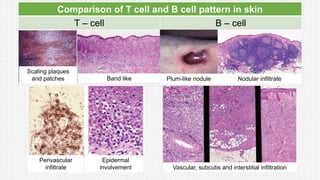
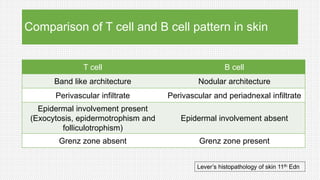
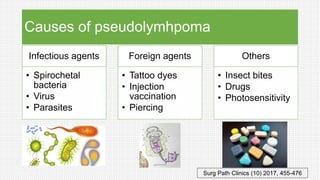
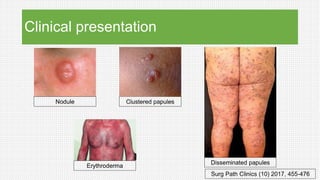
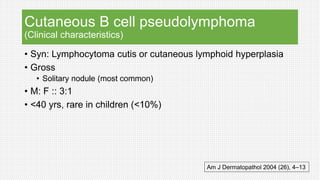
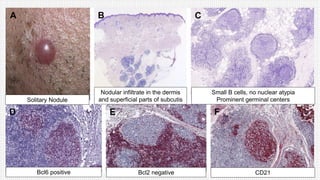
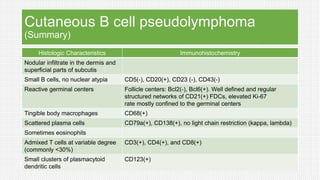
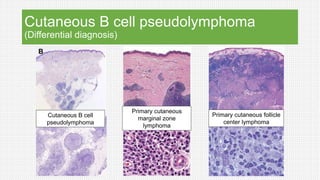
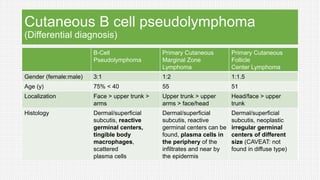
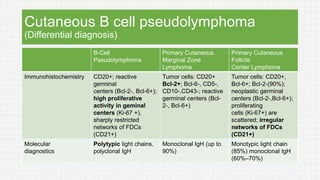
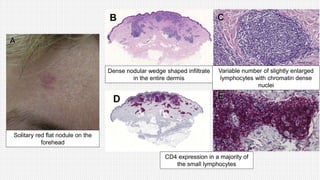
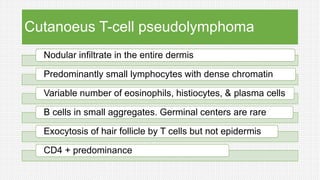
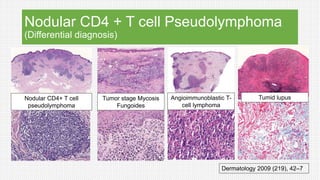
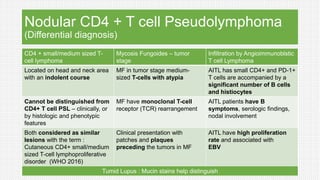
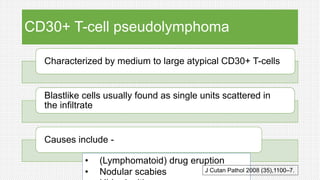
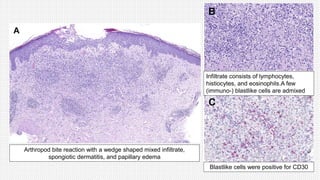
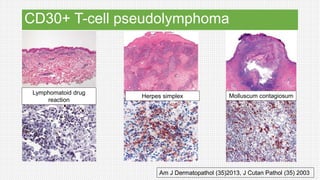
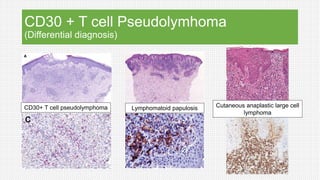
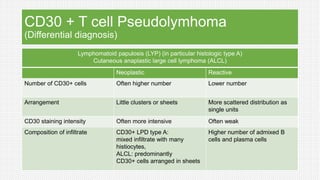
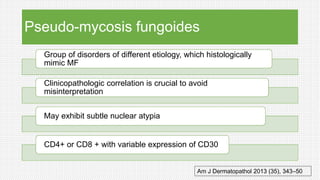
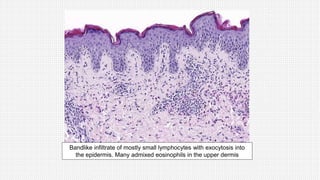
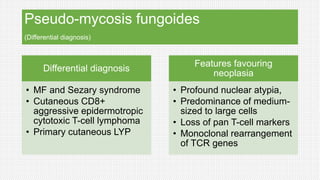
