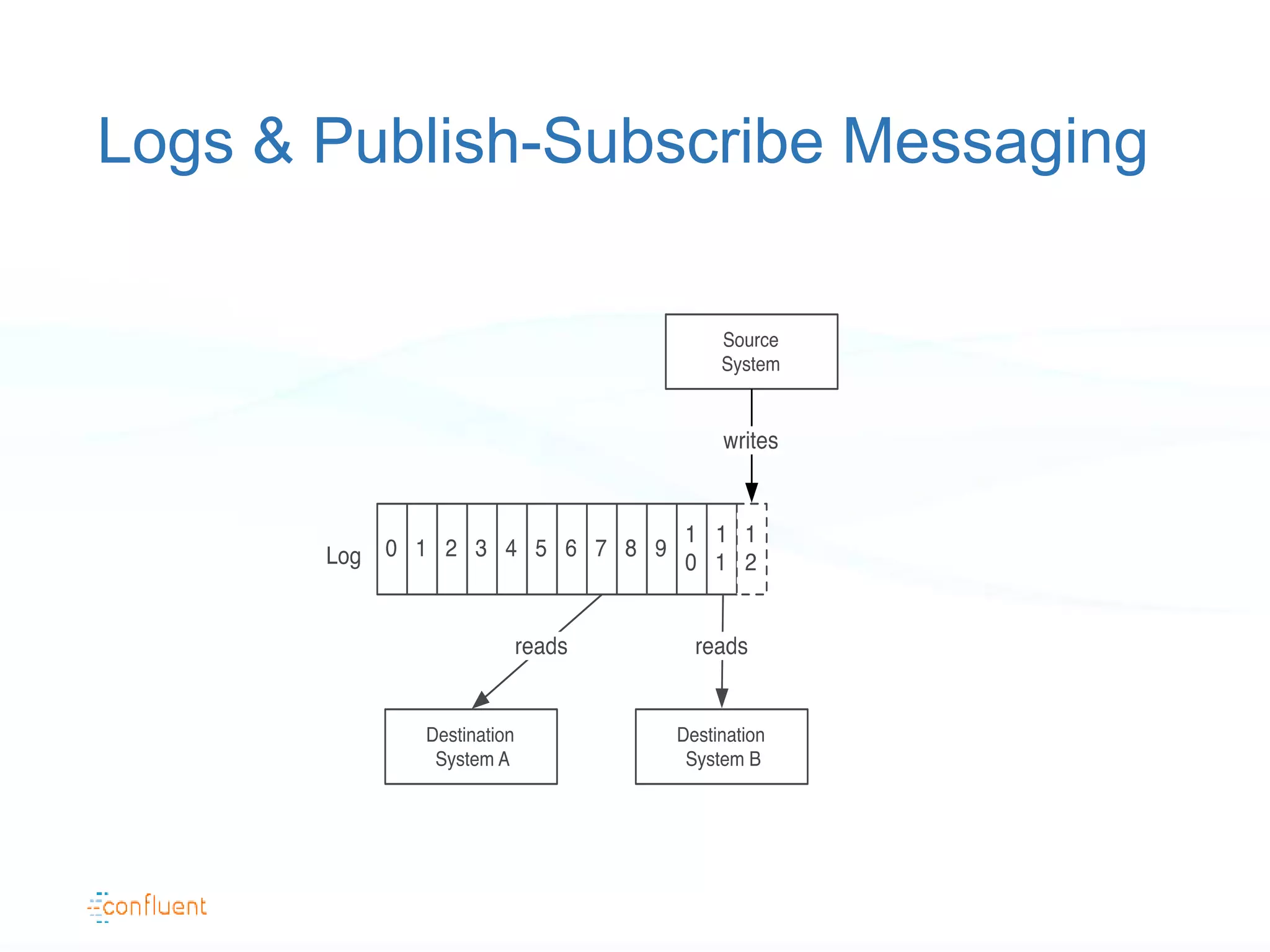
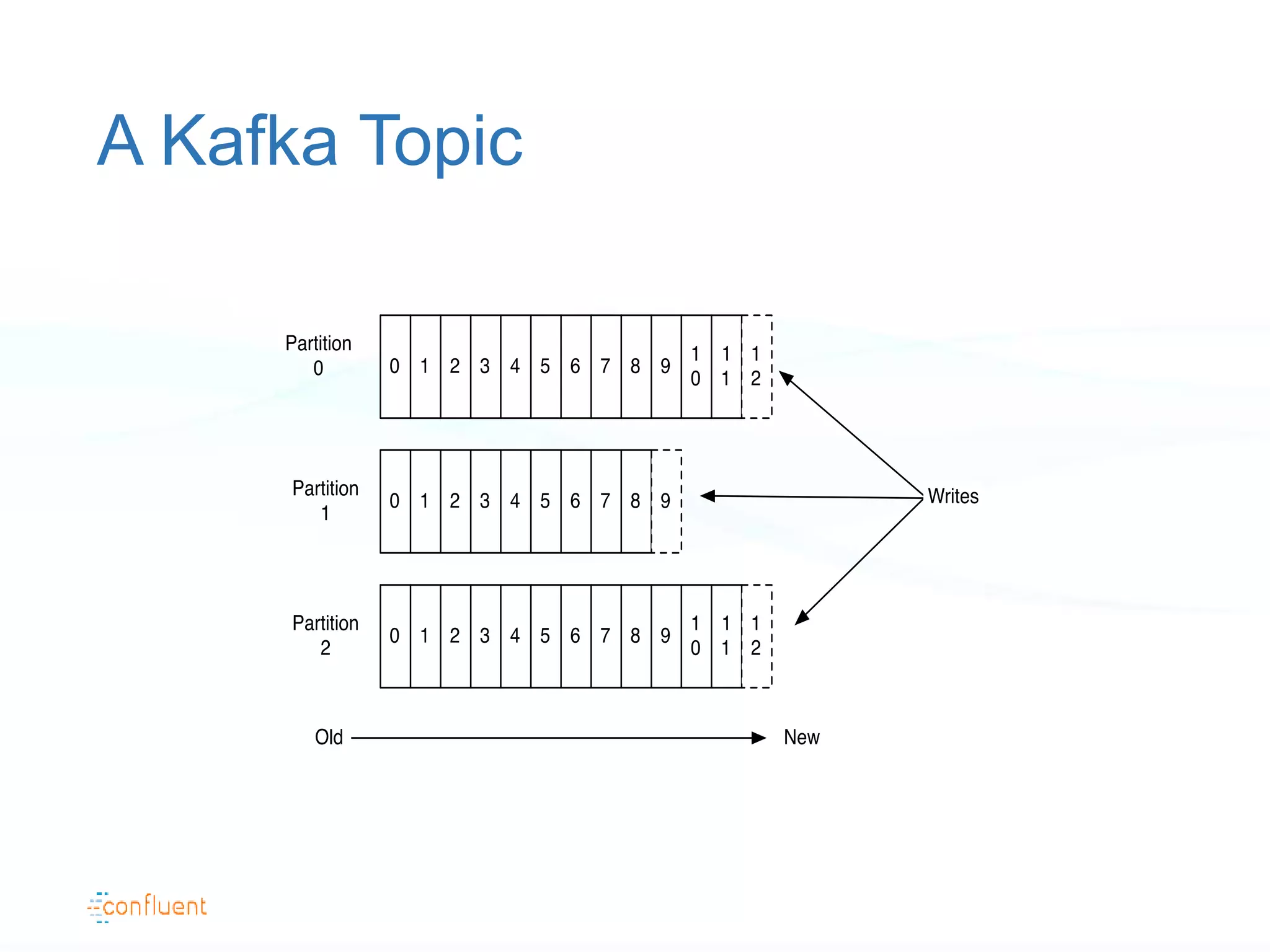
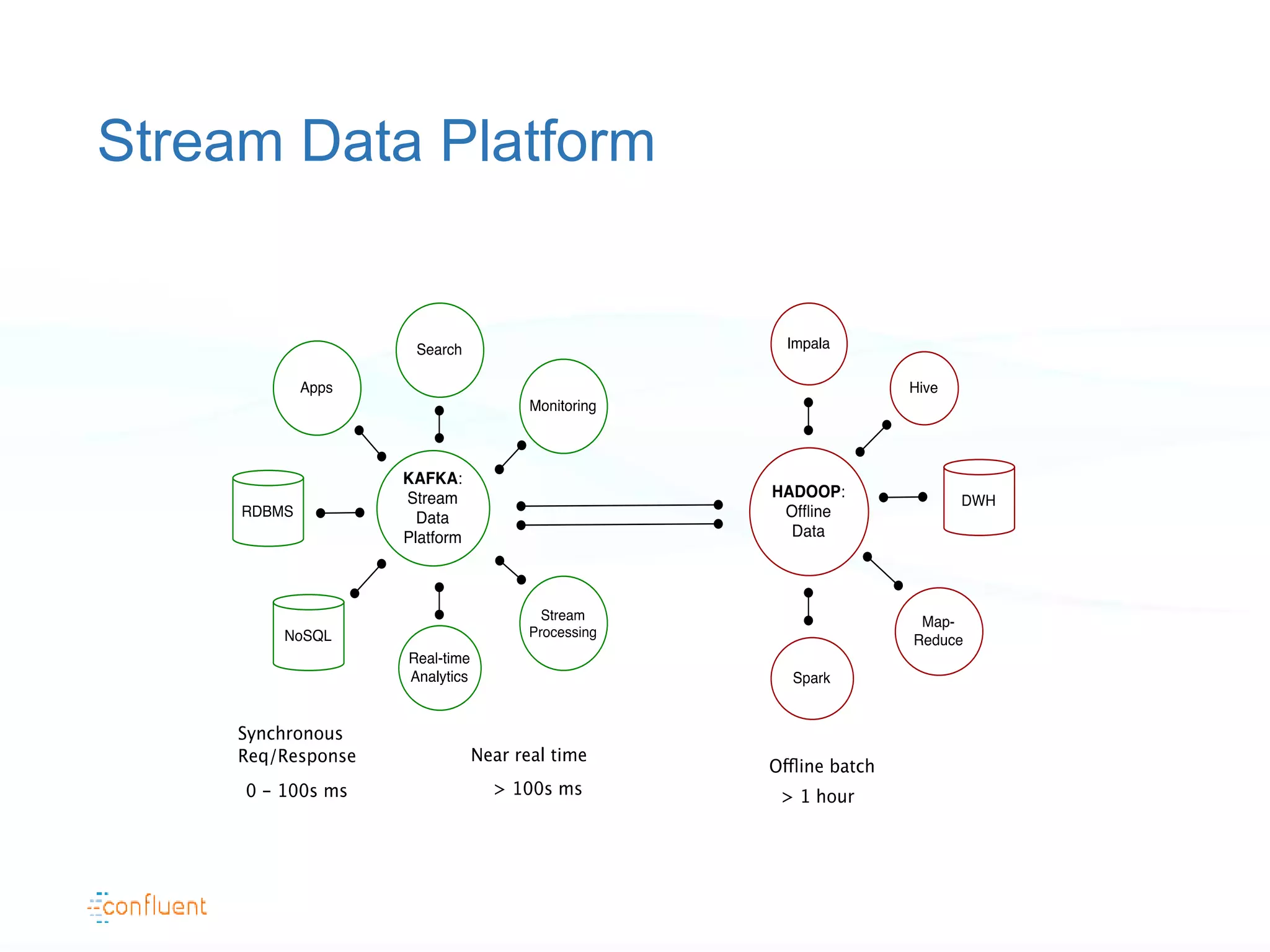
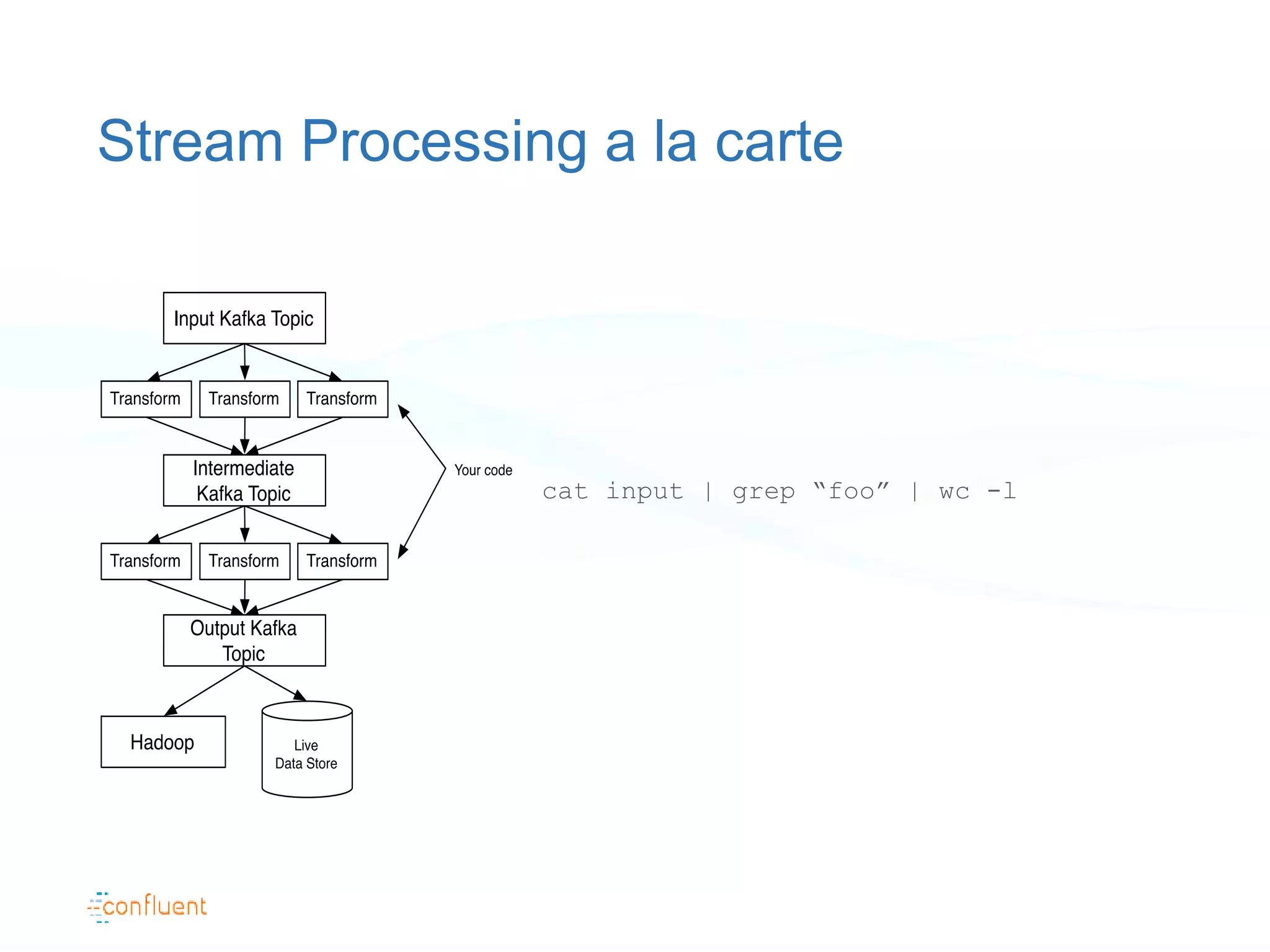
