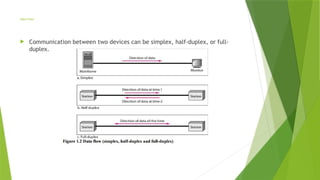
A computer network is a system of interconnected computing devices that exchange data and share resources using standardized communication protocols. Networks enable devices (such as computers, servers, routers, and switches) to communicate efficiently over wired or wireless media.
1. Key Components of a Computer Network
(A) Nodes (Devices)
End Devices (Hosts): Computers, smartphones, servers, IoT devices.
Network Devices: Routers, switches, hubs, modems, gateways, access points.
(B) Communication Media
Wired: Ethernet cables (Twisted pair, Coaxial, Fiber-optic).
Wireless: Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, Cellular (4G/5G), Satellite.
(C) Protocols
Define rules for data transmission.
Examples: TCP/IP, HTTP, FTP, DNS, DHCP, UDP, ICMP.
(D) Network Topology
Physical or logical arrangement of nodes.
Common topologies: Star, Bus, Ring, Mesh, Tree, Hybrid.
(E) Network Services
Data Transfer (File Sharing, Streaming)
Resource Sharing (Printers, Storage)
Communication (Email, VoIP, Video Conferencing)
Remote Access (SSH, RDP, VPN)