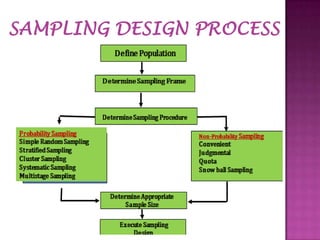
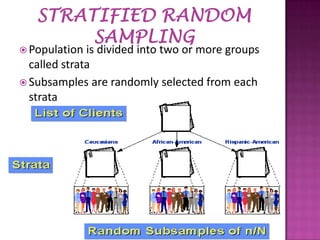
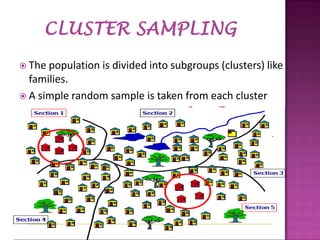
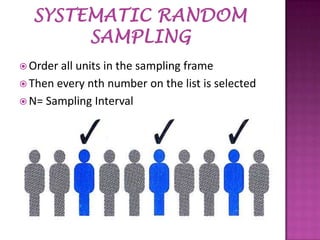
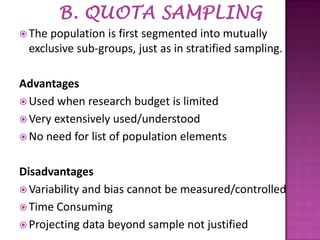
Sampling is the process of selecting a subset of individuals from within a population to estimate characteristics of the whole population. There are several sampling techniques including simple random sampling, stratified sampling, cluster sampling, systematic sampling, and non-probability sampling. Each technique has advantages and disadvantages related to accuracy, cost, and generalizability. Proper sampling helps reduce sampling errors and increase the reliability of making inferences about the population from a sample.