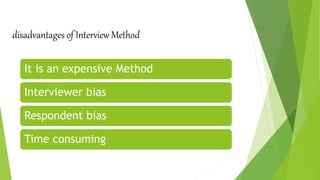
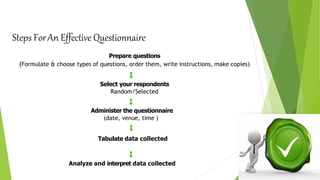
This document discusses various methods for collecting data for research purposes. It describes primary data collection methods like observation, interviews, questionnaires, and surveys which involve directly collecting original data. Secondary data collection involves using existing data collected by others. The key primary data collection methods covered are observation, interviews, questionnaires, and their types and steps. The advantages and disadvantages of each method are also outlined.