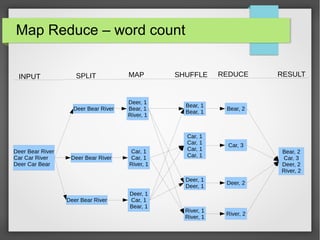
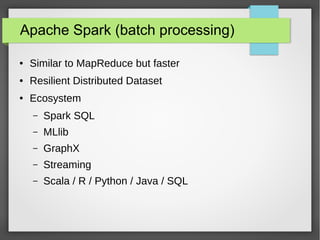
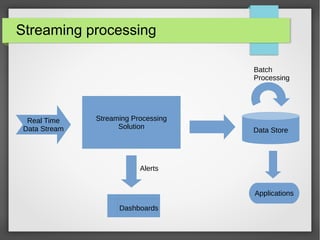
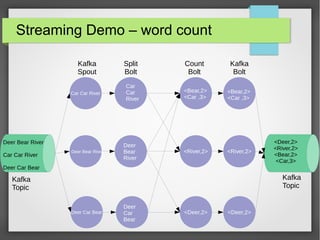
The document discusses big data streaming processing using Apache Storm, covering key concepts like batch and streaming processing, NoSQL persistence, and relevant frameworks like Kafka. It highlights the characteristics, pros and cons of big data, and introduces various data models and processing modes. Additionally, it provides an overview of storm architecture, its components, and a streaming processing demo with an emphasis on scalability, monitoring, and design considerations for big data applications.









![FOSSCOMM 2016
THANK YOU :-)
[ Updates / Questions / Comments ]
@qiozas](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bigdatastreaming-fosscomm2016-160419185832/85/Big-Data-Streaming-processing-using-Apache-Storm-FOSSCOMM-2016-35-320.jpg)