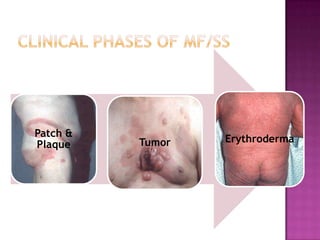
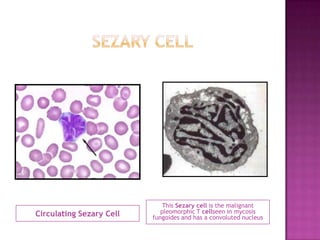
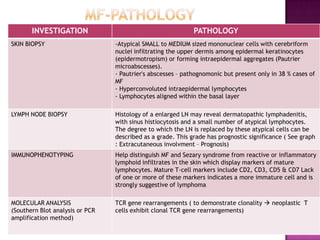
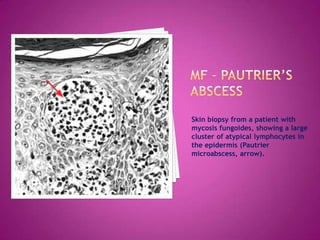
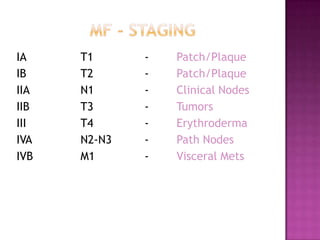
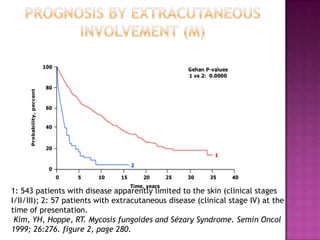
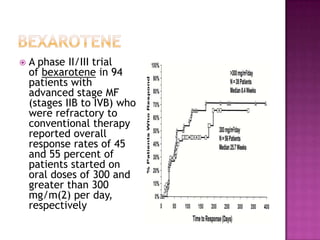
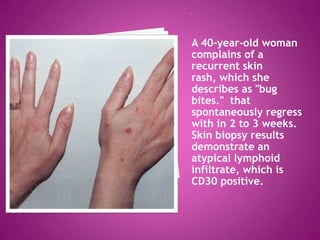
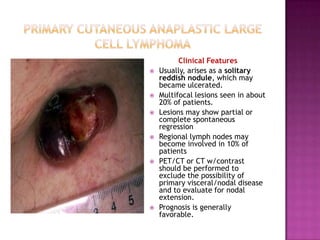
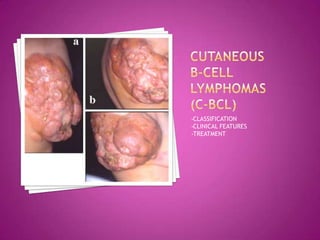
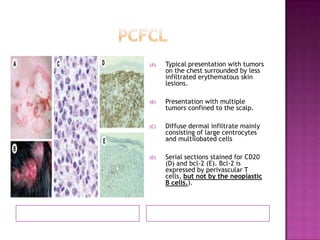
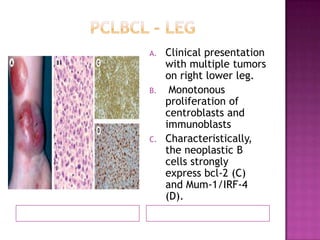
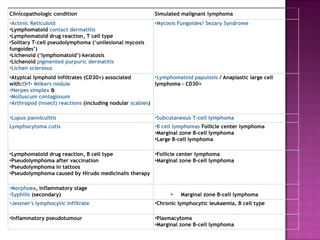
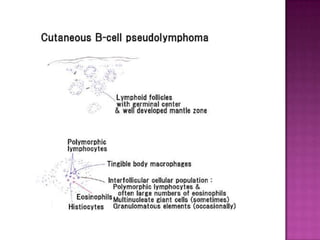
This document discusses primary cutaneous lymphomas, specifically mycosis fungoides. It notes that mycosis fungoides accounts for about 50% of primary cutaneous lymphomas and presents as erythematous patches or plaques on the skin that can progress to tumors or generalized erythema. Diagnosis involves skin biopsy showing atypical lymphocytes in the epidermis and classification using the WHO-EORTC system. Prognosis depends on stage, with patch/plaque stage having the best survival and visceral involvement the worst. Treatment aims to control symptoms and involves skin-directed therapies like phototherapy or topical chemotherapy as well as systemic therapies for advanced disease.