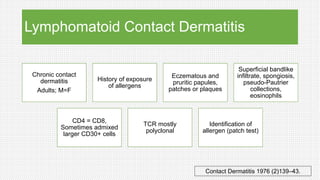
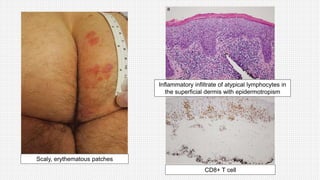
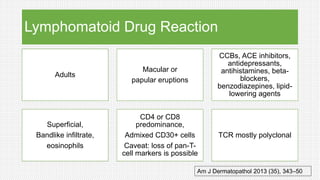
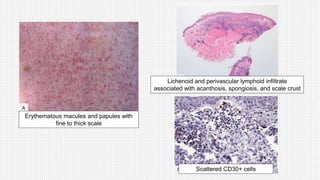
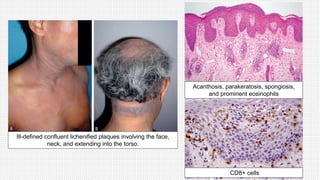
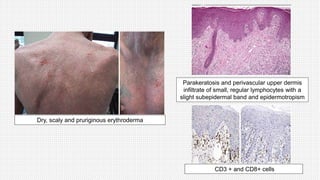
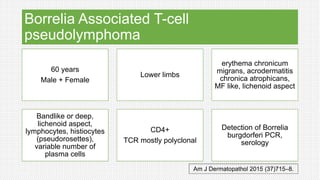
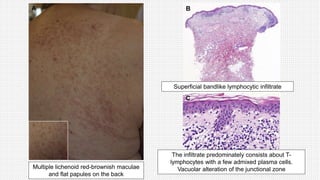
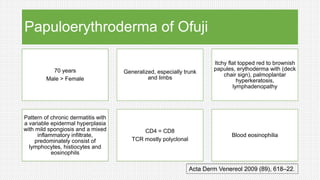
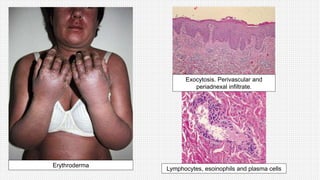
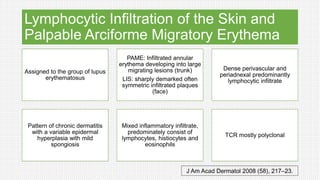
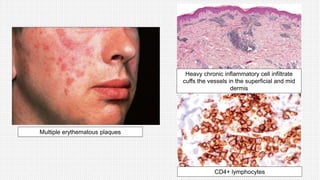
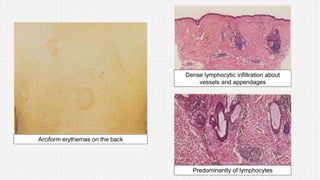
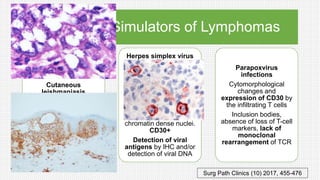
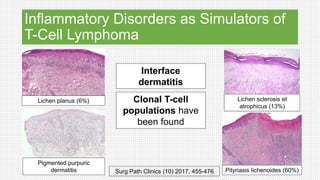
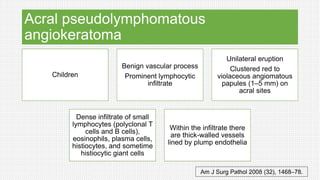
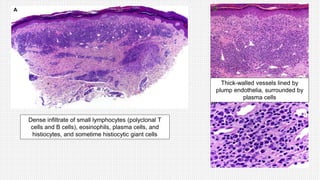
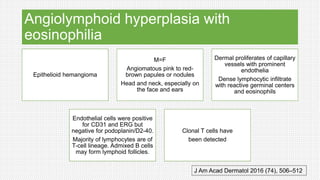
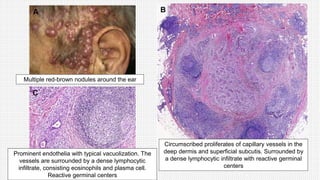
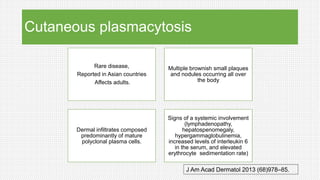
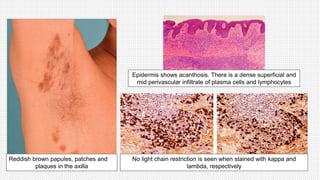
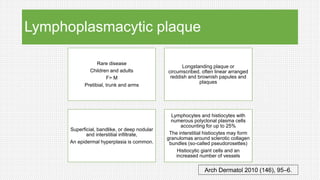
