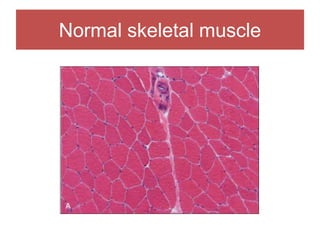
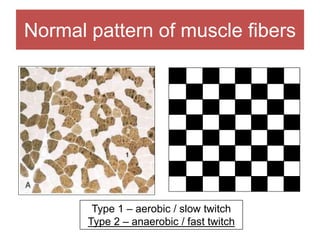
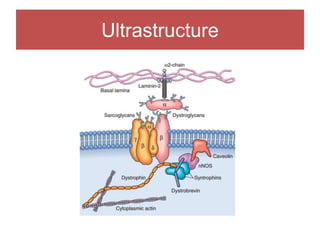
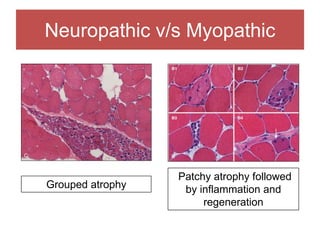
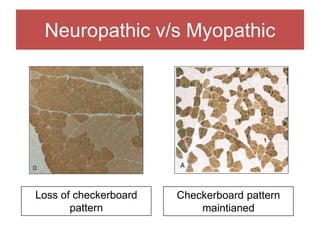
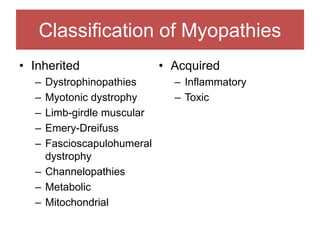
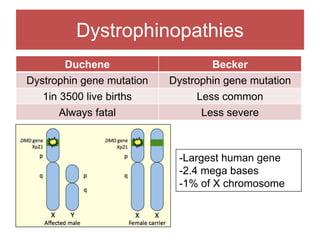
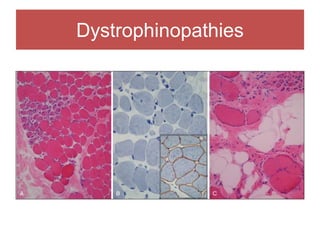
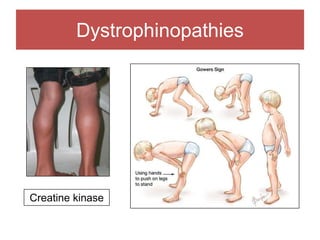
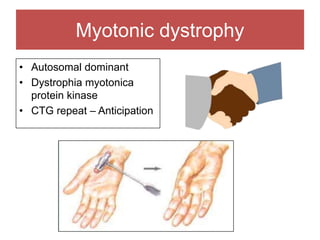
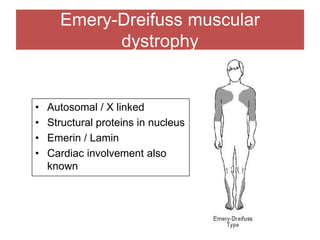
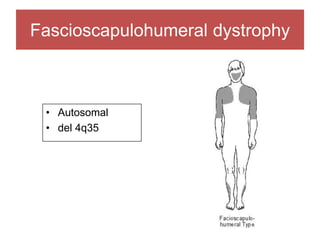
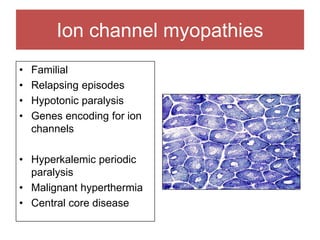
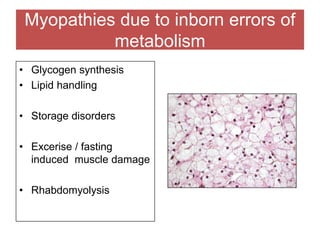
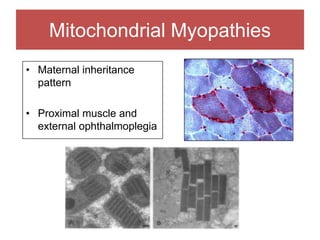
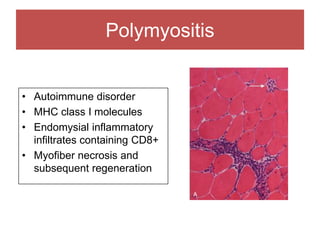
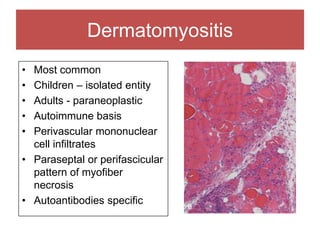
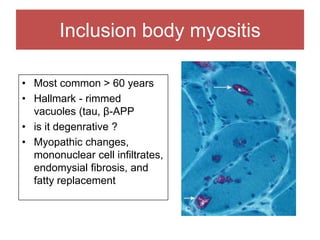
The document discusses various myopathies, detailing their histological characteristics, classifications, and clinical significance. It covers inherited myopathies such as dystrophinopathies and myotonic dystrophy, as well as acquired forms like inflammatory and toxic myopathies. The document highlights specific conditions, their pathogenesis, and associated muscle fiber changes.