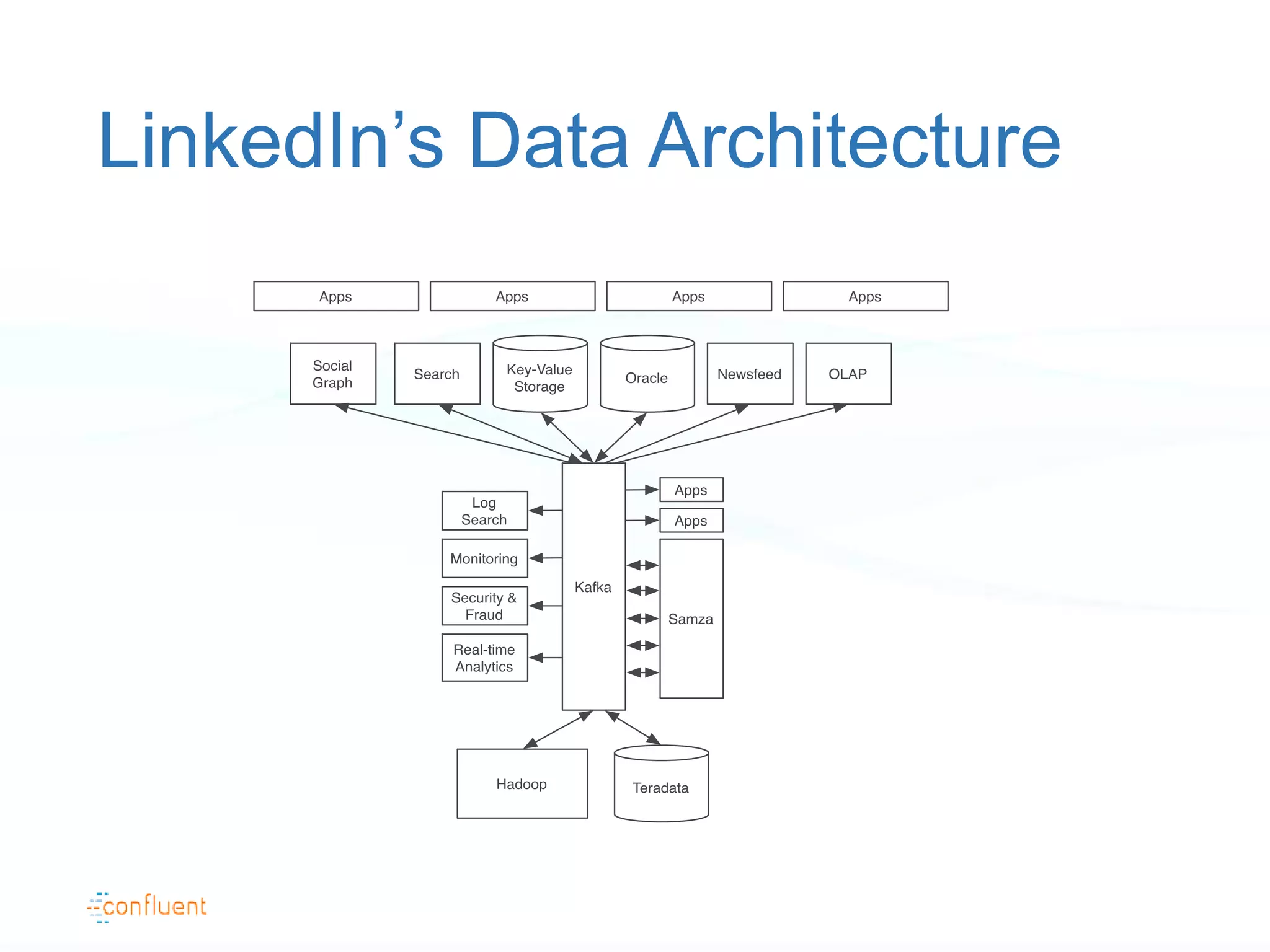
The document discusses the evolution of data handling at LinkedIn, highlighting the shift towards a stream data platform to manage diverse data sources and formats. It introduces Apache Kafka, designed to provide scalable and efficient stream processing, and outlines its key features like message ordering, persistence, and fault tolerance. The use of Kafka at LinkedIn results in handling over 1.2 trillion messages written and 3.4 trillion messages read daily, contributing to a wide range of applications including search and social networking.