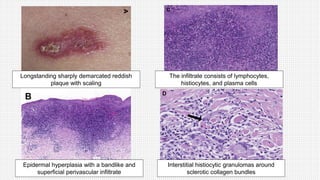
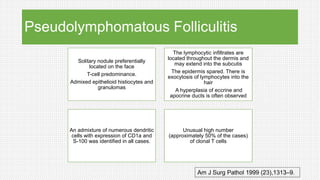
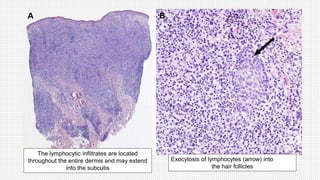
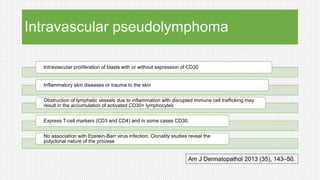
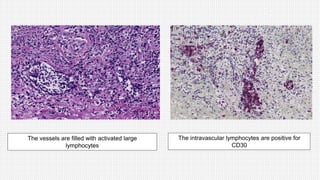
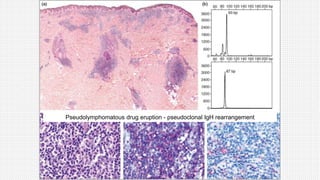
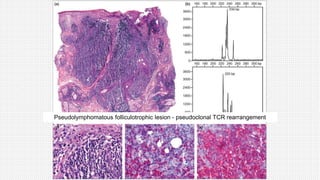
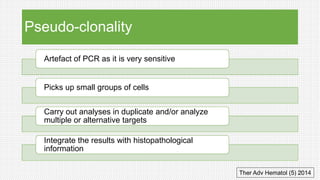
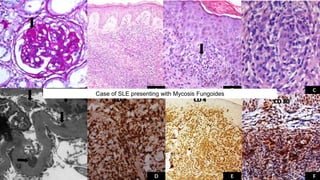
The document discusses cutaneous pseudolymphoma, defining it as a group of skin lesions with lymphocyte-rich infiltrates that mimic cutaneous lymphoma. It provides detailed classifications, clinical presentations, and histopathological features associated with various subtypes, including both T-cell and B-cell pseudolymphomas, their differential diagnoses, and important immunohistochemical markers. Highlights include clinical correlations, important causes, and specific diagnostic considerations for differentiating pseudolymphomas from true lymphomas.