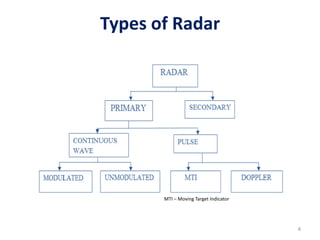
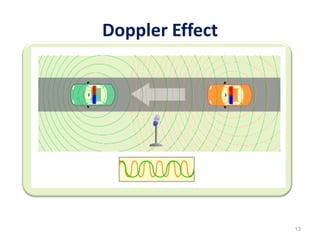
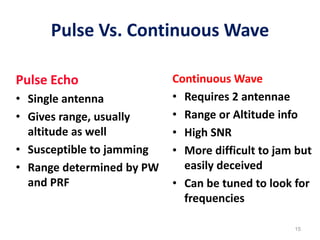
Radar uses electromagnetic waves to detect objects at a distance by transmitting pulses and measuring their reflection. The document discusses the basic principles and components of pulse transmission radar and continuous wave radar. It explains key terms like pulse width, repetition frequency, and Doppler shift. The types of modulation used in radar systems are also outlined.